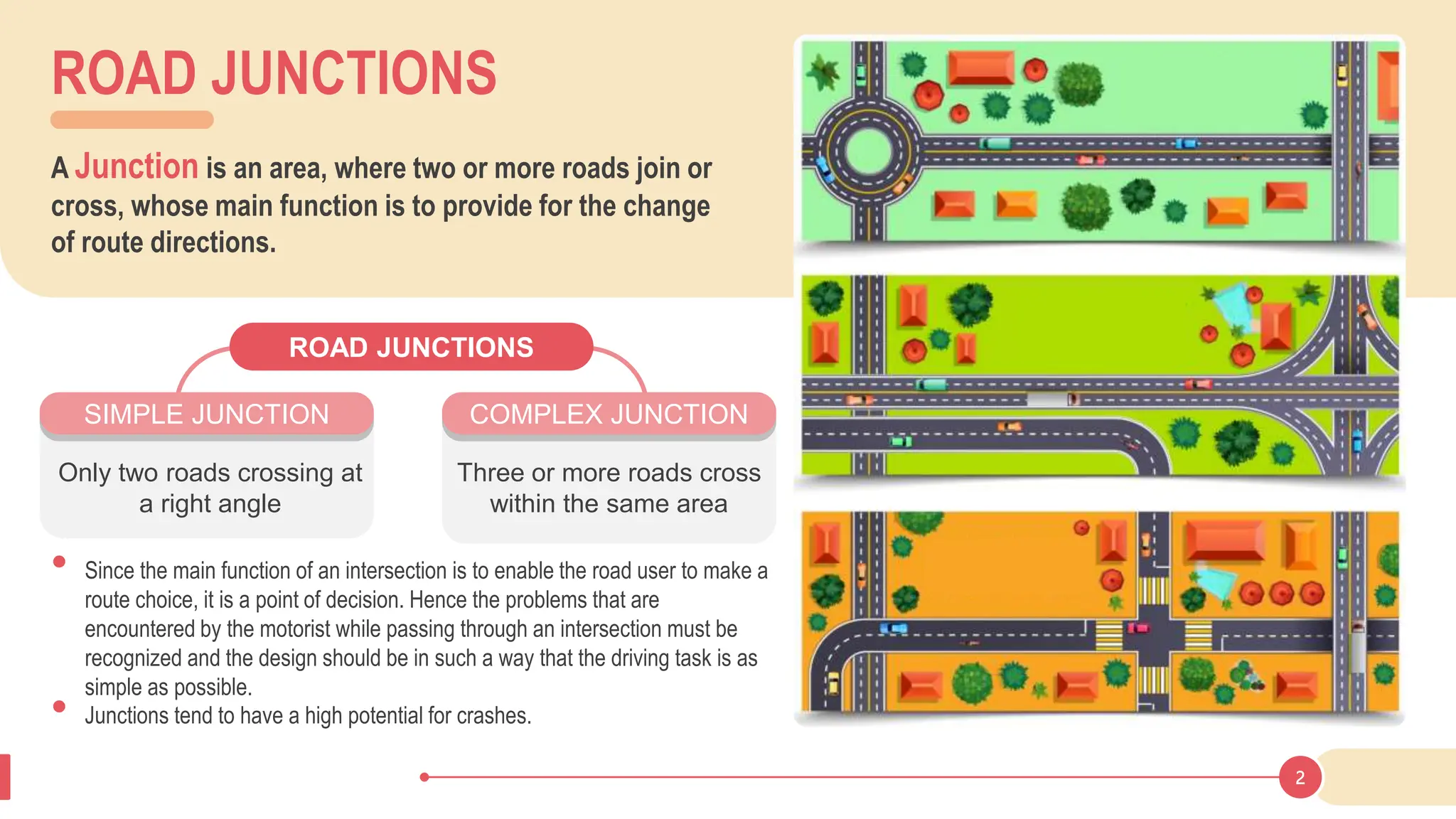
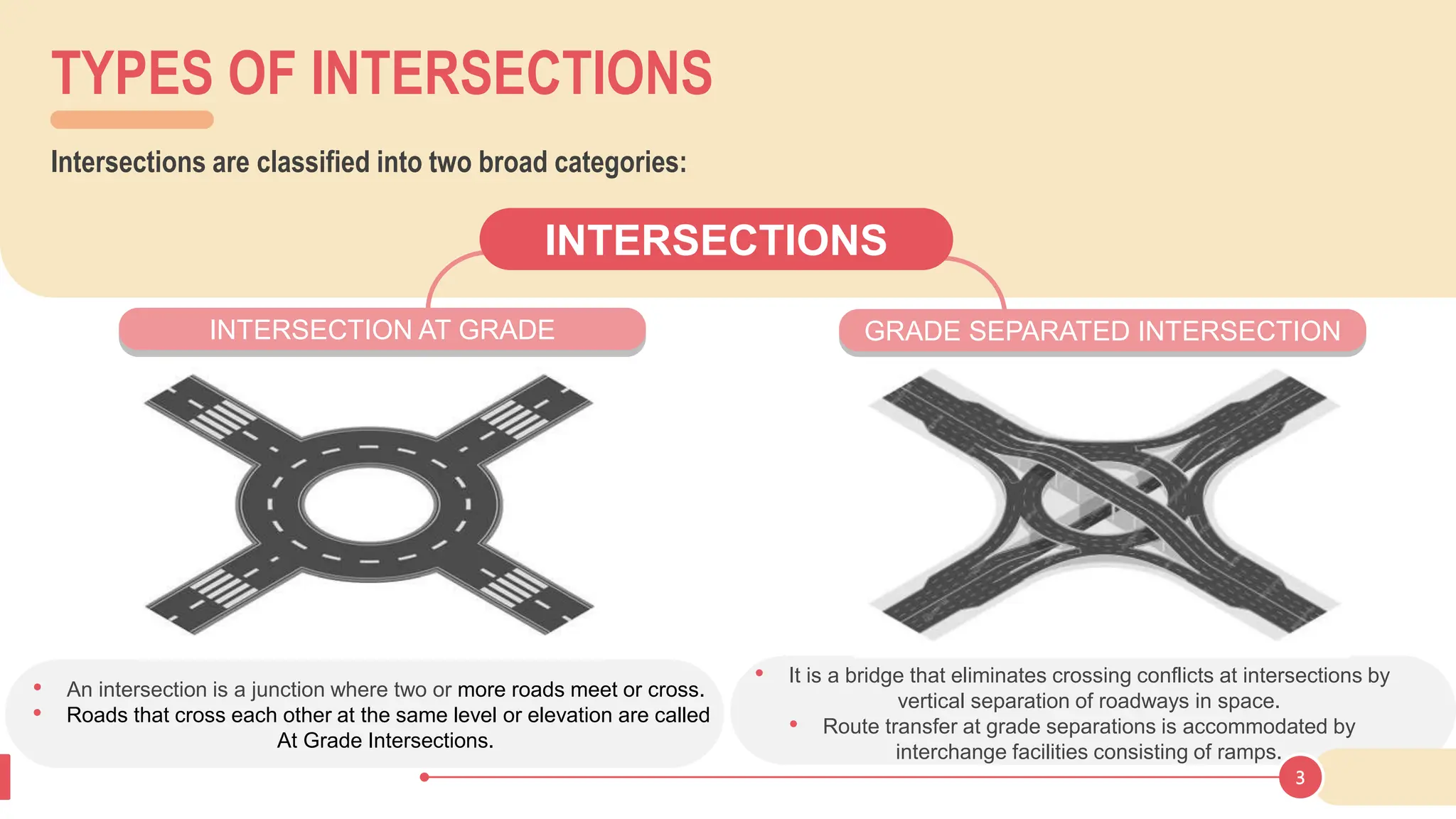
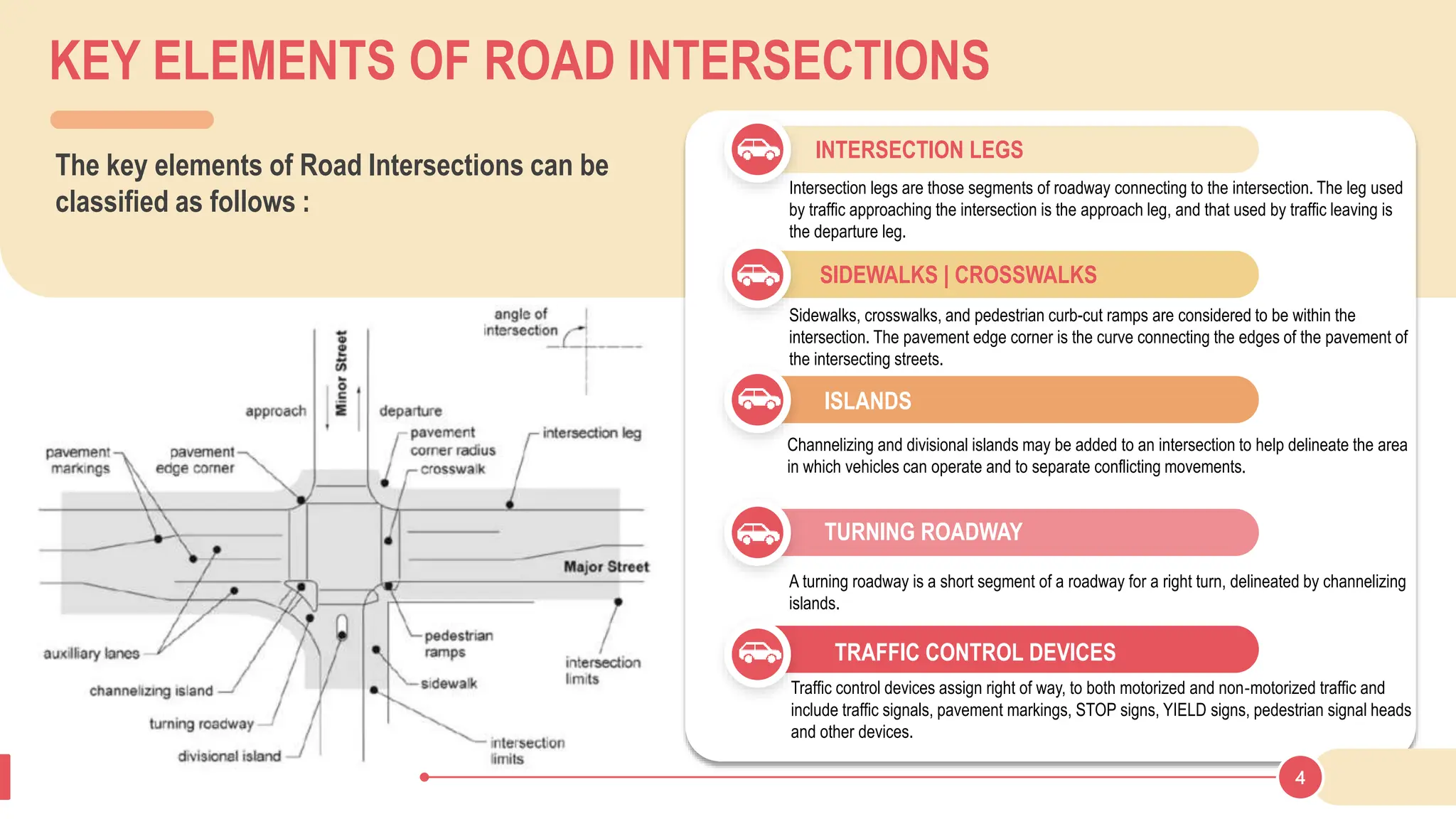
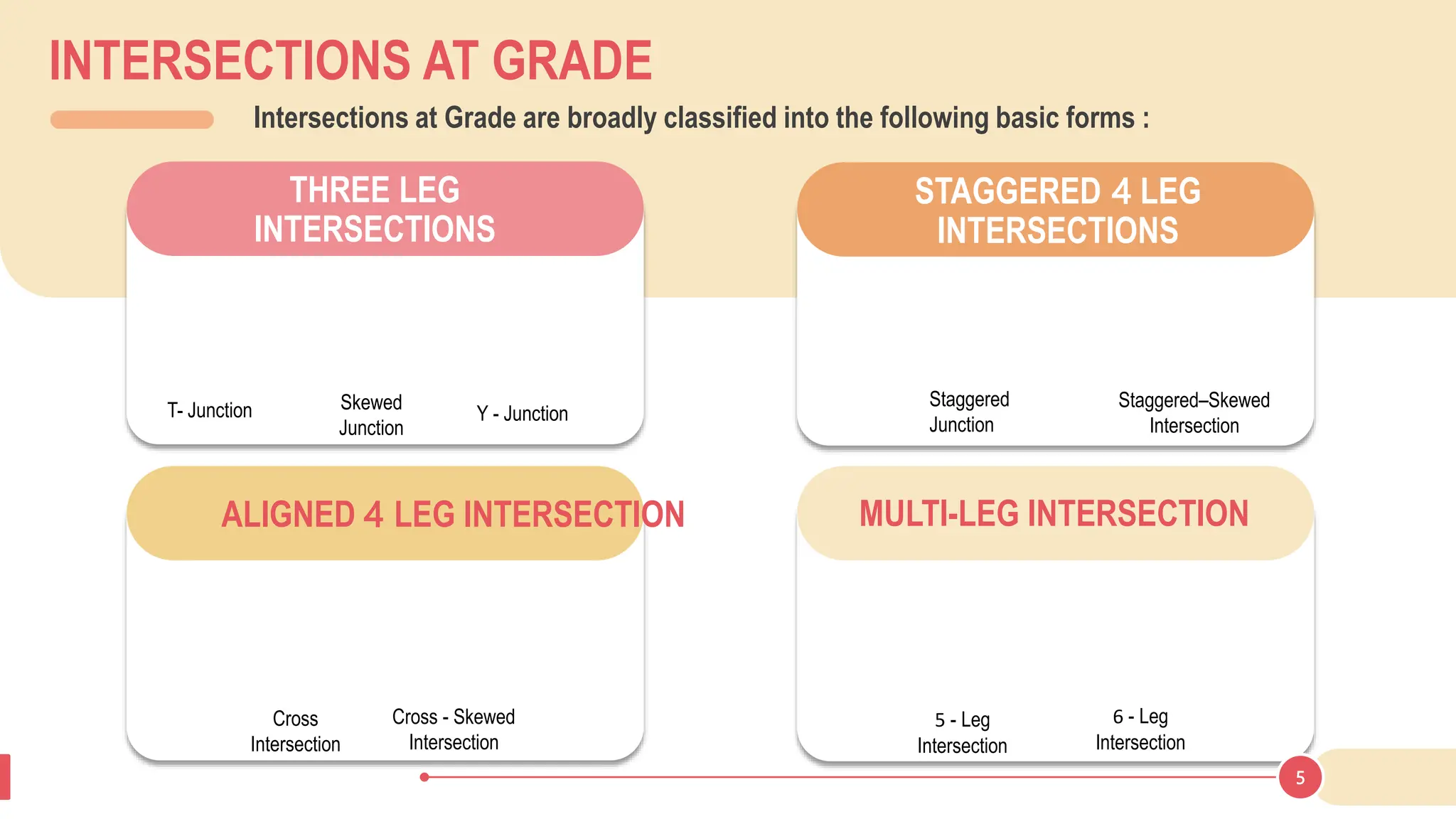
