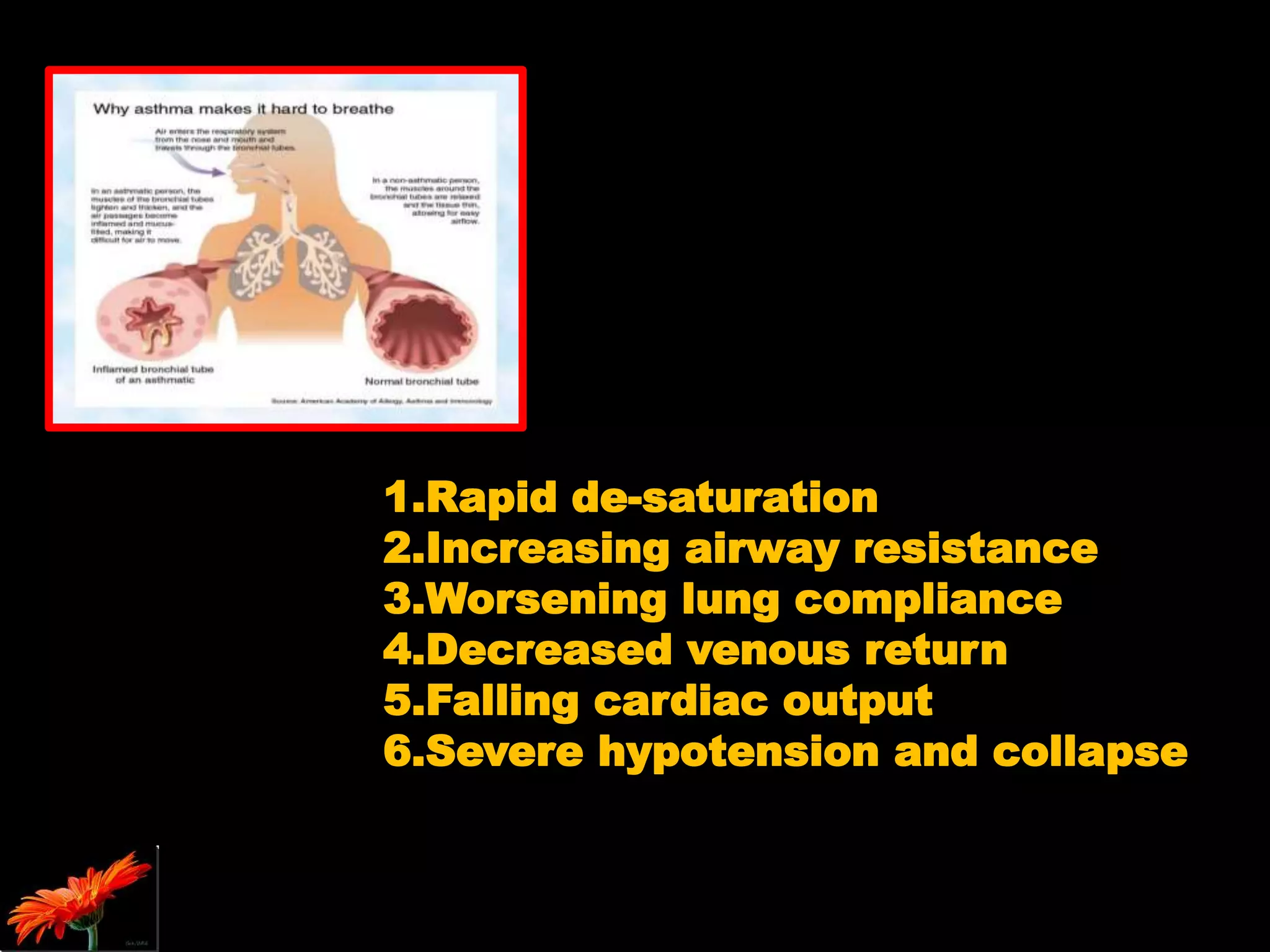
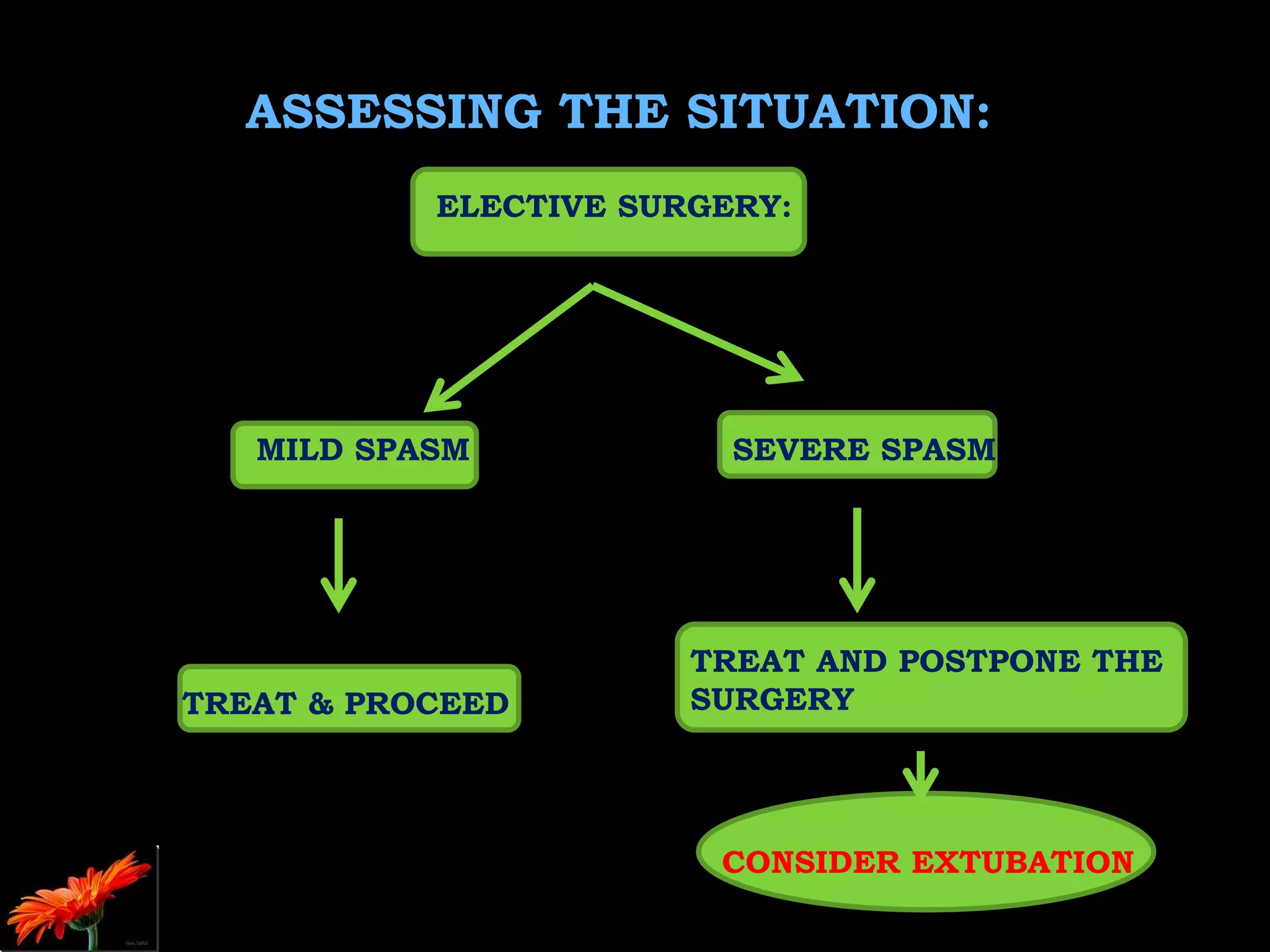
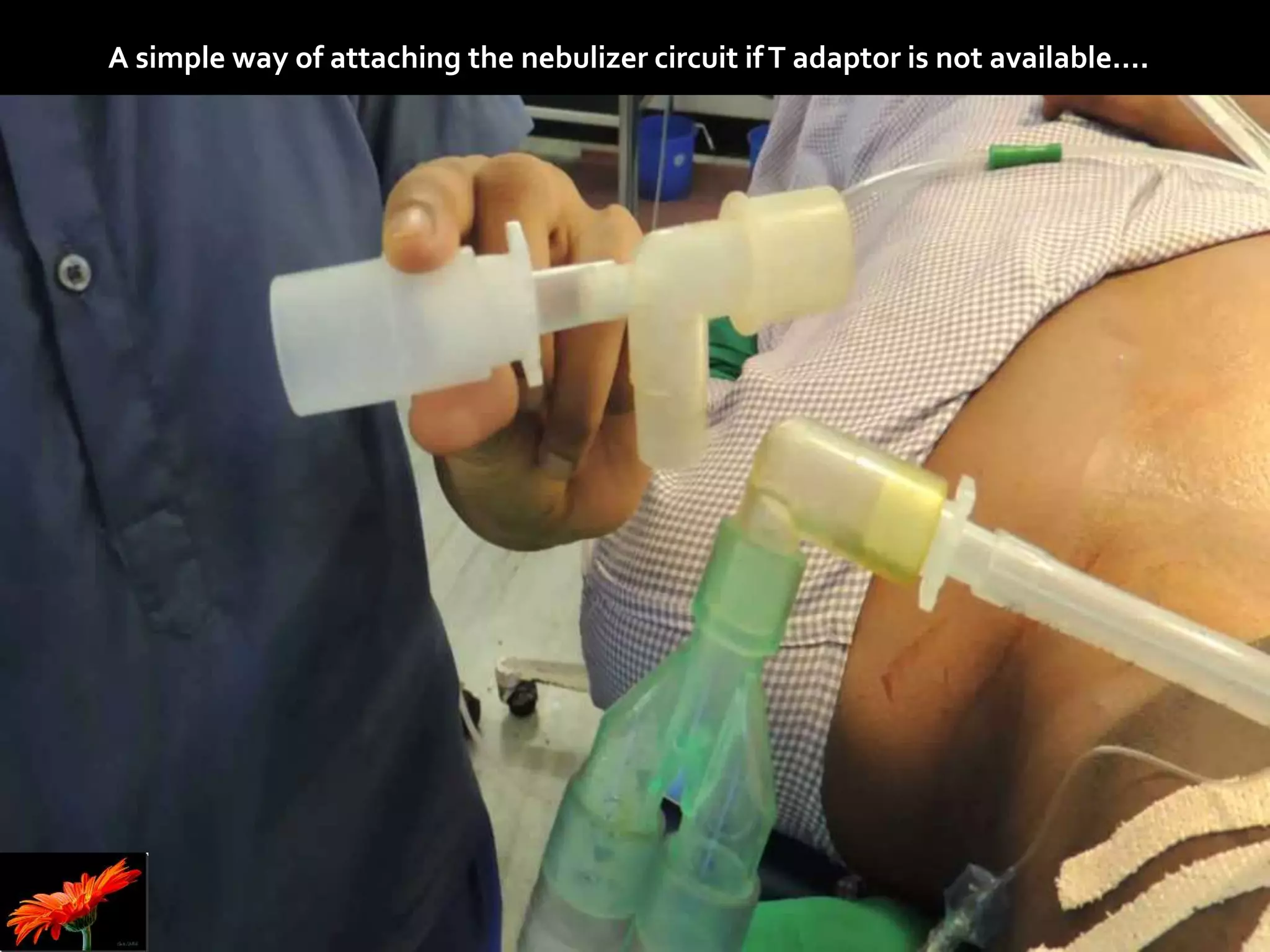
