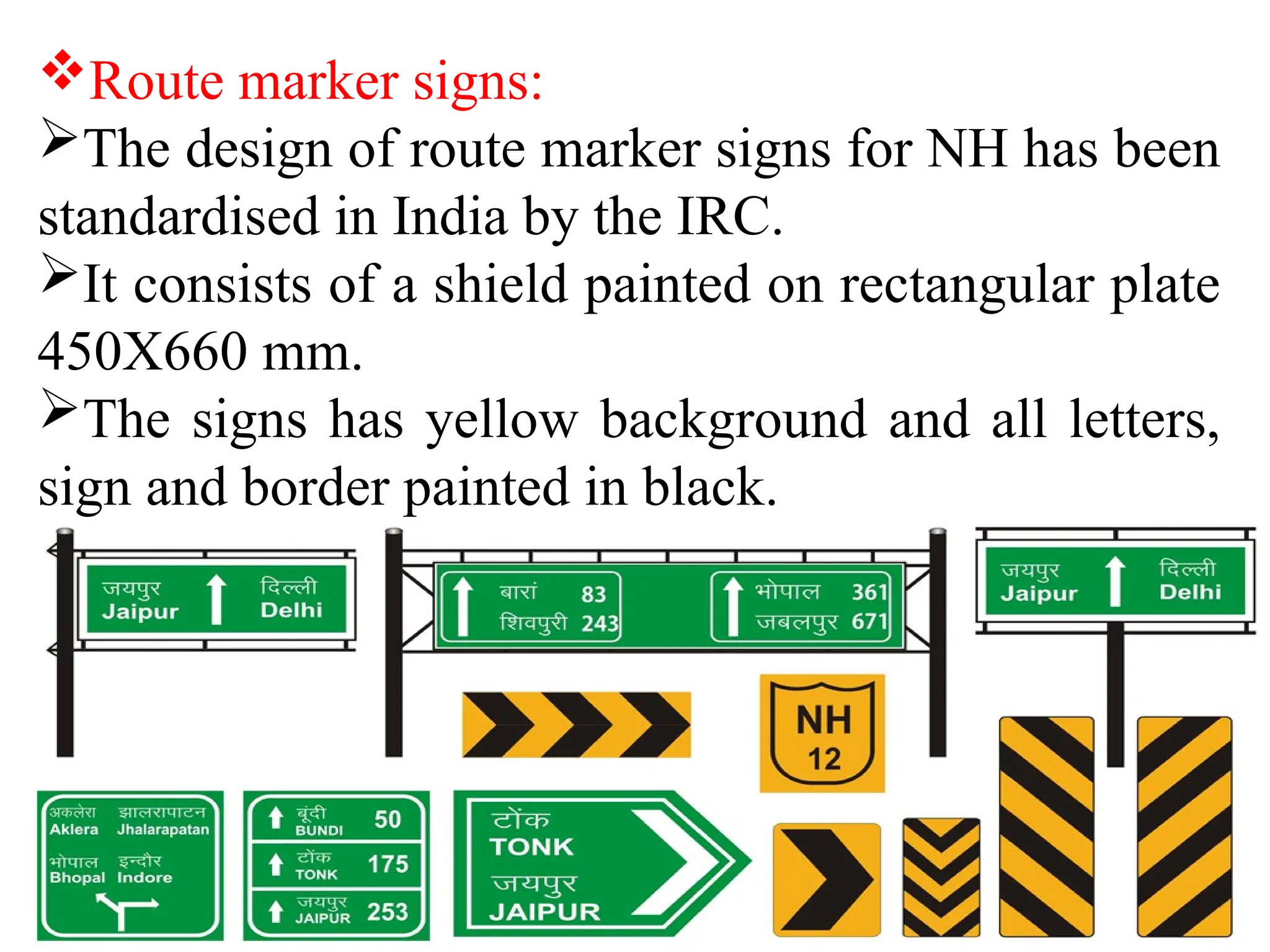
The document outlines traffic engineering elements, focusing on traffic control devices such as signs, signals, markings, and traffic islands, highlighting their types and functions. It describes mandatory, warning, and informatory signs as adopted by the government of Gujarat, while discussing advantages and disadvantages of traffic signals in enhancing road safety. Additionally, it covers the purpose and types of traffic islands, emphasizing their role in improving traffic flow and safety.