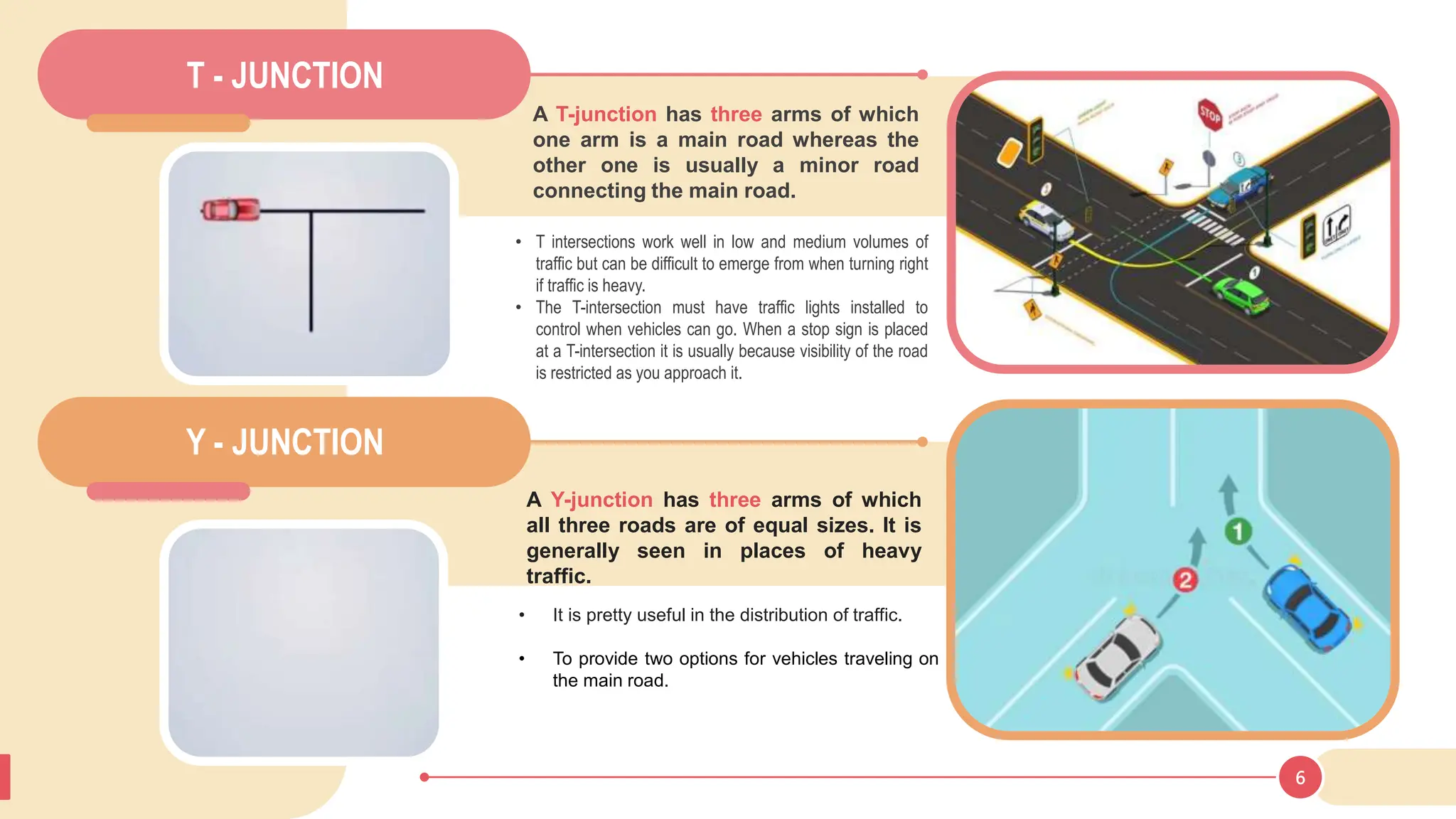
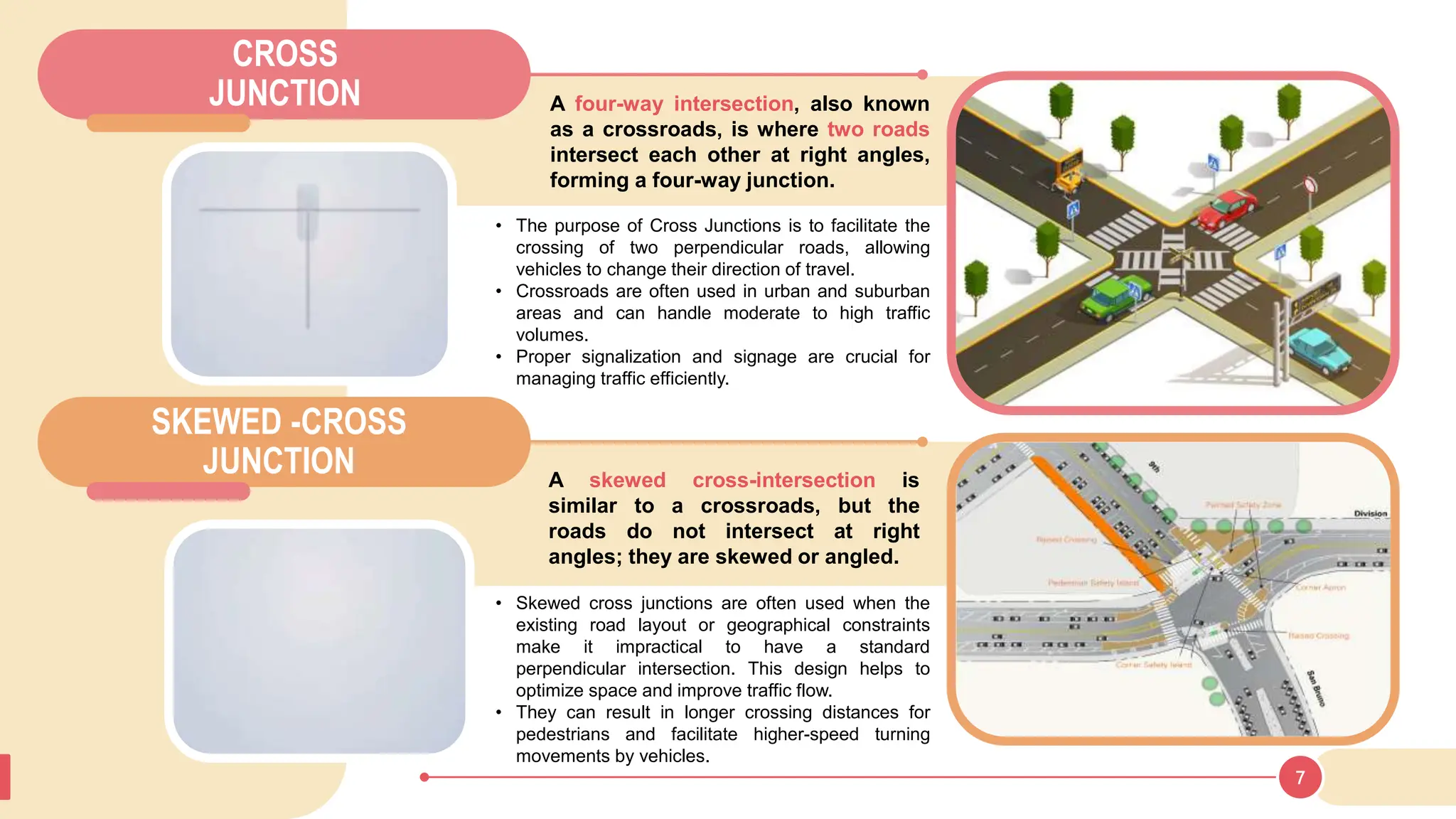
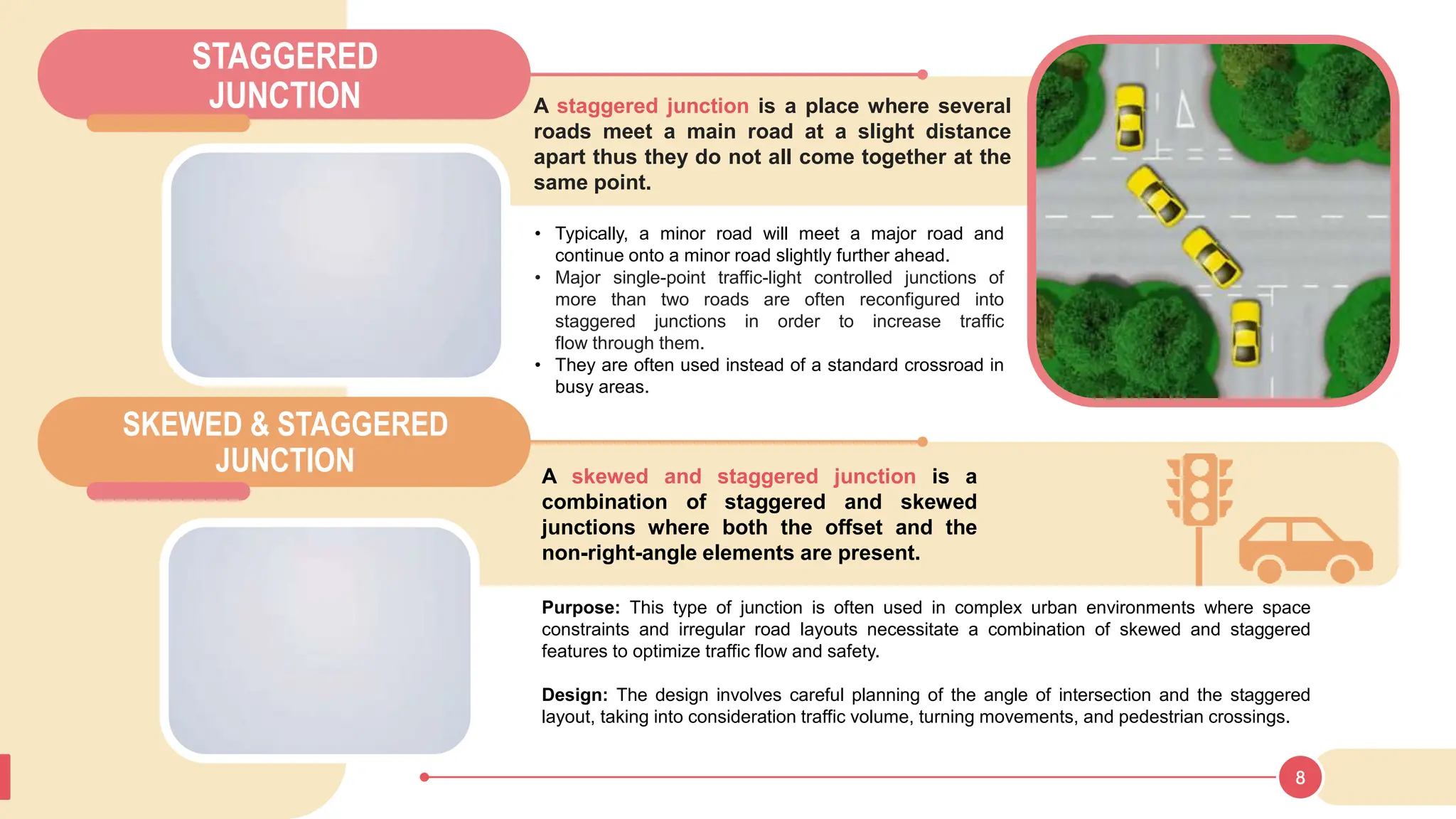
