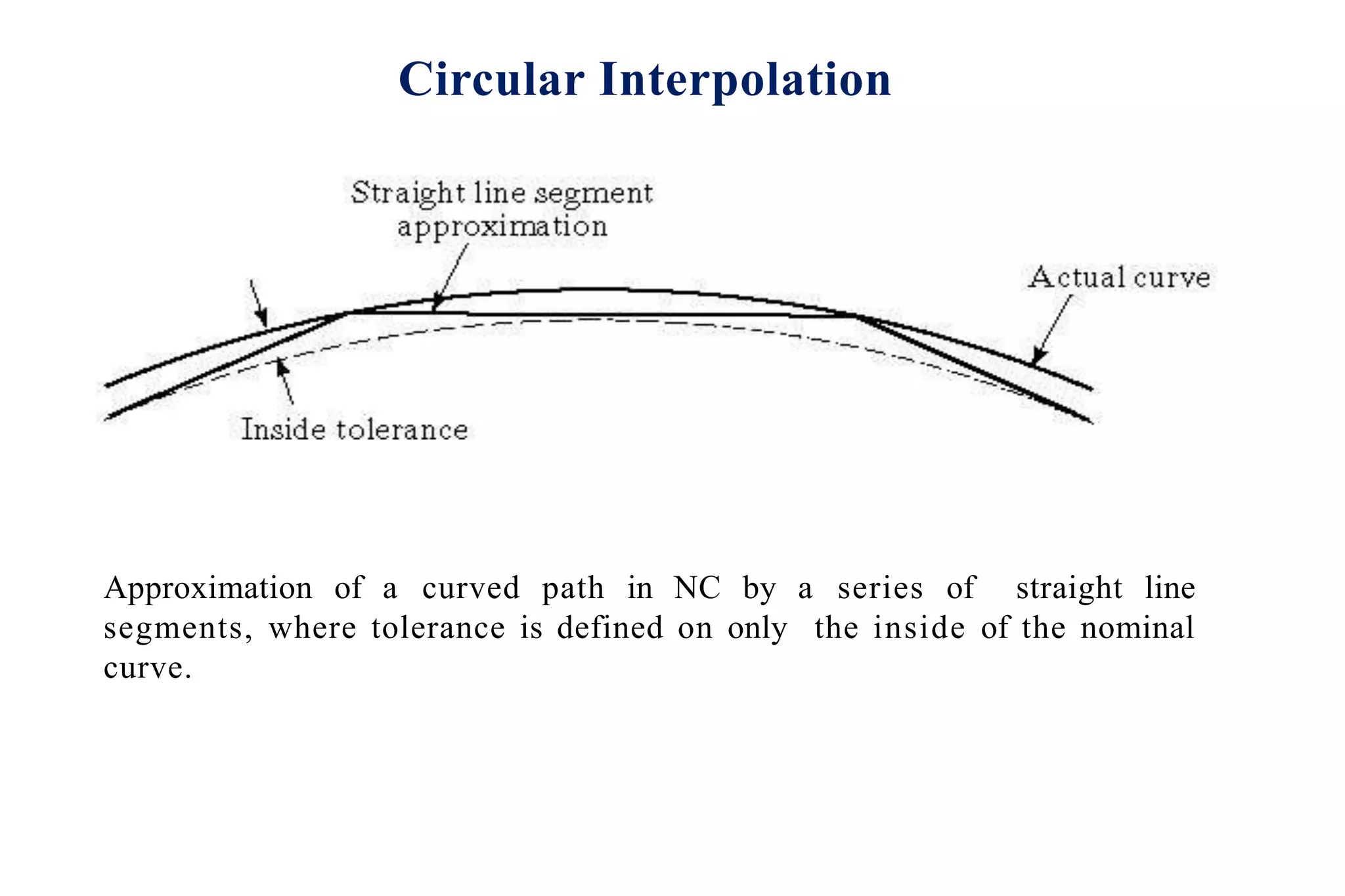
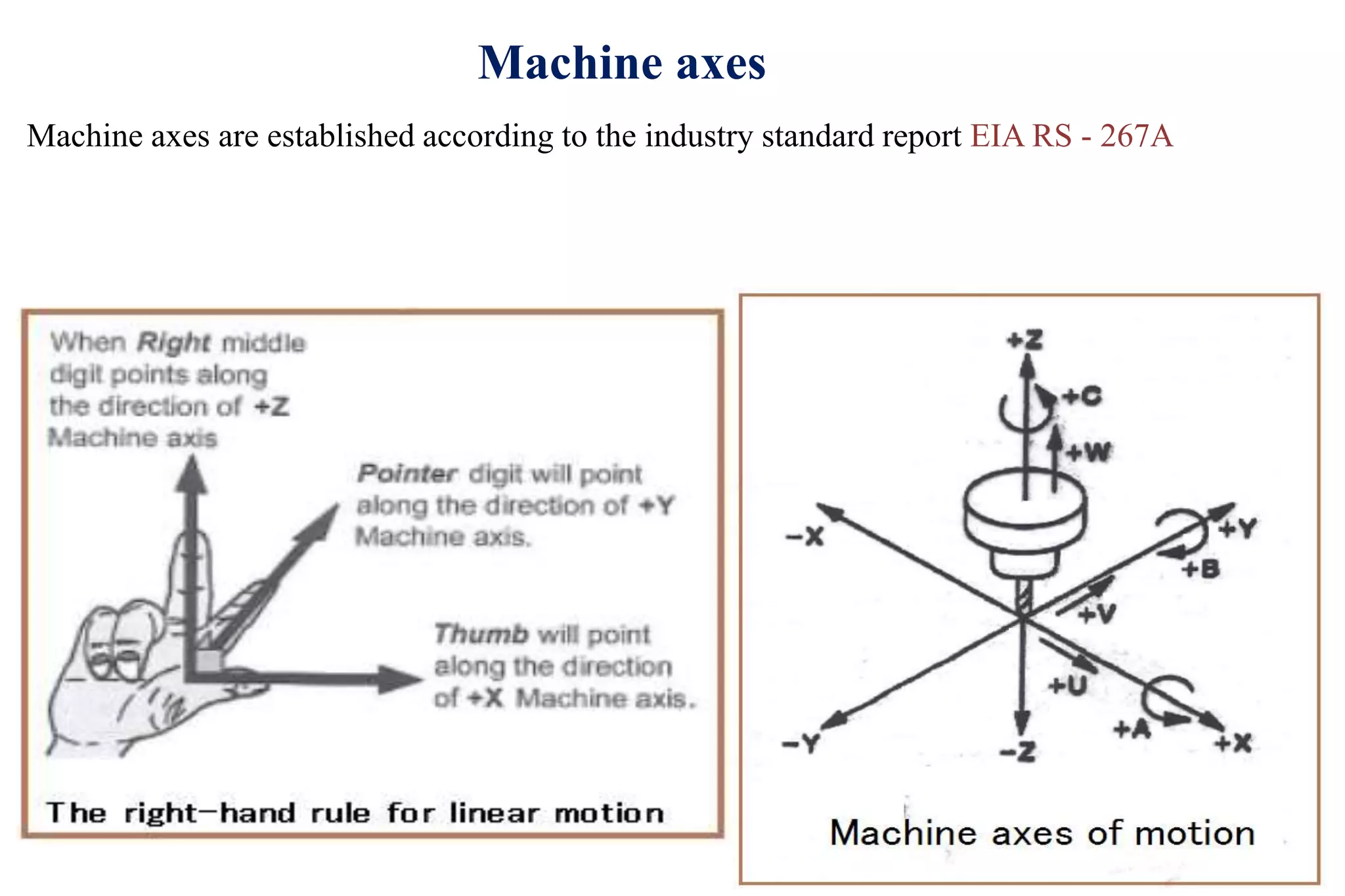
