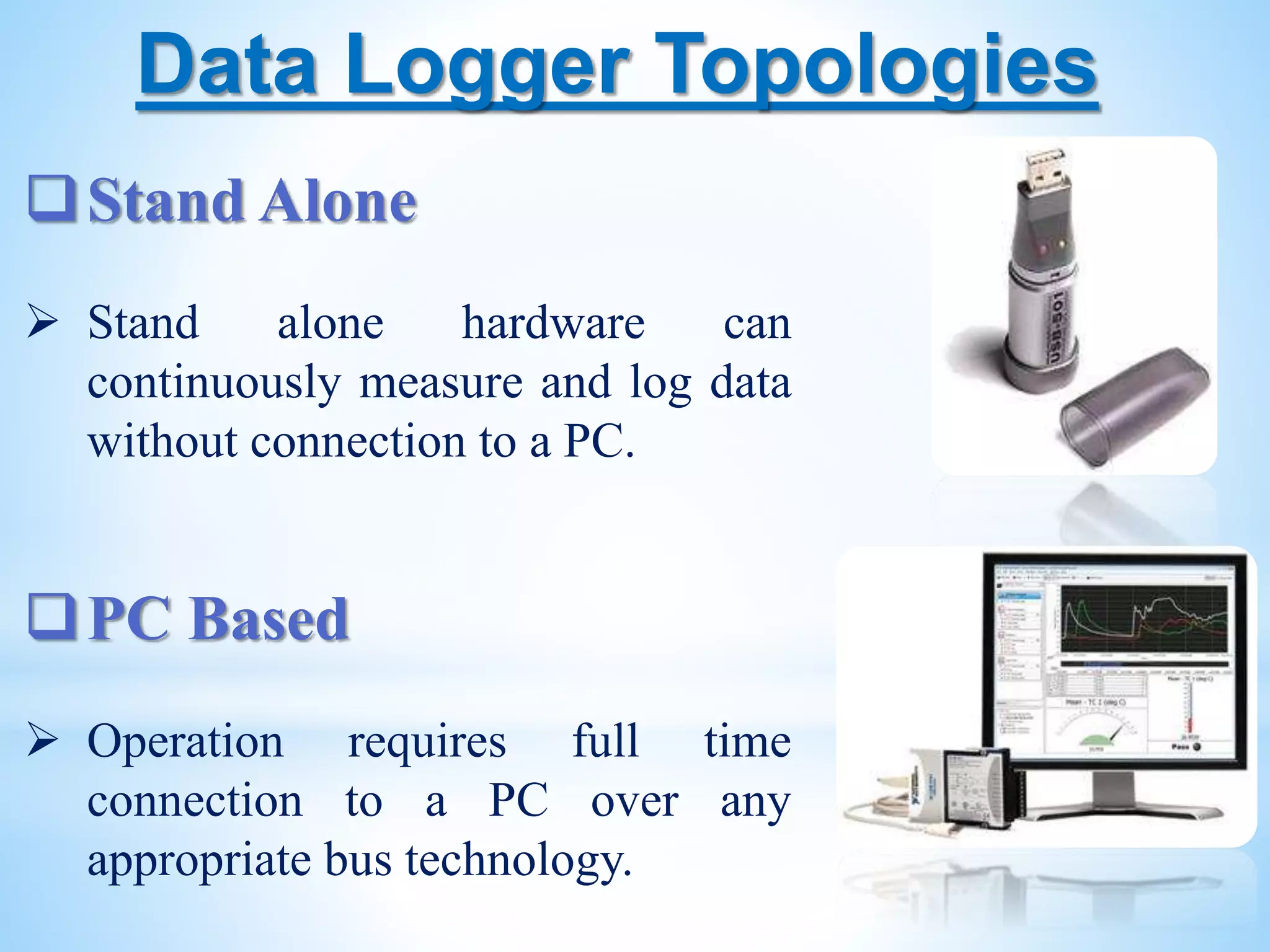
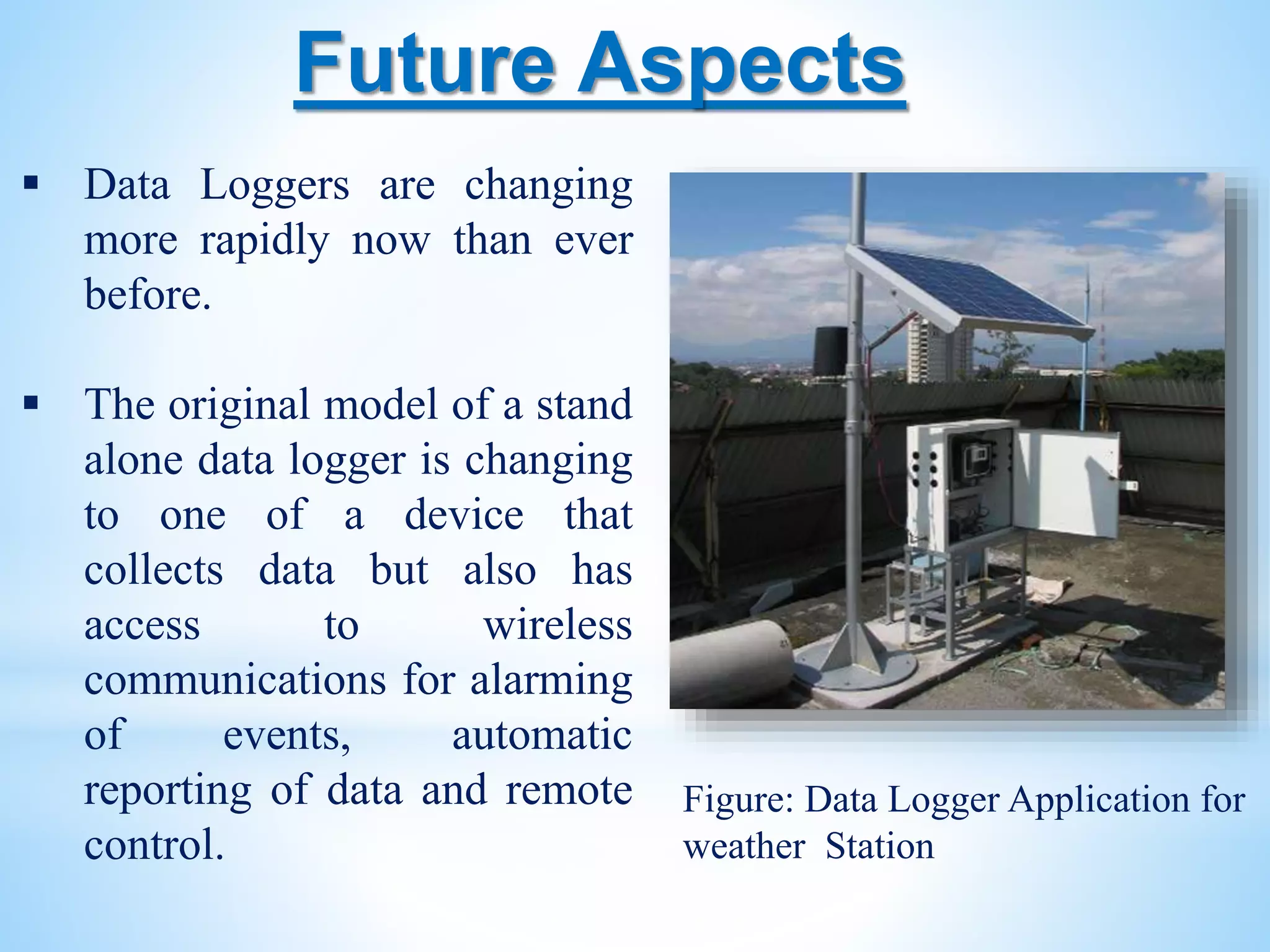
The document discusses data loggers, devices that gather and store data over time, primarily focusing on temperature measurement. It details the components and design of a microcontroller-based data logger, its implementation, and its growing applications in various industries. The document also highlights the advantages and disadvantages of data logging, along with its evolving nature towards enhanced wireless communication capabilities.