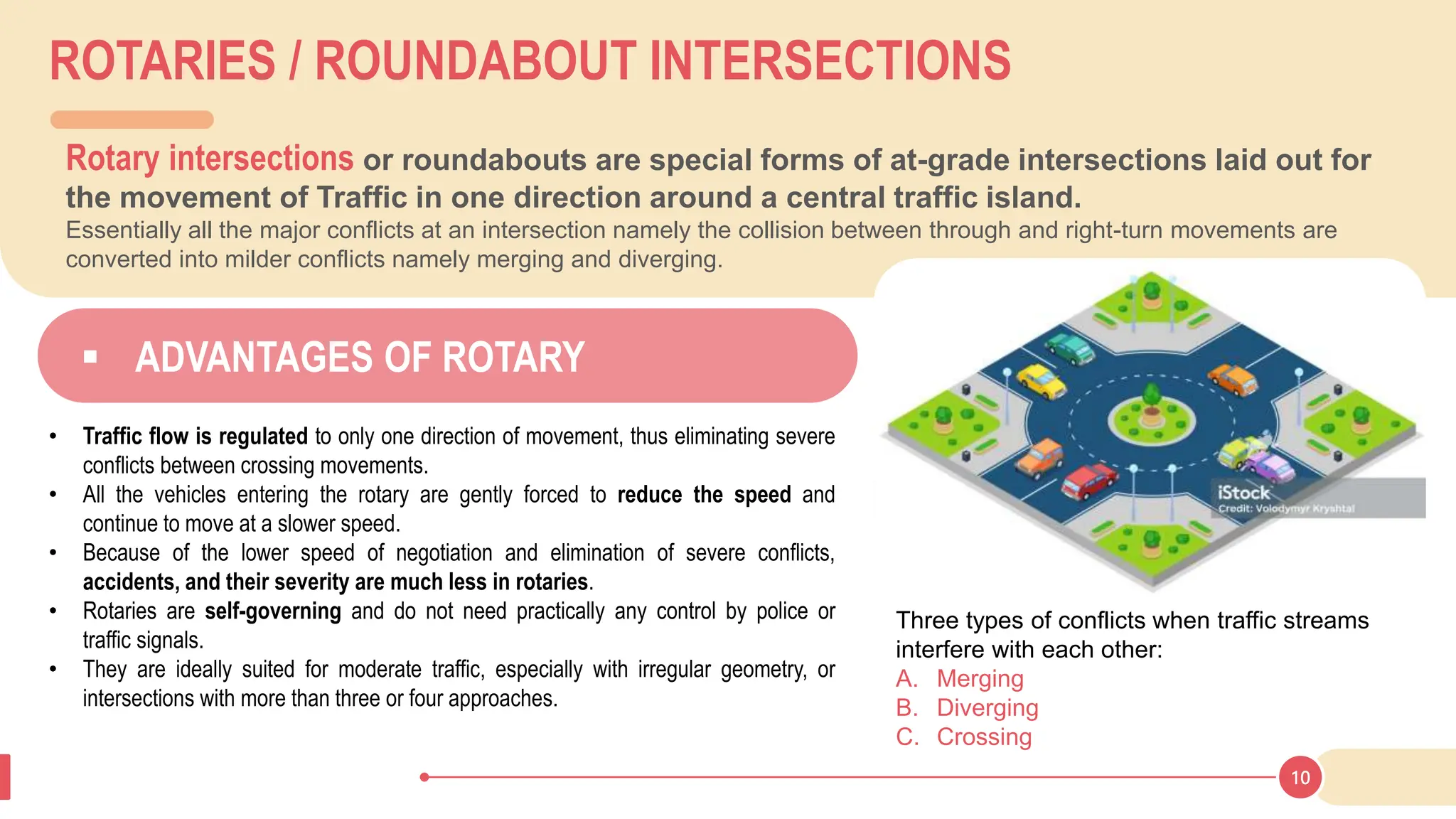
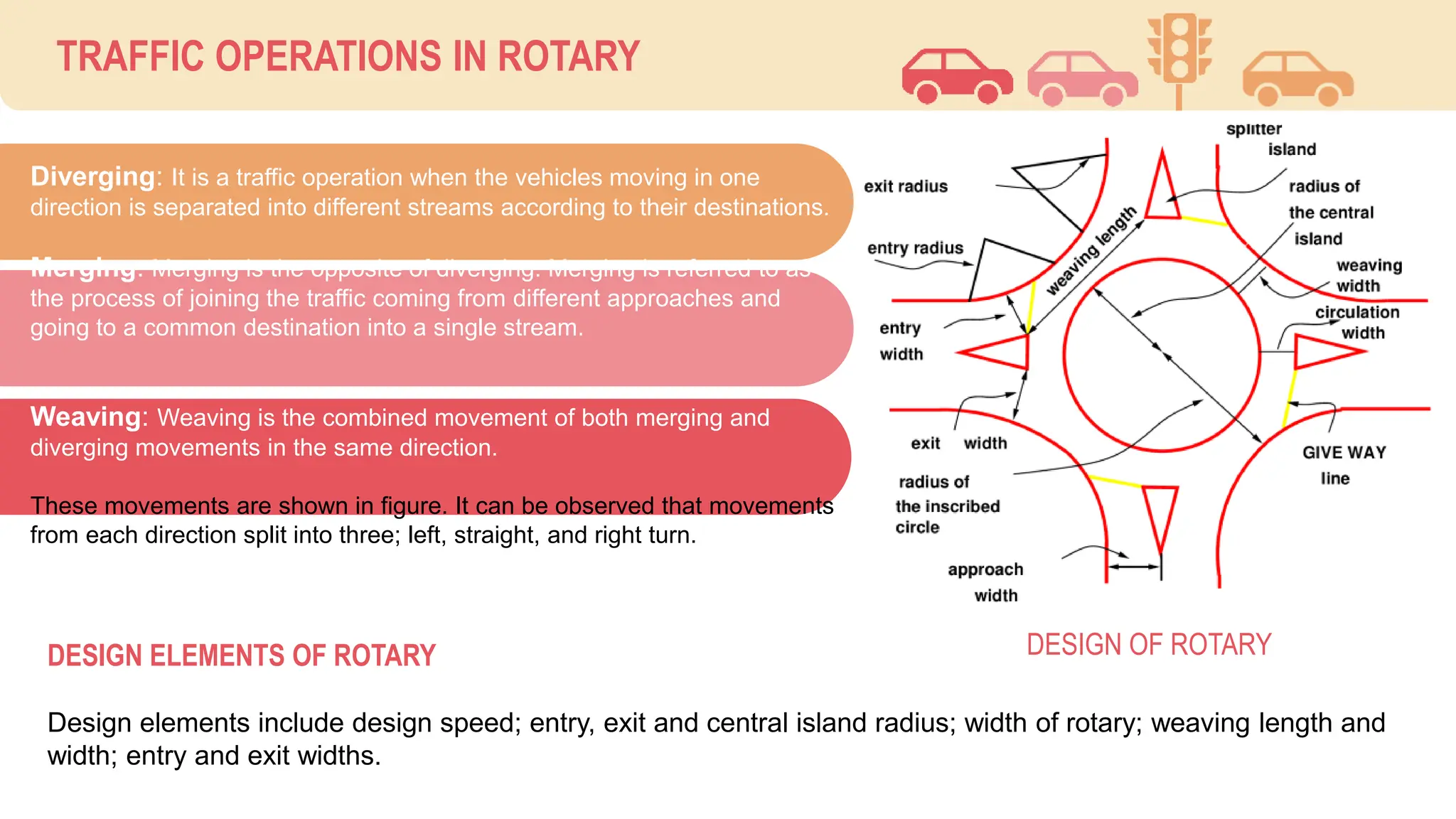
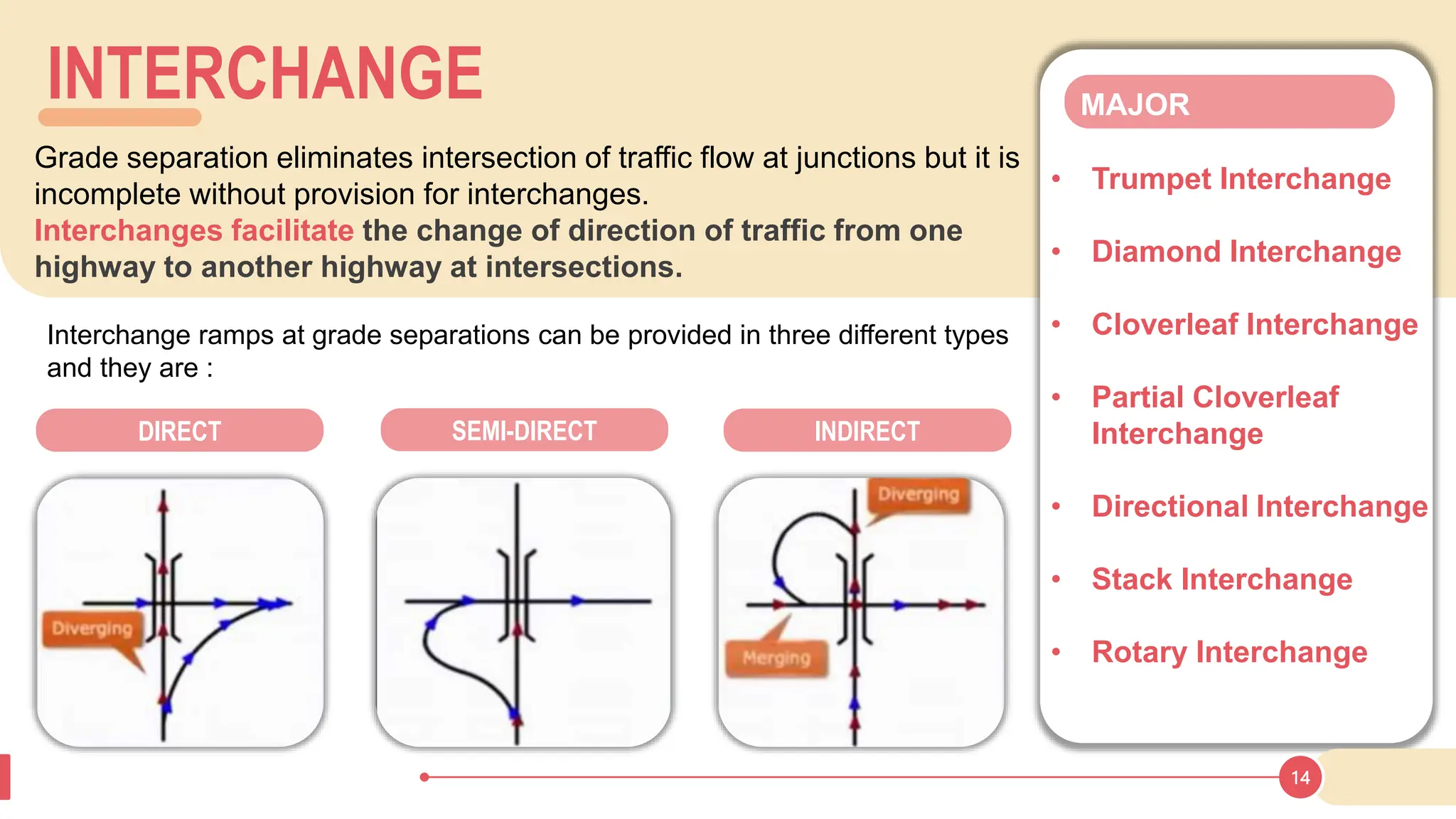
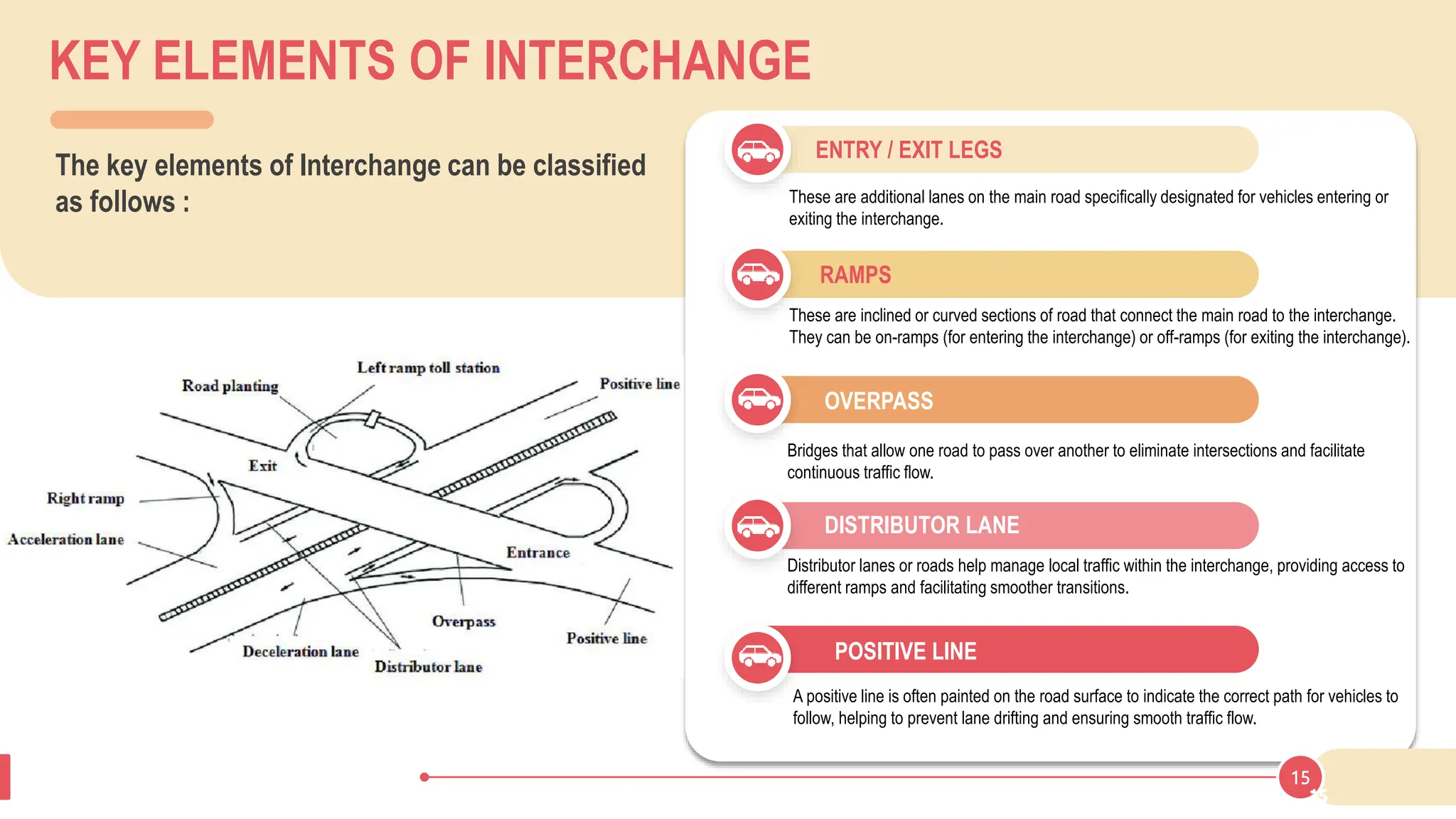
