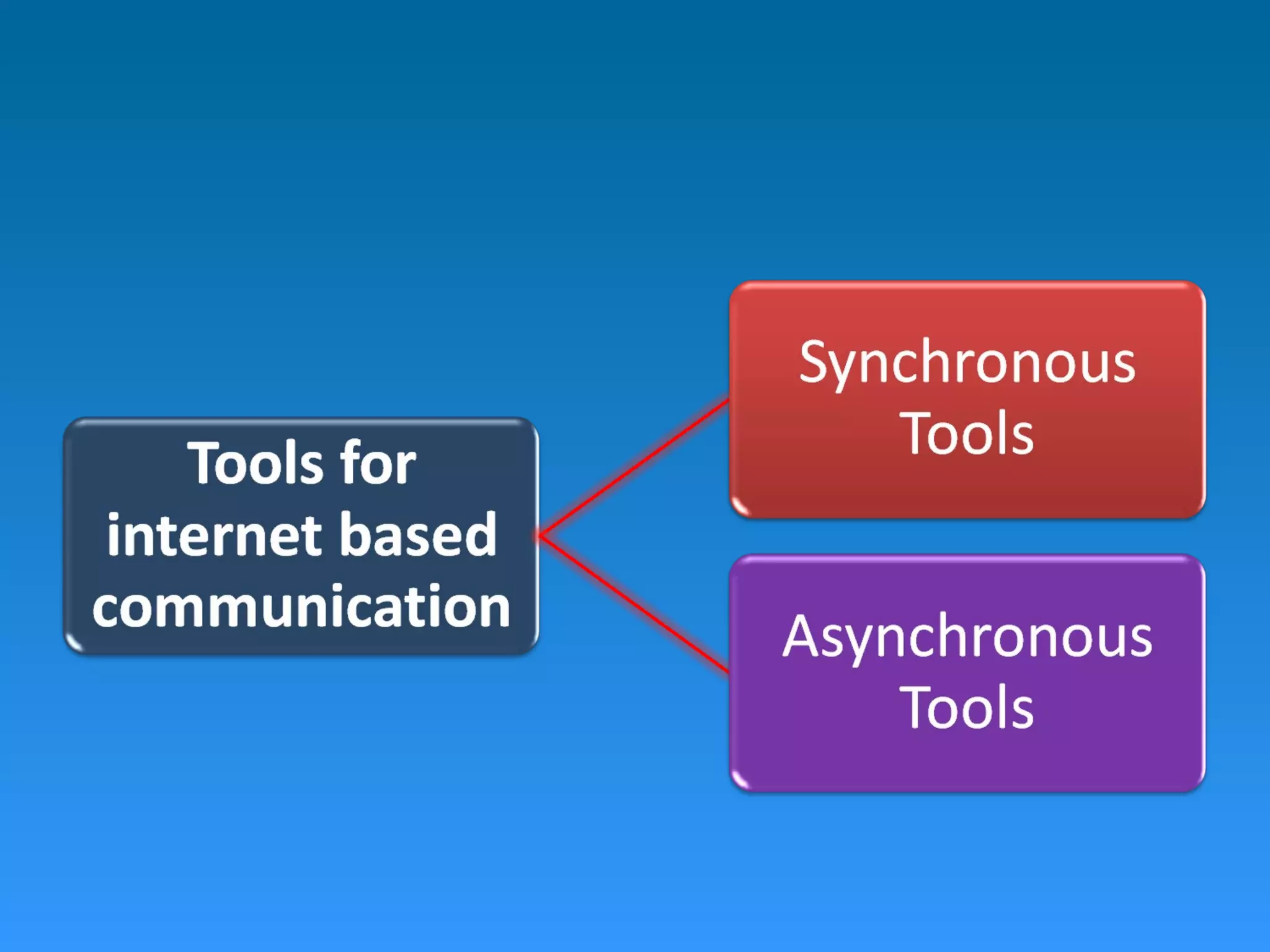
The document provides an overview of the internet and networks, detailing their history, terminologies, and communication tools such as synchronous and asynchronous methods. It also explores various internet services like email, blogs, chat, and videoconferencing, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages in educational contexts. Additionally, it covers initiatives like INFLIBNET, N-List, and Shodhganga aimed at improving access to educational resources and fostering communication among institutions.