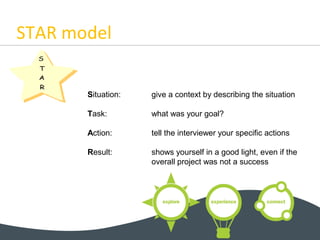
This document provides guidance on preparing for and succeeding in job interviews. It discusses the importance of researching the company and role, being prepared to answer common question types like motivational and competency-based questions, and making a strong first impression through body language, eye contact and a firm handshake. The STAR model is recommended for structuring answers to competency questions. Interviewers assess a candidate's fit based on whether they can, will and fit the job. Being confident, speaking clearly and providing concrete examples from past experiences are keys to interview success.