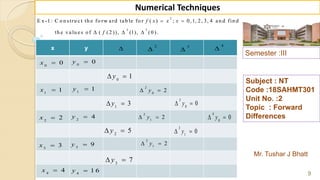
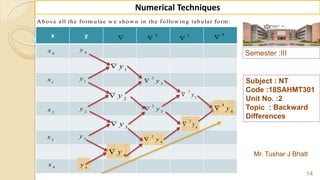
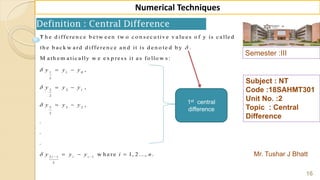
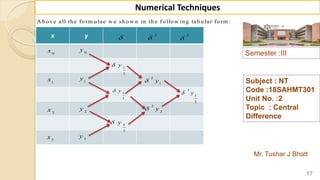
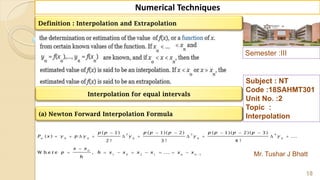
The document outlines the topic of 'Forward Differences' as part of a course on numerical techniques, emphasizing finite differences and interpolation methods. It includes definitions, types of differences (forward, backward, and central), and presents various interpolation formulas like Newton's and Lagrange's. Additionally, it details the properties of the operators and provides examples and tables for better understanding.
![Semester :III
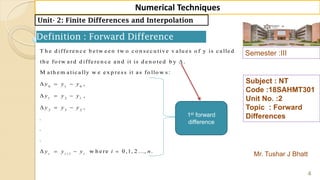
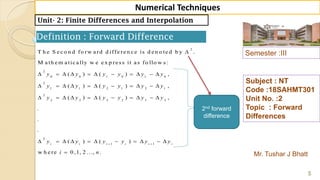
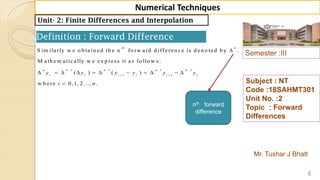
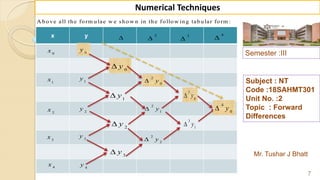
Mr. Tushar J Bhatt
Subject : NT
Code :18SAHMT301
Unit No. :2
Topic : Forward
Differences
8
Numerical Techniques
P roperties of the operator :
1 . [ ( ) ( )] ( ) ( )
w h ere ' ' an d ' ' are co n stan ts.
a f x b g x a f x b g x
a b
2 . [ ( ) ] ( ) w h ere 'c' is co n stan t.c f x c f x
3 . ( ) ( )
w h e re ' ' a n d ' ' a re p o s itiv e in te g e rs .
m n m n
f x f x
m n
4 . [ ( ) ( )] ( ) ( )f x g x f x g x
5 . [ ] 0 w h ere 'c' is co n stan tc ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nt-unit-2-201021070655/85/Interpolation-in-Numerical-Methods-8-320.jpg)

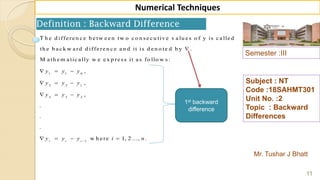
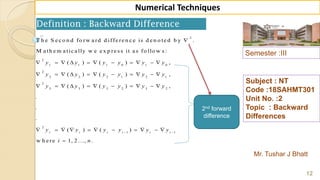
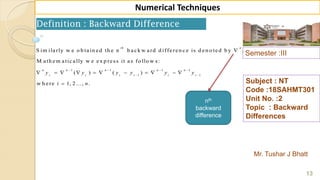
![Semester :III
Mr. Tushar J Bhatt
Subject : NT
Code :18SAHMT301
Unit No. :2
Topic : Backward
Differences
15
Numerical Techniques
P roperties of the operator :
1 . [ ( ) ( )] ( ) ( )
w h ere ' ' an d ' ' are co n stan ts.
a f x b g x a f x b g x
a b
2 . [ ( ) ] ( ) w h ere 'c' is co n stan t.c f x c f x
3 . ( ) ( )
w h e re ' ' a n d ' ' a re p o s itiv e in te g e rs .
m n m n
f x f x
m n
4 . [ ( ) ( )] ( ) ( )f x g x f x g x
5 . [ ] 0 w h ere 'c' is co n stan tc ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nt-unit-2-201021070655/85/Interpolation-in-Numerical-Methods-15-320.jpg)

