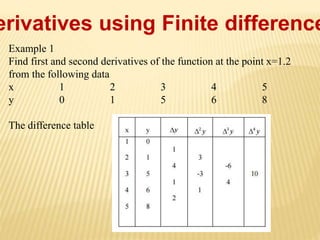
This document discusses numerical differentiation, which is the process of finding the numerical value of the derivative of a given function at a given point. It notes that if the x-values are equally spaced, derivatives are calculated using Newton's forward or backward interpolation formulas, while if they are not equally spaced, a difference formula is used. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating derivatives from given data using finite difference methods like Newton's forward and backward difference formulas.