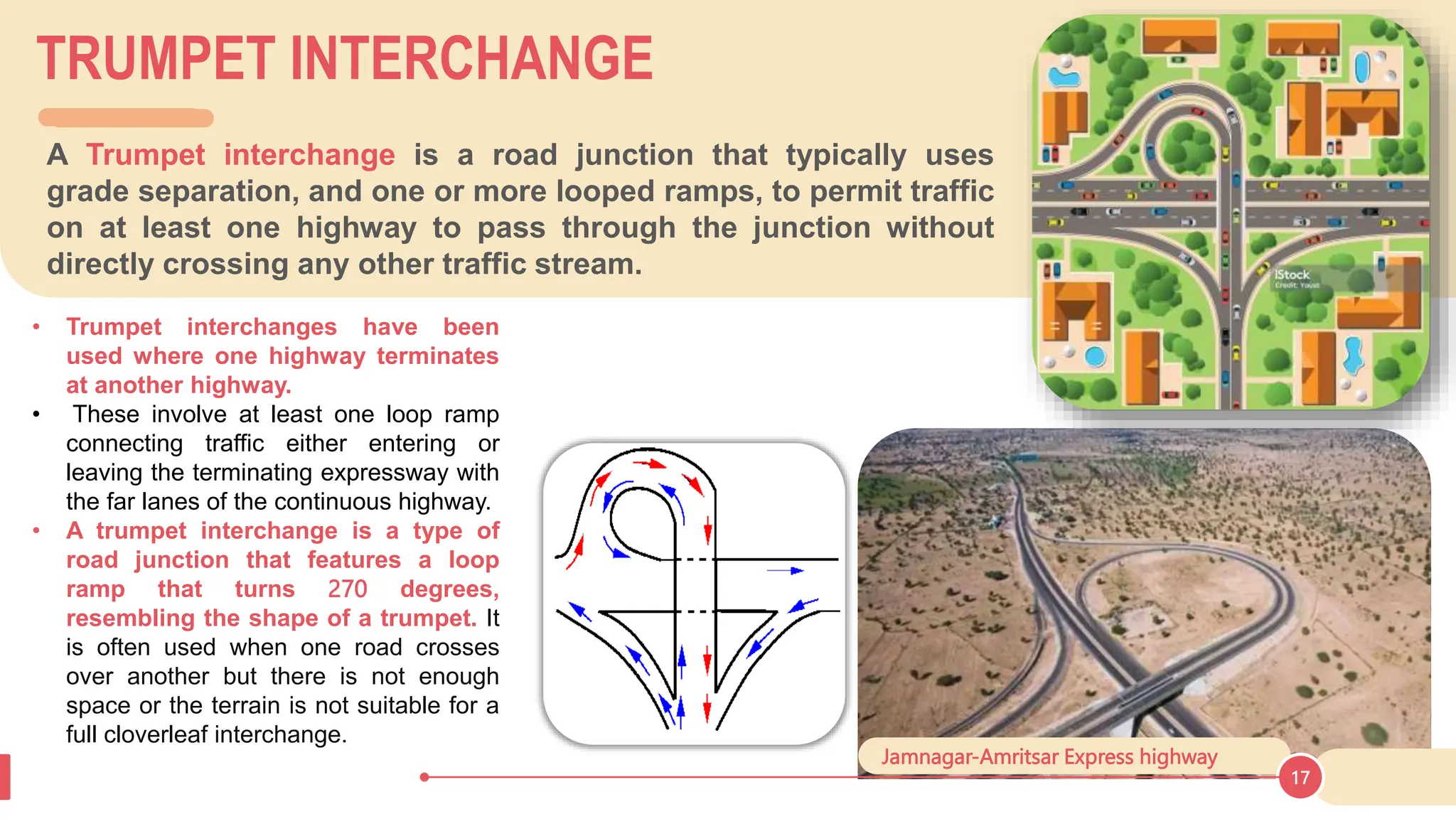
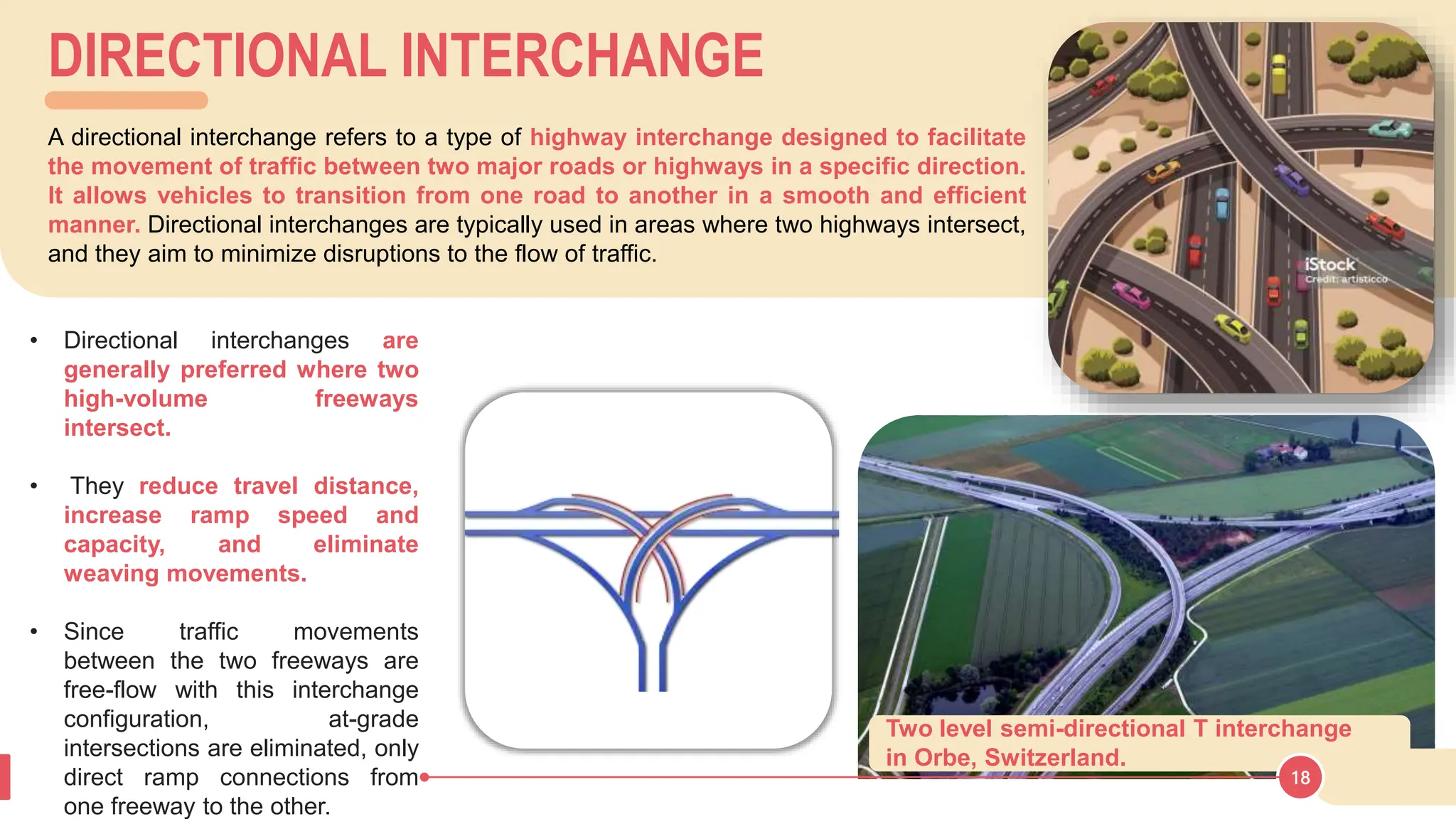
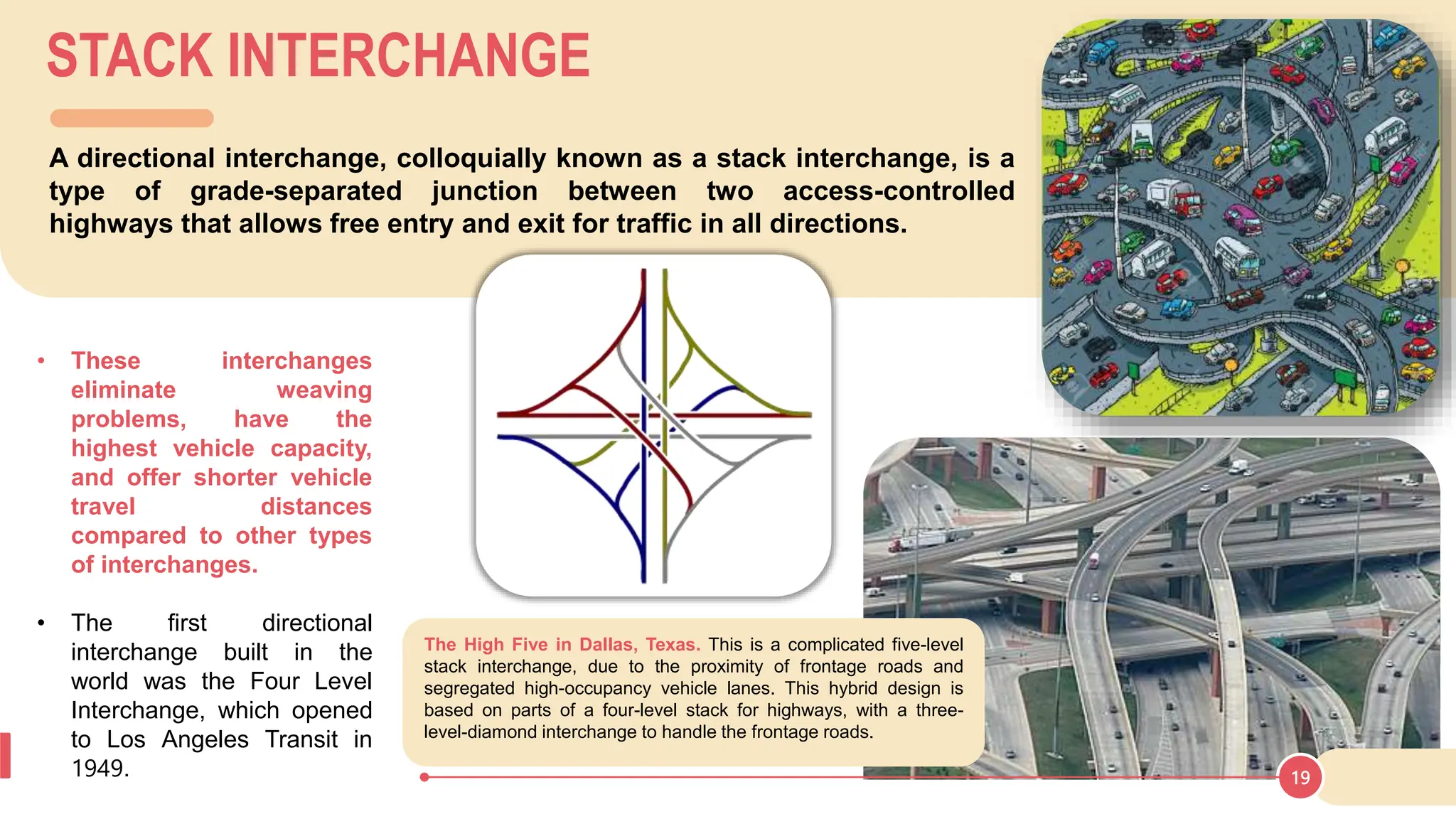
