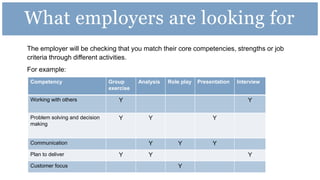
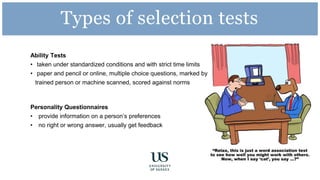
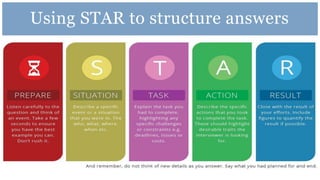
The document provides information and advice about preparing for and performing well at assessment centers for jobs or internships. It discusses what to expect at assessment centers, including selection tests, presentations, group tasks, and interviews. It offers tips for completing tests, delivering presentations, participating in group exercises, and interviewing. Sample exercises and schedules are provided. Resources for practicing and getting additional help from the careers center are also listed.