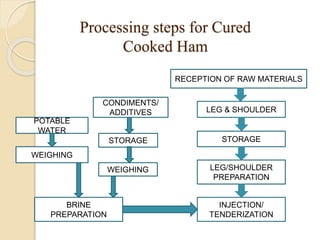
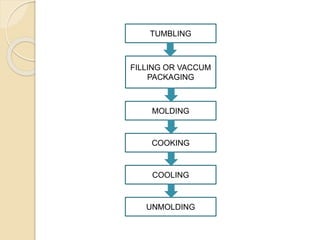
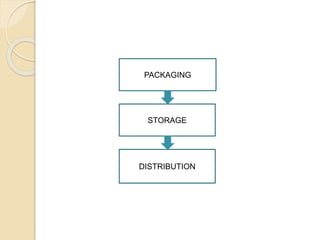
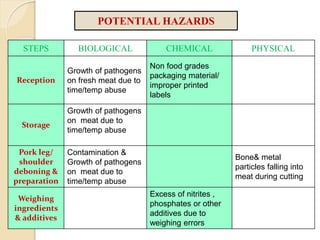
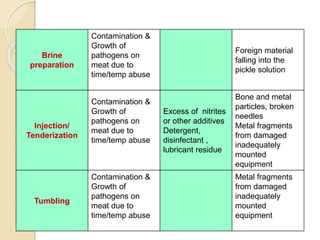
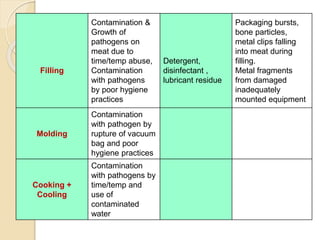
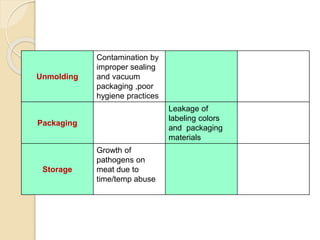
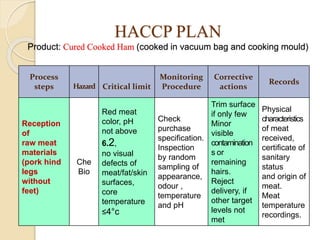
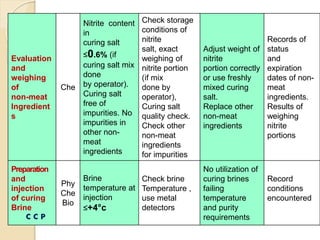
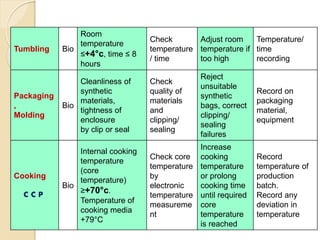
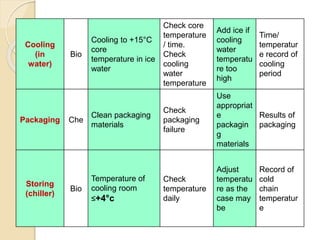
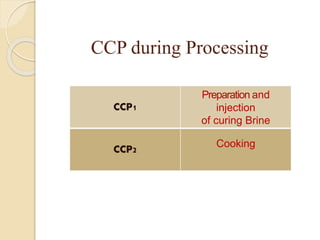
This document discusses the implementation of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) in the meat industry. It covers the 7 principles of HACCP and provides examples of how to apply it in meat processing plants. Specifically, it analyzes the processing steps for cured cooked ham and identifies potential biological, chemical and physical hazards at each step. It then outlines the HACCP plan for cured cooked ham production, identifying critical control points and establishing critical limits and monitoring procedures. Finally, it provides recommended microbiological criteria for fresh meat.