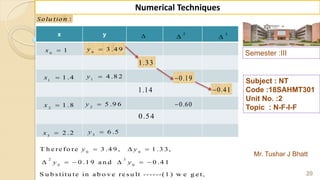



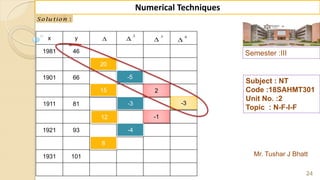


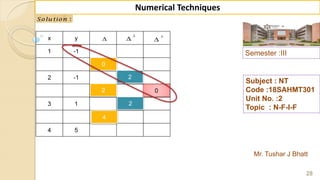




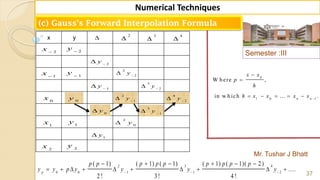
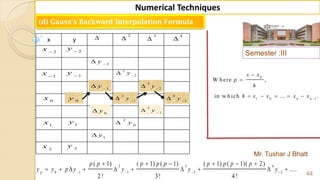
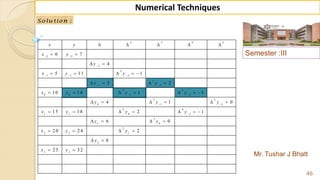
![Semester :III
Mr. Tushar J Bhatt
38
Numerical Techniques
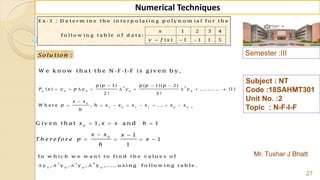
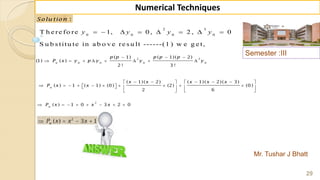
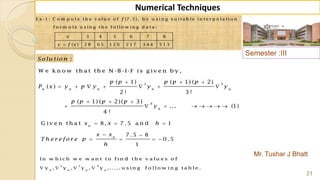
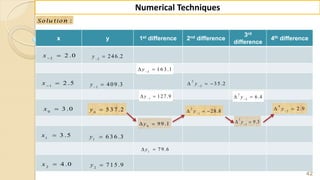
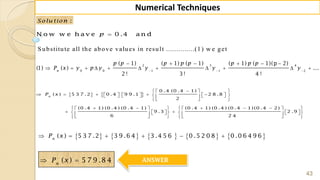
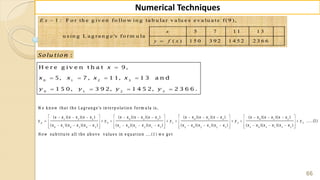
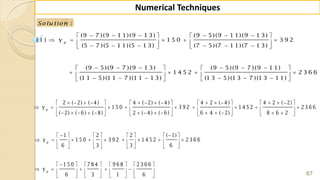
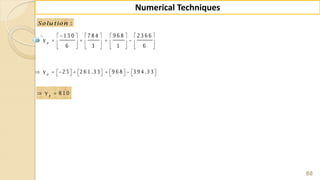
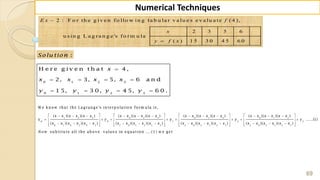
E x -1 : F in d ( 2 2 ) fro m th e fo llo w in g ta b u la r v a lu e s u sin g
G a u ss's fo rw a rd fo rm u la .
2 0 2 5 3 0 3 5 4 0 4 5
3 5 4 3 3 2 2 9 1 2 6 0 2 3 1 2 0 4
f
x
y
S o lu tio n :
W e k n o w th a t th e G -F -I-F is g iv e n b y ,
2 3 4
0 0 1 1 2
( 1) ( 1) ( 1) ( 1) ( 1)( 2)
....
2 ! 3! 4 !
p
p p p p p p p p p
y y p y y y y
1
0
0
H e re w e w a n t to fin d ( ) w h e re 2 2, S o 2 2 is lie s in th e in te rv a l [2 5, 3 0 ] ,
in w h ic h 2 2 is v e ry n e a r to 2 5 ra th e r th a n 3 0 th e re fo re w e c h o o s e 2 5 .
2 2 2 5 3
0 .6
5 5
f x x x
x
x x
p
h](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nt-unit-2-201021070655/85/Interpolation-in-Numerical-Methods-38-320.jpg)
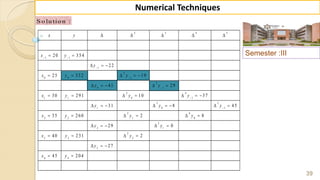

