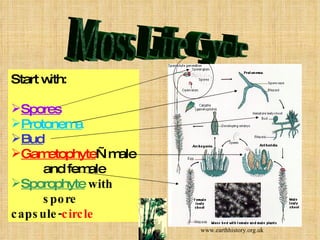
Plants live on land and in water, ranging from microscopic to huge trees. The first plants were likely algae that washed ashore and developed adaptations like cell walls and waxy cuticles to survive on land. Early land plants reproduced with spores but later evolved vascular tissues and roots, stems, and leaves. Plants are divided into two major groups: nonvascular plants like mosses that lack true stems and roots, and vascular plants like ferns and seed plants that have transport tissues.