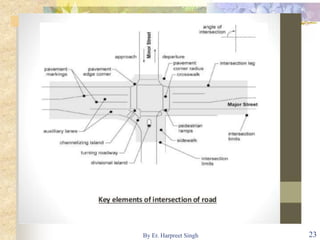
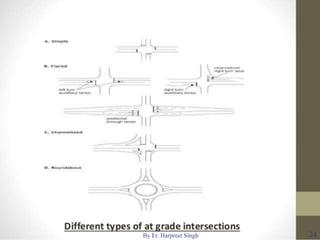
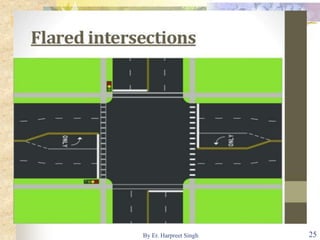
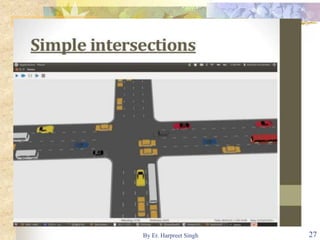
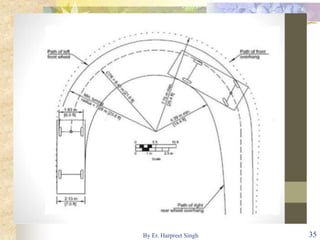
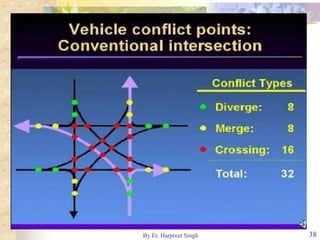
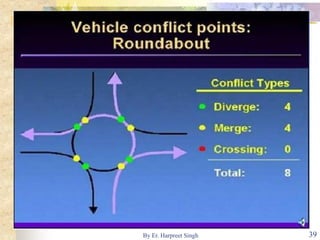
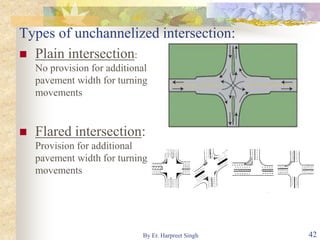
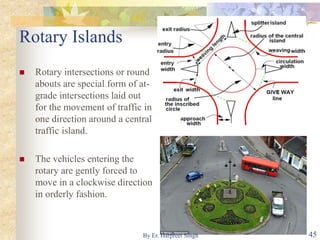
The document discusses various types of road intersections, including grade-separated interchanges and at-grade intersections, detailing their designs, classifications, and functionalities. It describes different interchange types like underpasses, overpasses, and cloverleafs, and outlines design considerations for vehicles, bicycles, and pedestrians at intersections. Additionally, it highlights the importance of traffic islands, rotary intersections, and control mechanisms to enhance safety and efficiency in traffic flow.