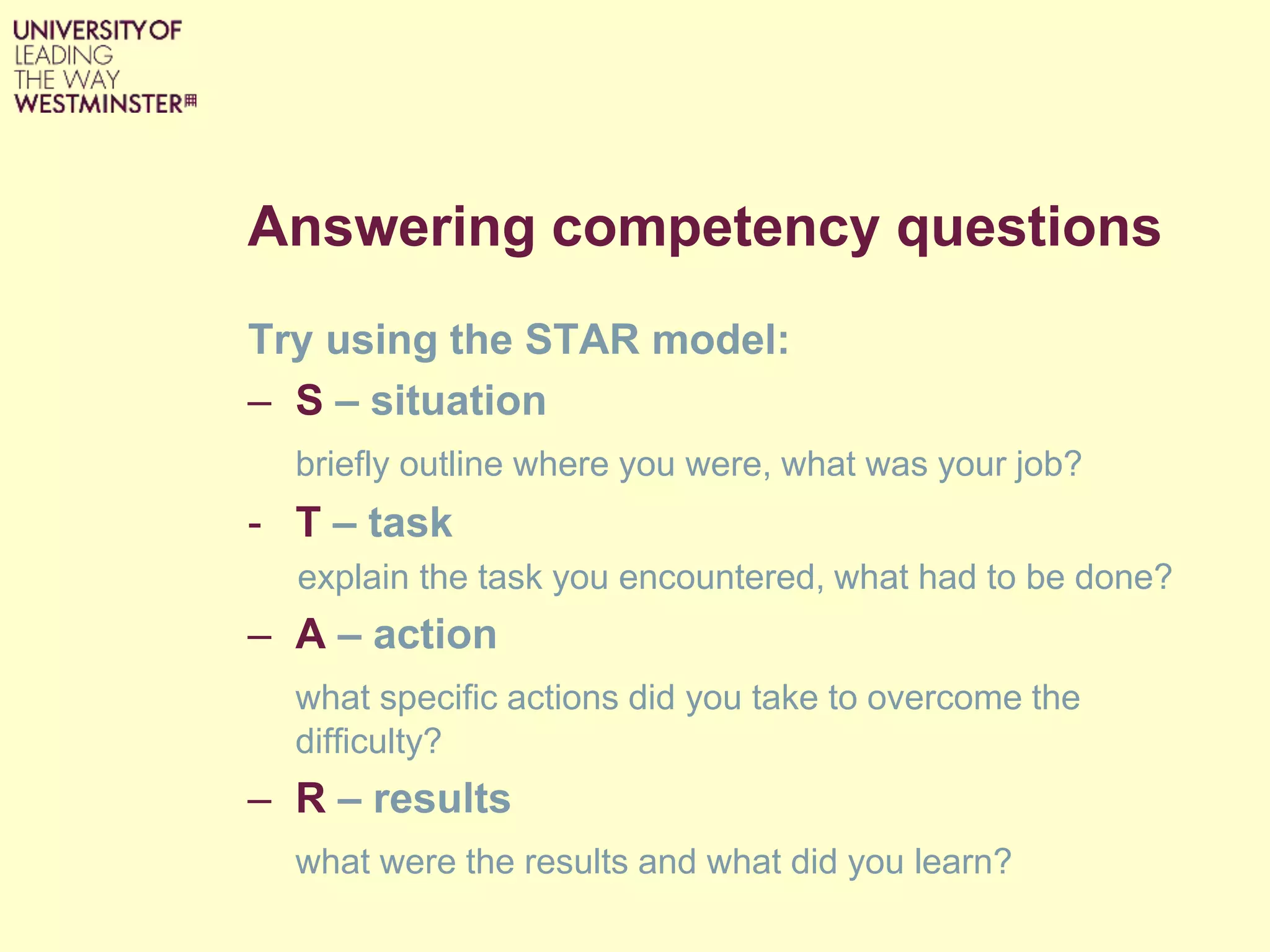
The document is a guide for succeeding in job interviews, focusing on preparation strategies, employer expectations, and effective interview techniques. It emphasizes the importance of researching self, the job, and the organization, as well as practicing answers to common interview questions. Key points include the STAR model for competency questions, appropriate interview behavior, and tips for showcasing enthusiasm and knowledge during the interview process.