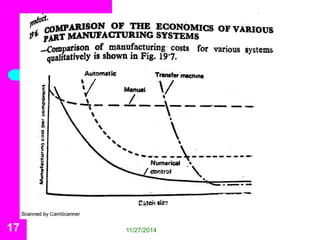
Transfer machines are integrated systems that perform multiple machining operations sequentially, allowing for maximum production rates. They come in various types, including in-line, rotary indexing table, and drum type, each suited for different arrangements and operations. Although they offer high precision and efficiency, transfer machines have limitations such as high initial costs and reduced flexibility.