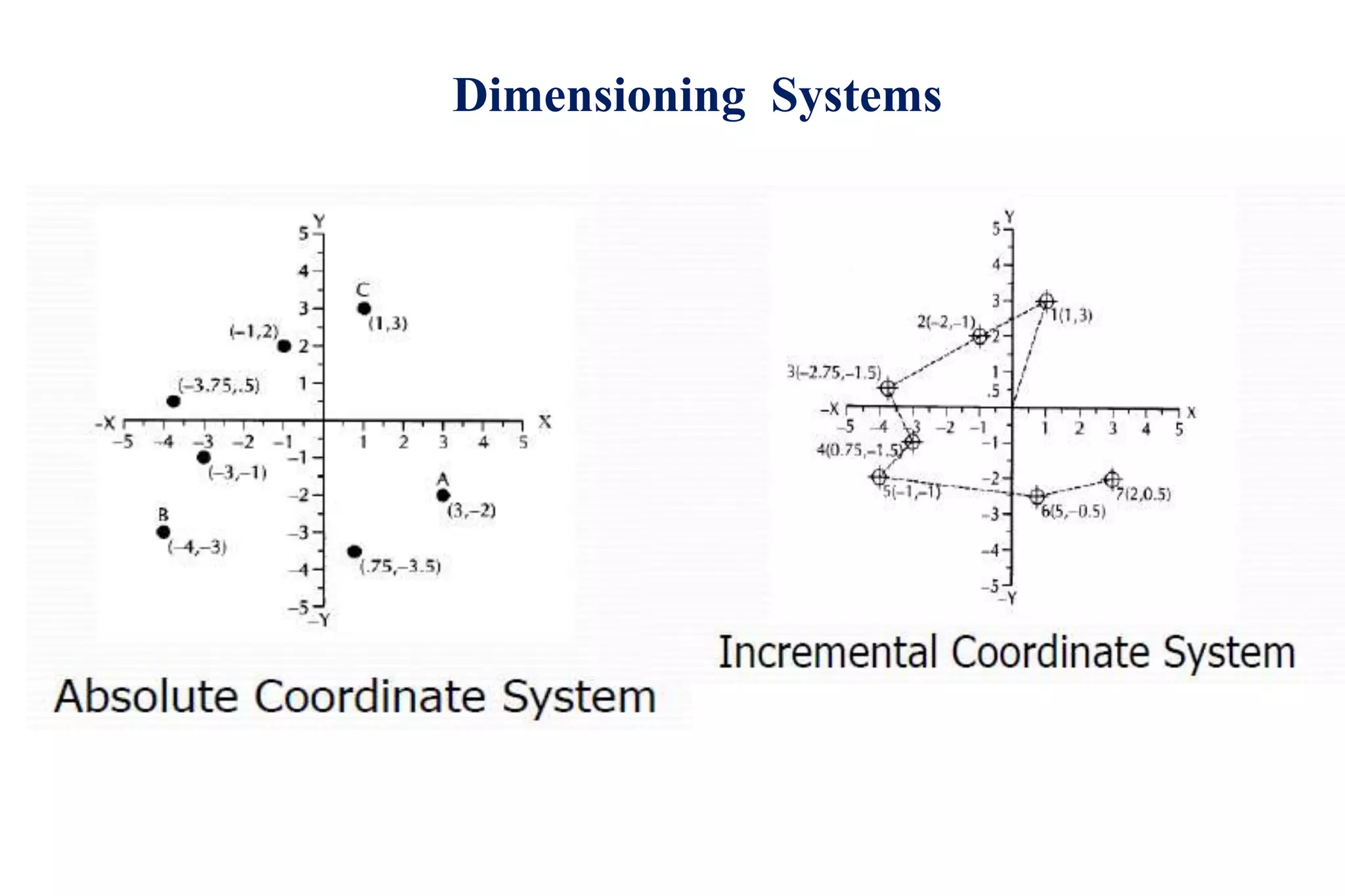
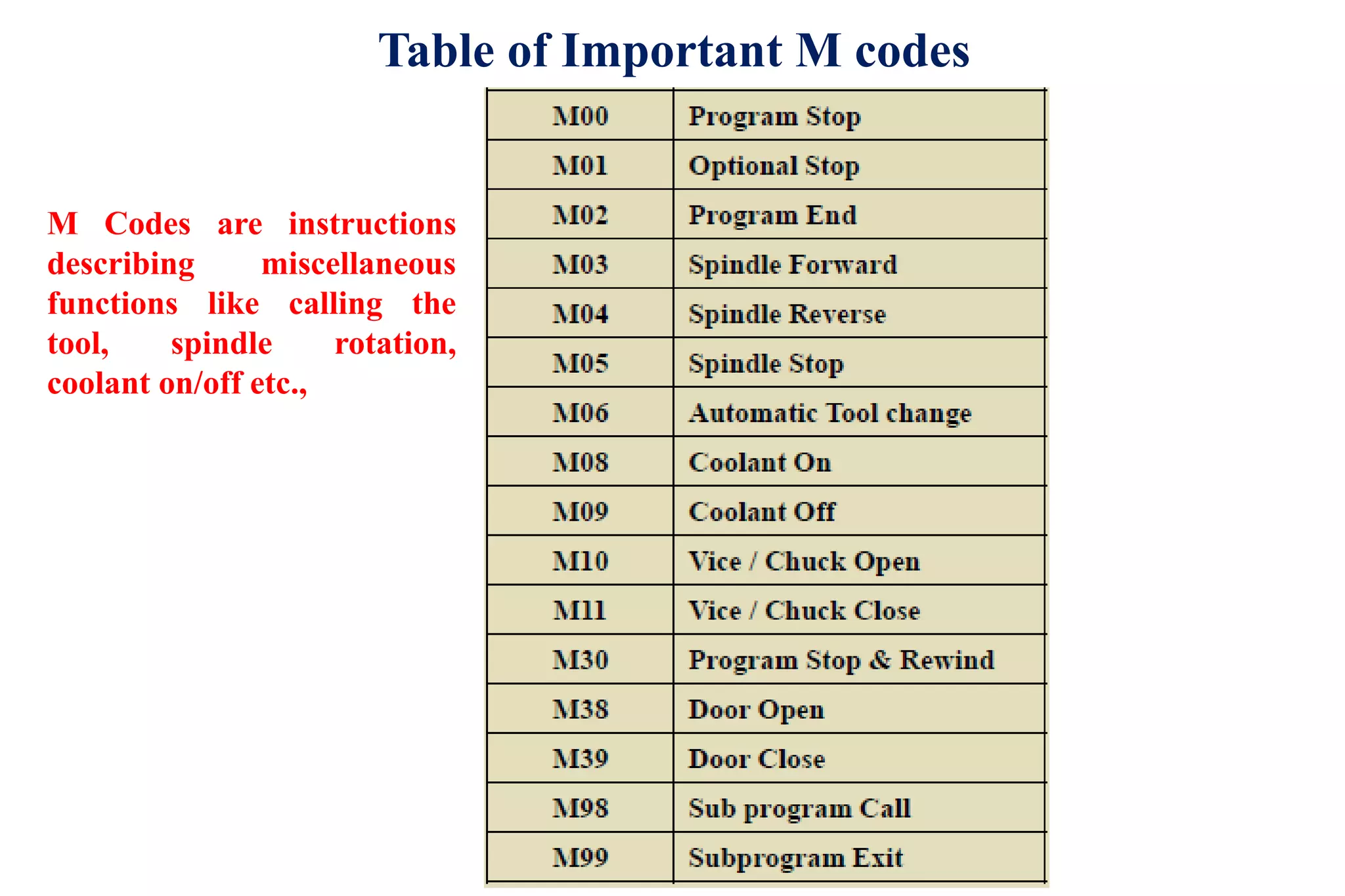
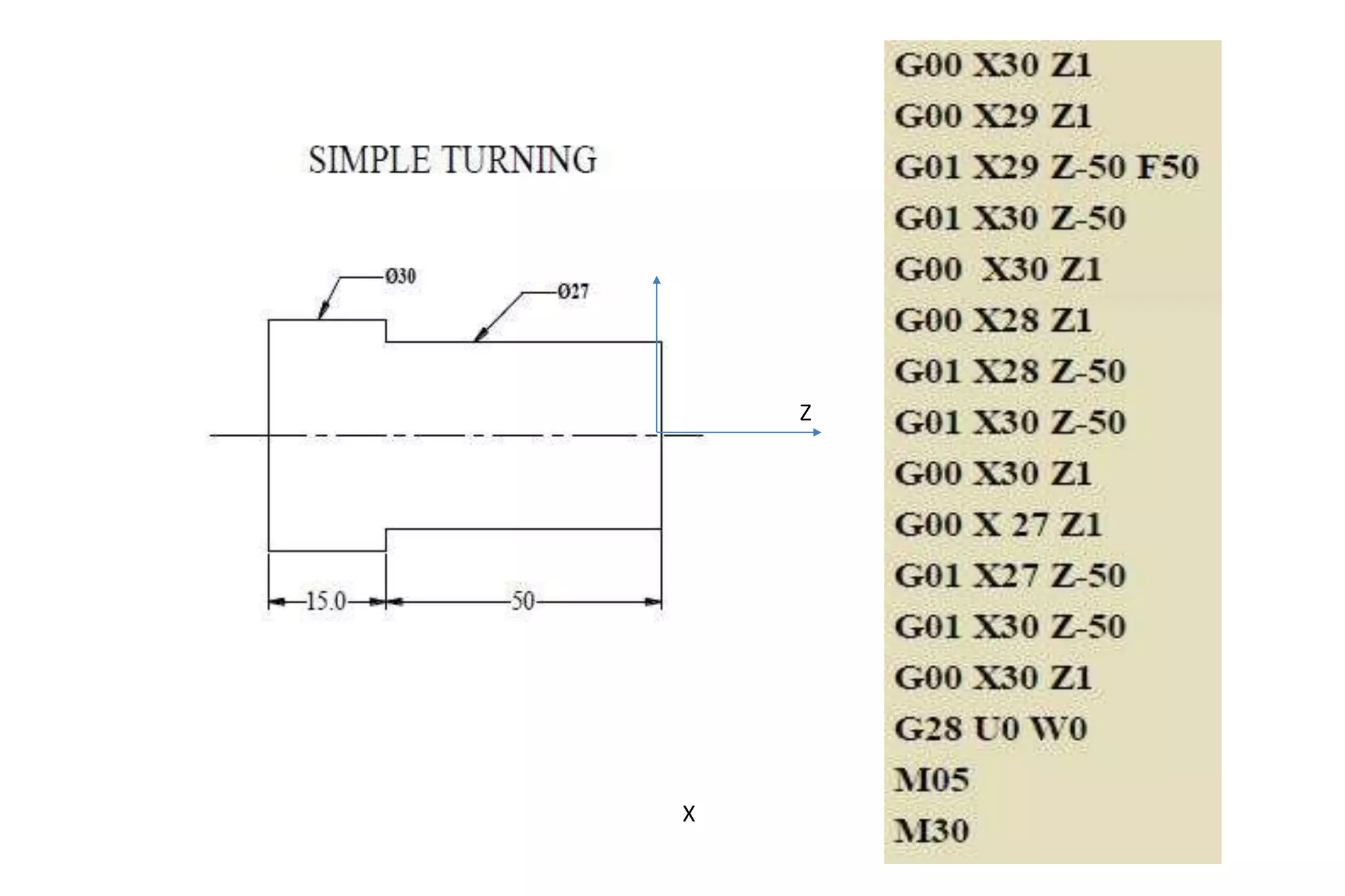
