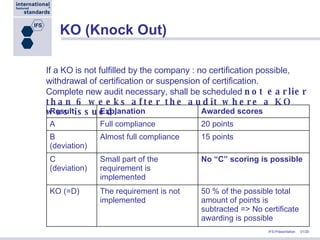
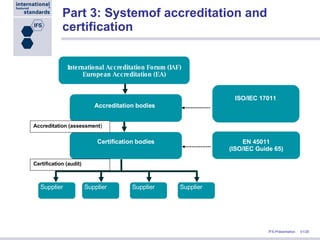
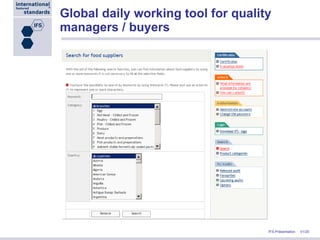
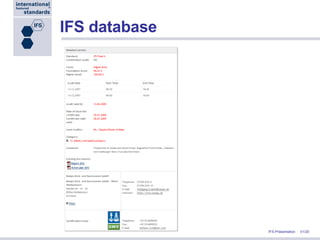
Stephan Tromp, the managing director of IFS, presented at the NRA Conference in Atlanta about the role of IFS in the supply chain, focusing on the importance of a standardized food safety system to improve cost efficiency and compliance in food safety audits. IFS provides a common framework for quality assurance, facilitating a unified evaluation system accepted by over 9,500 certification bodies globally, and is supported by major retailers in Europe and beyond. The presentation also highlighted IFS's commitment to continuous improvement and the development of e-tools to streamline auditing processes and enhance transparency in food supply chains.
































![Thank you for your attention ! Contact: Mr. Stephan Tromp General Manager IFS Phone: 0049-(0)30-726-250-70 Fax: 0049-(0)30-726-250-79 E-Mail: [email_address] www.ifs-online.eu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20081022ifstromp-1225901743068923-8/85/International-Featured-Standards-Presentation-38-320.jpg)