1) This chapter discusses how money supply, interest rates, and exchange rates are interrelated in both the short run and long run.
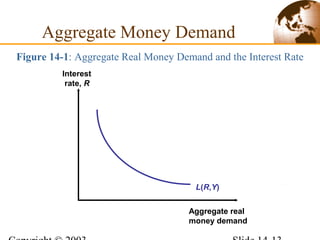
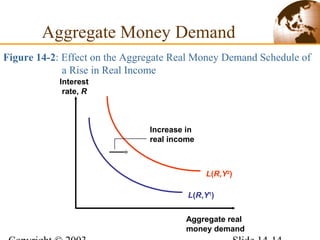
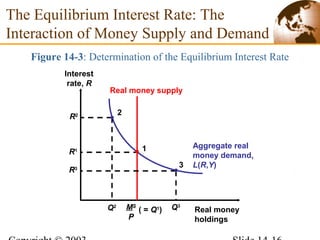
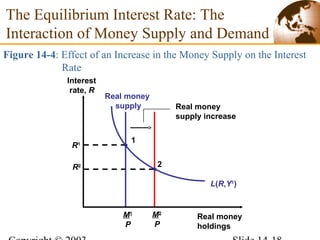
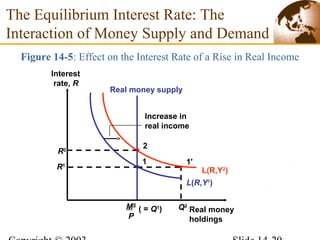
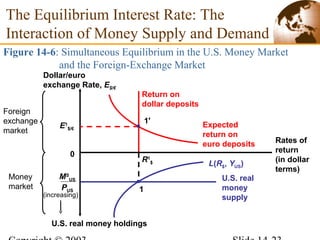
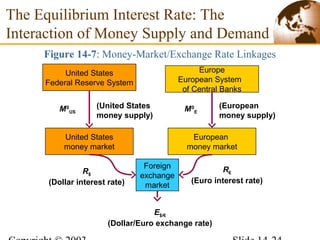
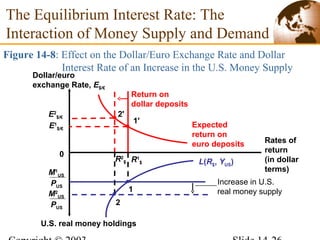
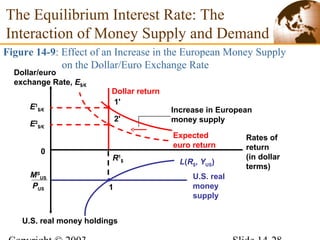
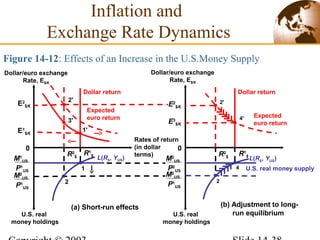
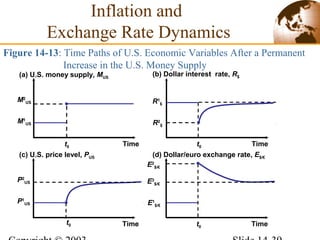
2) In the short run, changes to a country's money supply will affect its interest rates, which then feed through to impact exchange rates via interest rate parity. An increase in money supply lowers interest rates and causes currency depreciation.
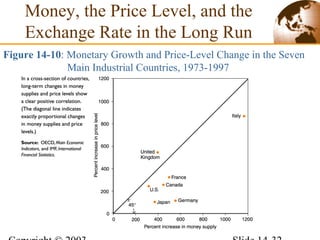
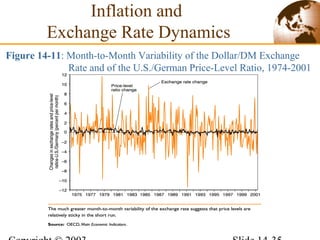
3) In the long run, a permanent increase in the money supply leads to a proportional increase in the price level but does not affect real output or interest rates. Higher long-term inflation correlates with higher monetary growth across countries.