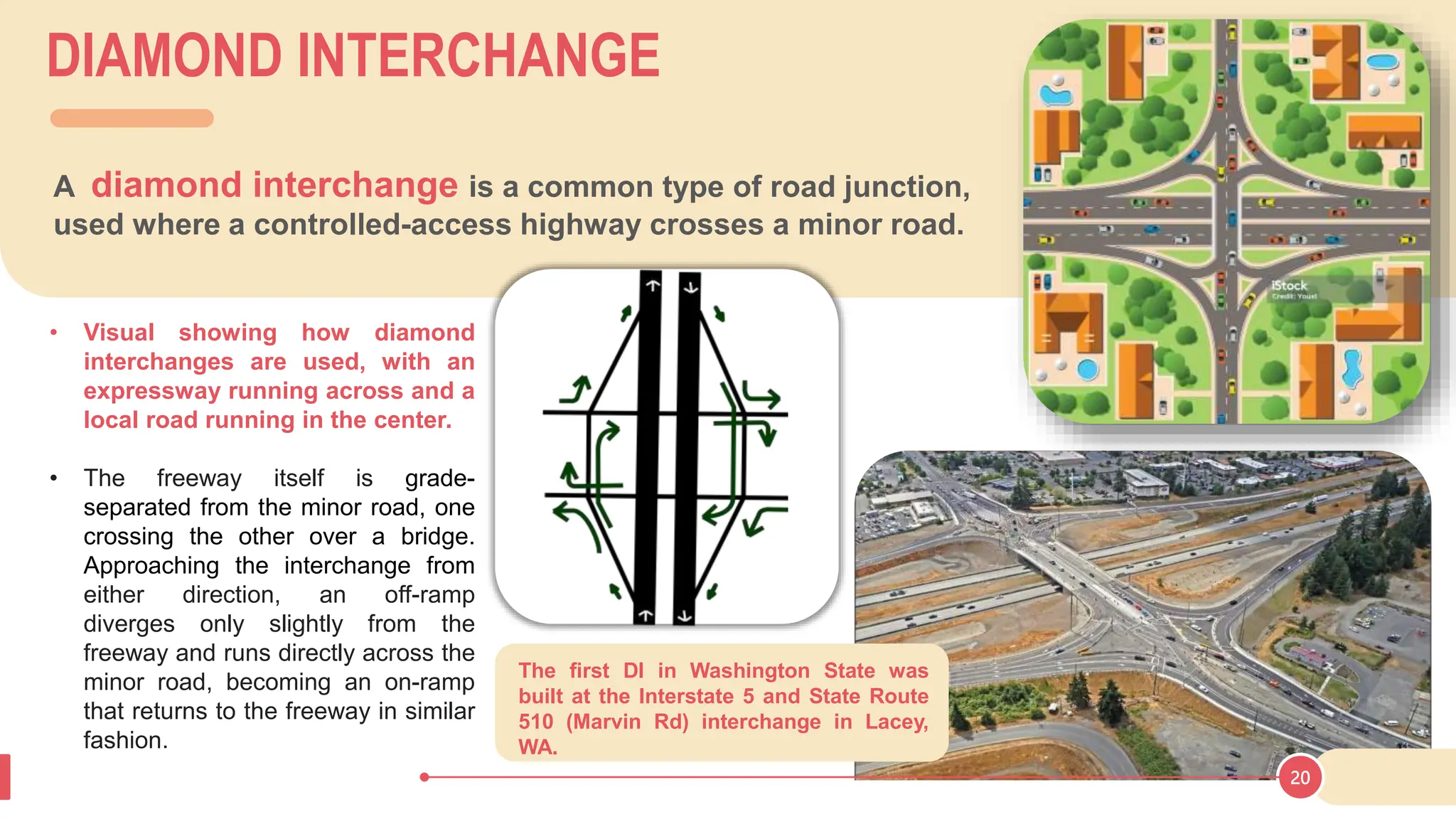
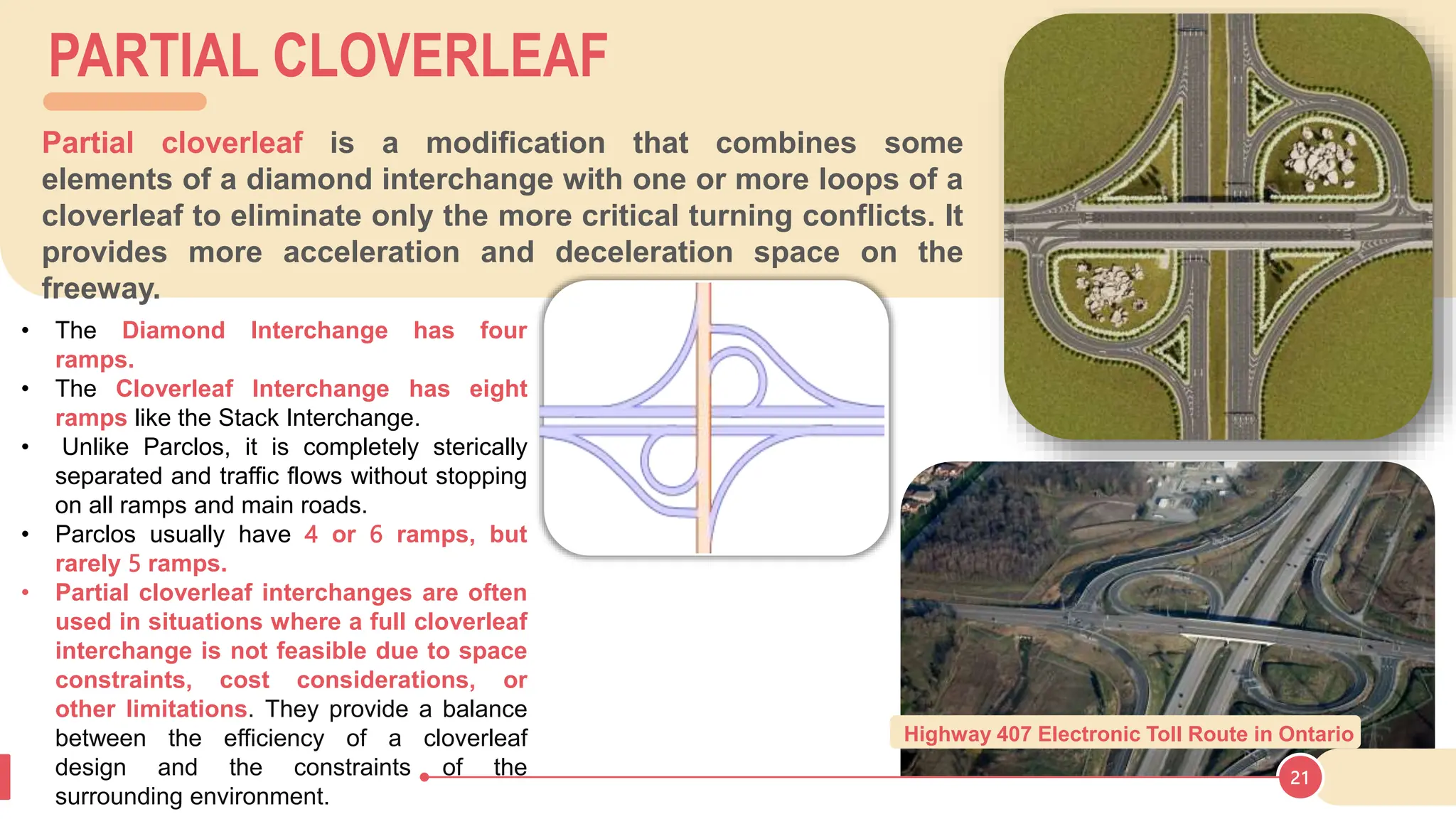
The document discusses various types of road junctions and interchanges, highlighting their design, classification, and traffic management features. It details different configurations like T-junctions, Y-junctions, roundabouts, and various forms of grade-separated intersections, emphasizing how these designs aim to optimize traffic flow and enhance safety. The conclusion underscores the importance of meticulous planning and innovation in creating effective transportation infrastructures.