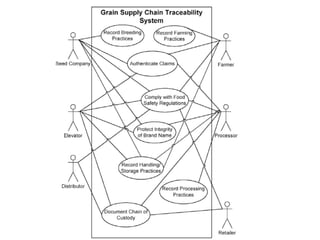
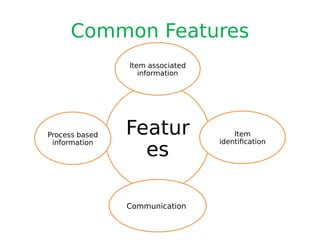
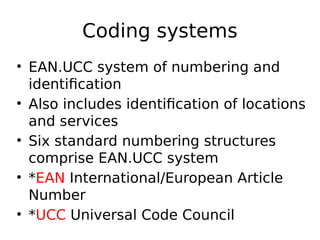
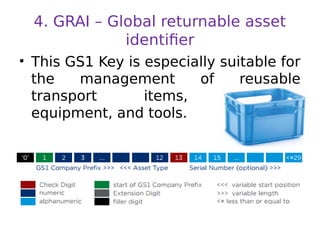
This document discusses food traceability, including definitions, functional roles, common features, and coding systems. It summarizes key aspects of traceability including tracking food through production and distribution, identifying origins, and supporting food safety, labeling, and risk assessment. It also outlines the most commonly used global traceability standards, including the GS1 system of numbering and identification codes that can track items, locations, logistics units and more through the supply chain.