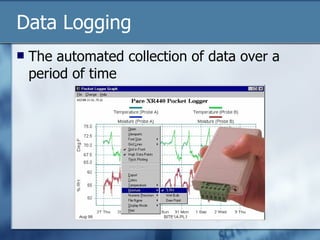
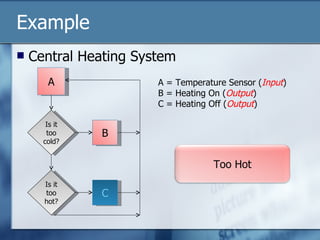
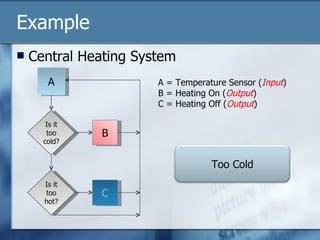
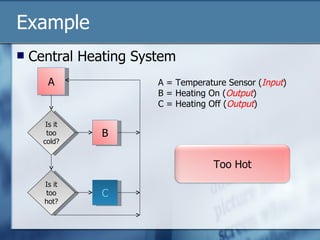
The document discusses data logging and control systems. It explains that sensors are used to collect analogue data that is converted to digital format for processing by computers. Data logging is used to monitor patients in hospitals by tracking vital signs over time. Control systems use input sensors to detect conditions and output devices to respond, like a central heating system turning heating on/off based on temperature readings. Instructions can be written to automate control of devices through processing input data and activating outputs.