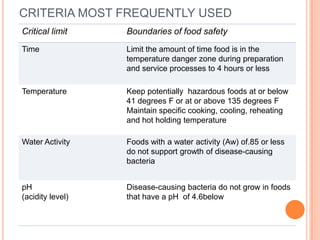
The document outlines the seven principles of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) system, which is a prevention-based food safety program that identifies hazards and monitors critical control points during food production to prevent foodborne illnesses. Key aspects of HACCP include identifying biological, chemical, and physical hazards; establishing critical limits for monitoring critical control points; and maintaining records to verify the effectiveness of the system. The principles aim to anticipate and control hazards before problems occur through monitoring at critical stages of food production.