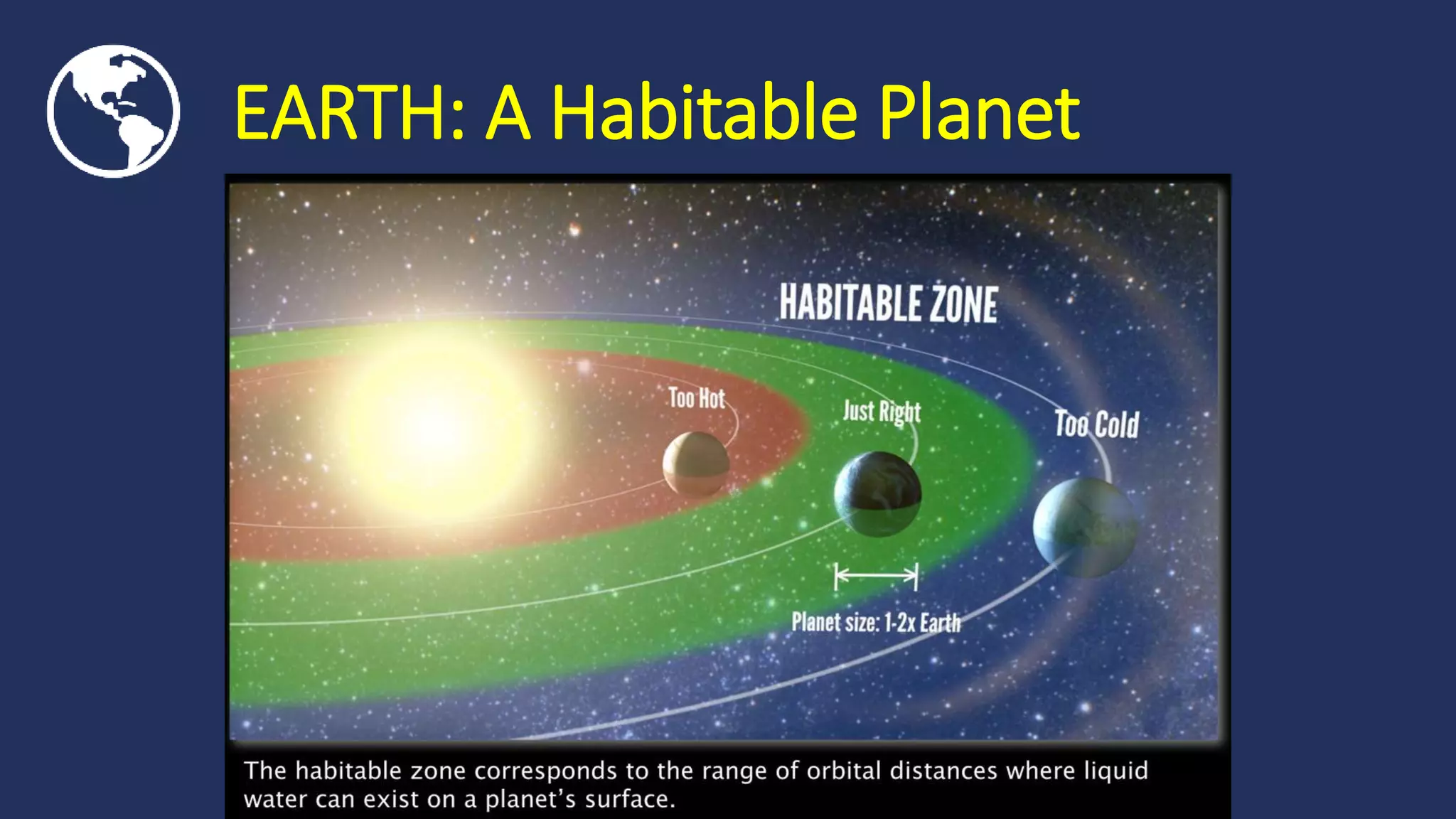
This document provides an overview of Earth and life science modules 1 and 2, which cover the origin and structure of Earth. Module 1 discusses Earth's history, structure, composition and processes. It also covers natural hazards. Module 2 examines Earth's four subsystems: the atmosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. Key details are provided on the role and composition of each subsystem and how they support life. The document concludes with activities for students to complete related to modules 1 and 2.