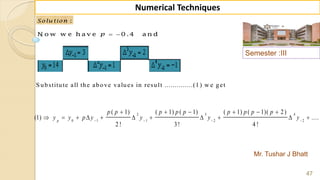


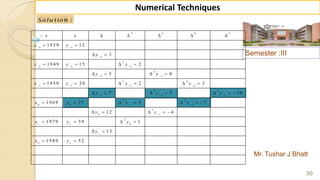
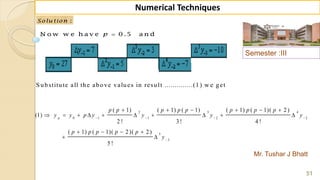
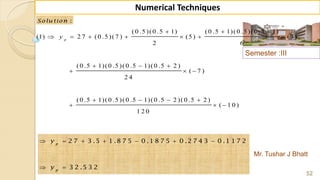

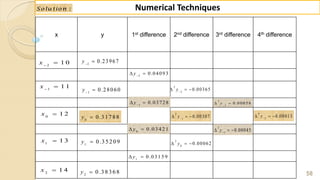
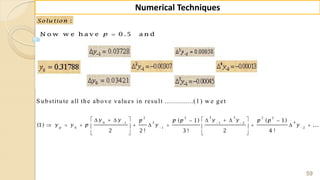


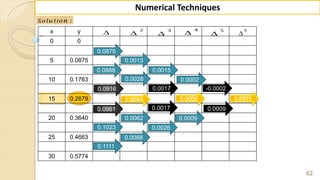


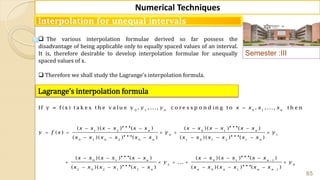
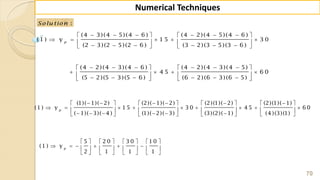

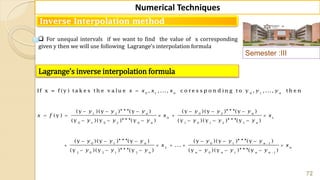

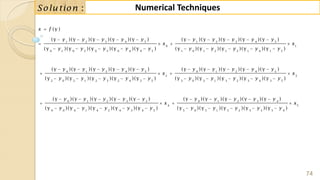



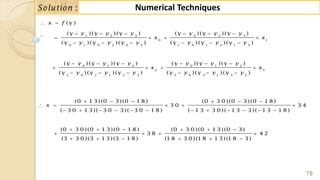

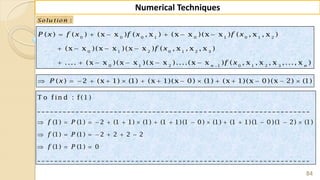
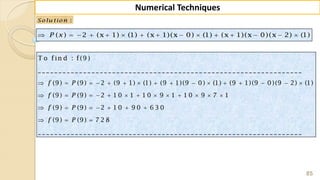
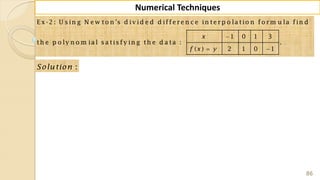
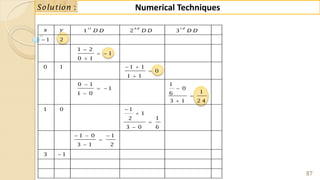