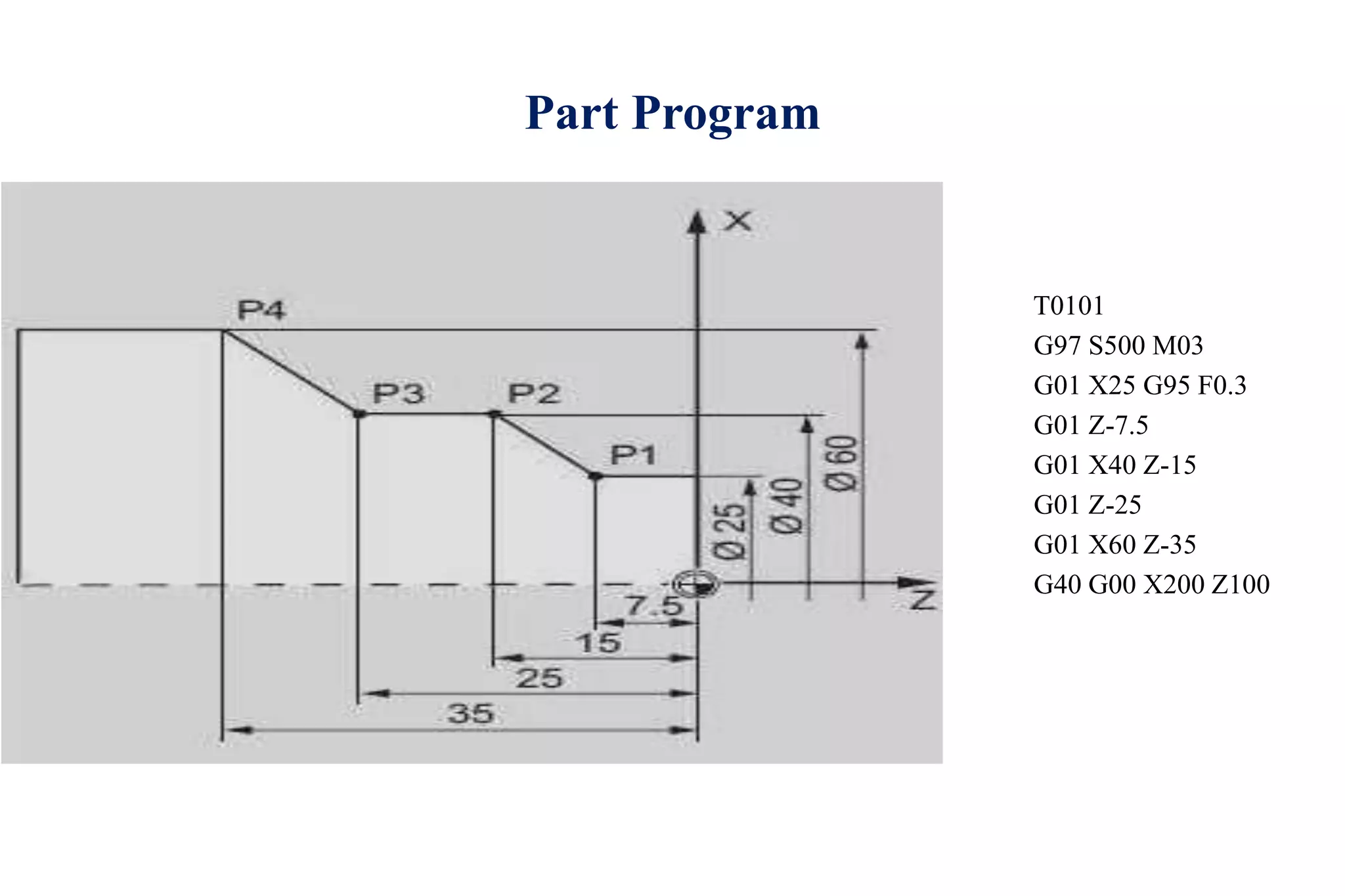
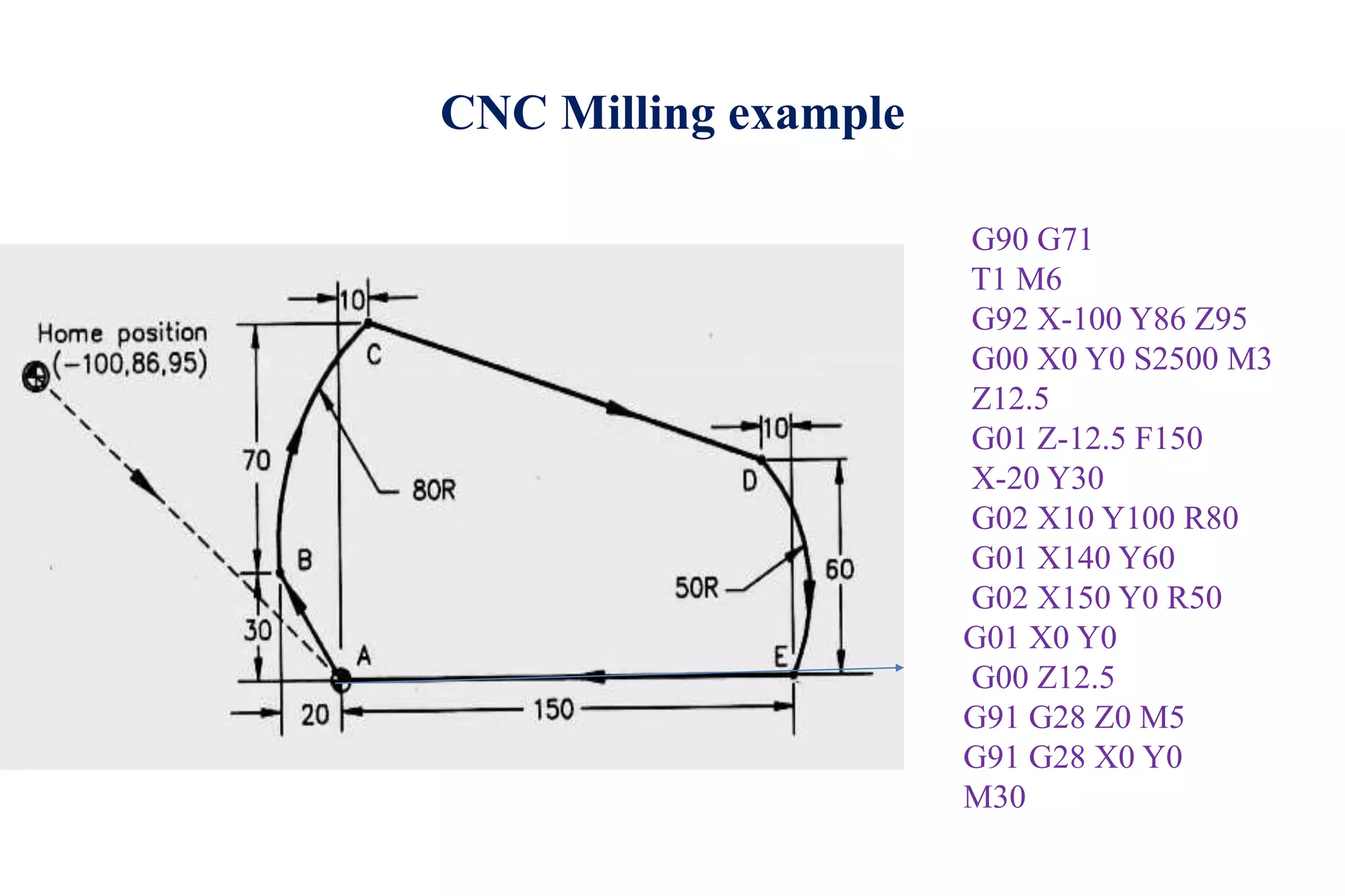
The document discusses various interpolation methods used in numerical control (NC) machining including linear, circular, helical, and higher order curve interpolation methods. It provides details on circular interpolation approaches and defines machine axes configurations. It also includes tables of important G and M codes used for CNC programming and examples of CNC milling part programs.