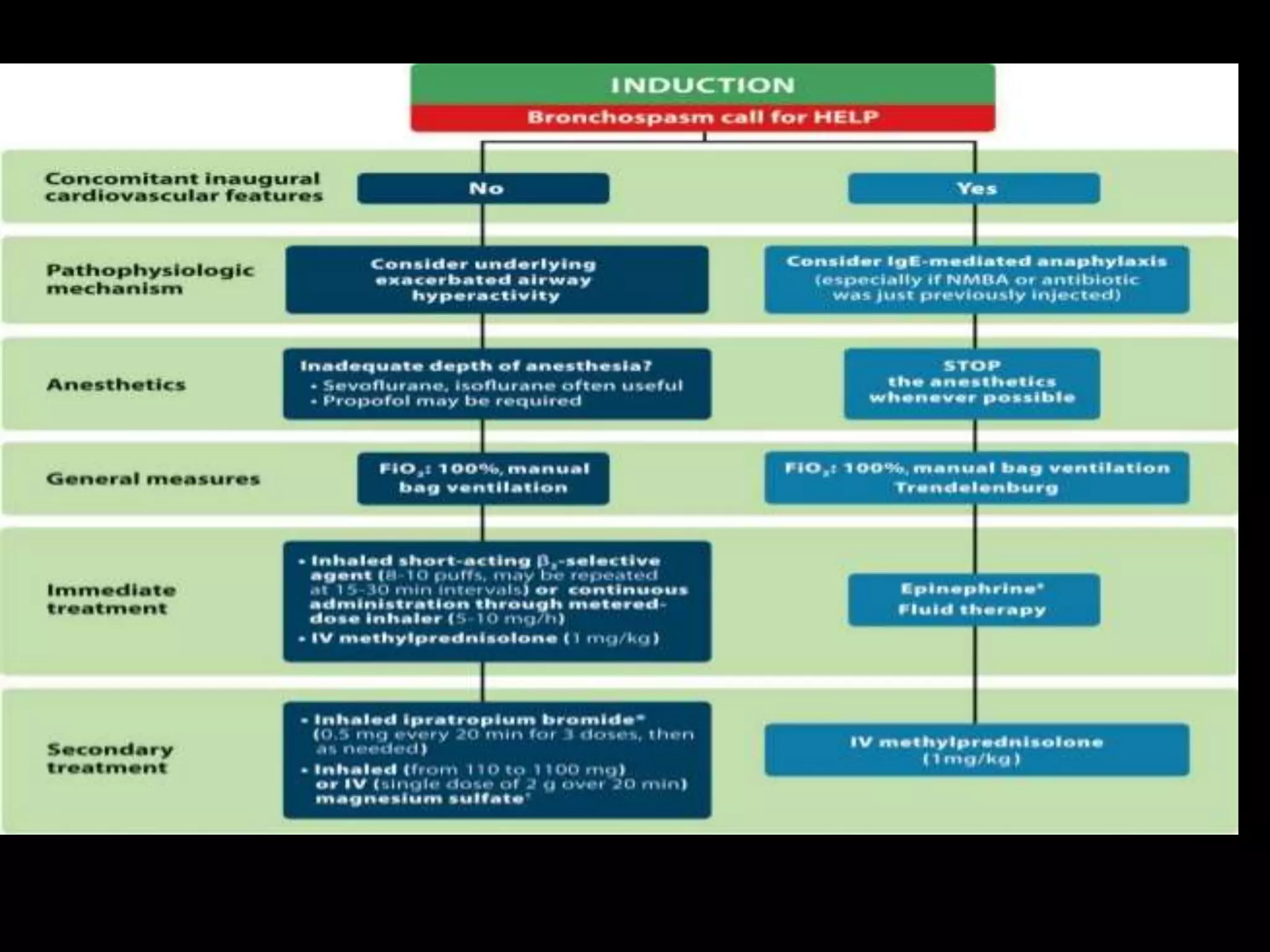
The document outlines bronchospasm during induction, its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and treatment with inhaled β2 agonists while suggesting preventive measures, including proper patient preparation and the use of regional anesthesia. The need for urgent intervention is highlighted due to the rapid deterioration in patient vitals during bronchospasm.