![90
Numerical Techniques
2
2
2
2
2
2 2
N o w ( ) ( ( ))
( ) ( )
( ) [ ( 1)] ( ......(1))
( ) ( 1) [ ], ( 1 is c o n s ta n t )
( ) ( 1) [ ( 1)] ( ......(1))
( ) ( 1) [ ]..................( 2 )
x x
x x h
x h x h
x h x h
x h x
f x f x
e e
e e e fr o m
e e e e
e e e e fr o m
e e e
1
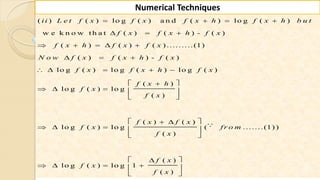
E x -1 : E v a lu a te th e fo llo w in g ( ) ( e ) ( ) (lo g ) ( ) (ta n ).
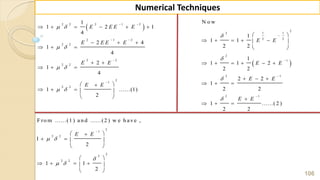
:
n x
i ii x iii x
S o lu tio n
H ere w e k n o w th at h e d ifferen tial o p erato r ( ) ( ) ( ).f x f x h f x
( ) ( ) ( )
x x h x h
i L e t f x e th e r e fo r e f x h e e e
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( 1).................(1)
x x h x x h
f x f x h f x
e e e e e e
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nt-unit-2-201021070655/85/Interpolation-in-Numerical-Methods-90-320.jpg)
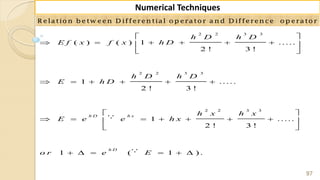
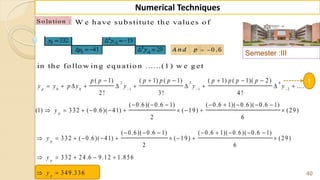
![91
Numerical Techniques
3 2
3 2
3 2
3 2
3 2
3 3
( ) ( ( ))
( ) ( )
( ) [( 1) [ ] ( ......( 2 ))
( ) ( 1) [ ], ( 1 is c o n s ta n t )
( ) ( 1) [ ( 1)] ( ......( 2 ))
( ) ( 1) [ ]..................(3)
x x
x h x
x h x h
x h x h
x h x
S im ila r ly f x f x
e e
e e e fr o m
e e e e
e e e e fr o m
e e e
F ro m resu lt .......(1 ), (2 ) an d (3 ) w e g et in g en eral
( ) ( 1) [ ]
n x h n x
e e e ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nt-unit-2-201021070655/85/Interpolation-in-Numerical-Methods-91-320.jpg)
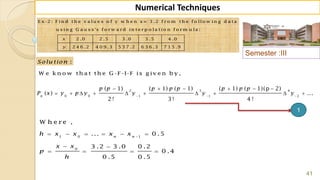
![92
Numerical Techniques
3 2
3 2
3 2
3 2
3 2
3 3
( ) ( ( ))
( ) ( )
( ) [( 1) [ ] ( ......( 2 ))
( ) ( 1) [ ], ( 1 is c o n s ta n t )
( ) ( 1) [ ( 1)] ( ......( 2 ))
( ) ( 1) [ ]..................(3)
x x
x h x
x h x h
x h x h
x h x
S im ila r ly f x f x
e e
e e e fr o m
e e e e
e e e e fr o m
e e e
F ro m resu lt .......(1 ), (2 ) an d (3 ) w e g et in g en eral
( ) ( 1) [ ]
n x h n x
e e e ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nt-unit-2-201021070655/85/Interpolation-in-Numerical-Methods-92-320.jpg)