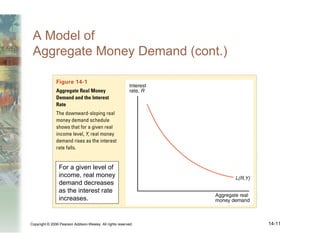
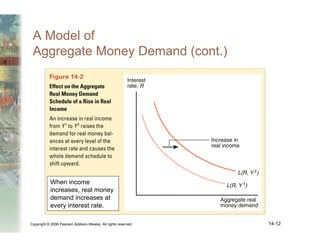
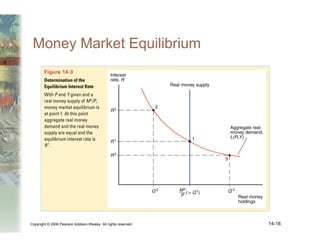
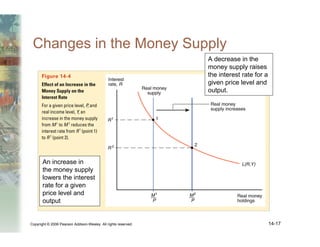
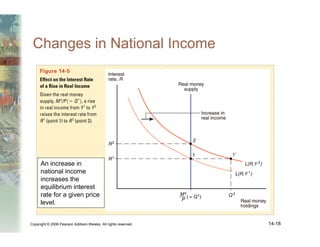
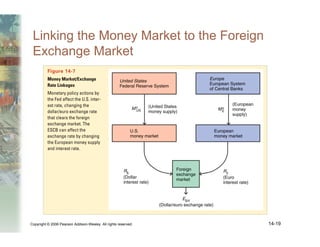
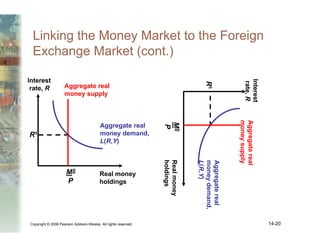
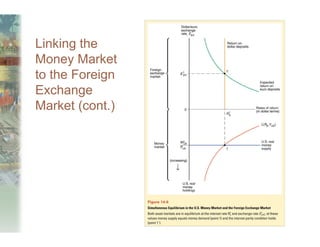
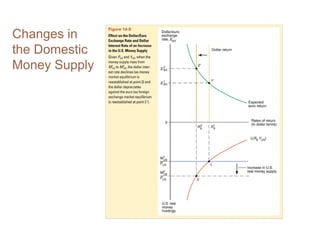
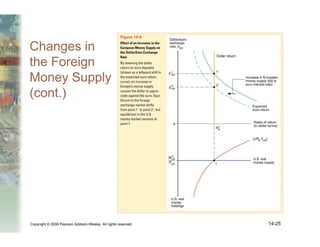
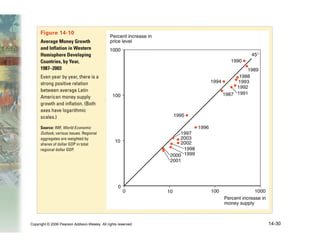
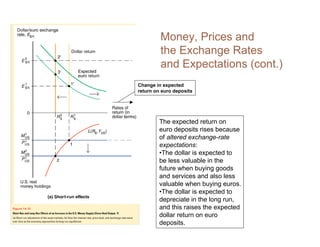
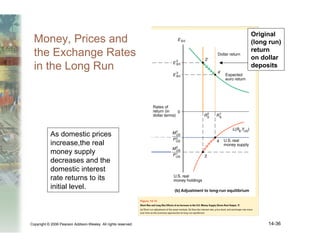
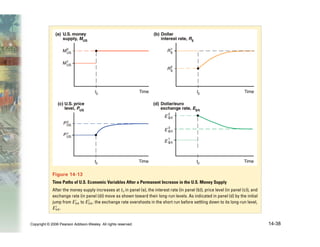
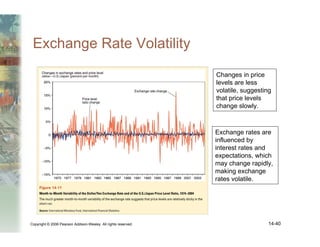
This document summarizes key concepts relating to money, interest rates, and exchange rates. It discusses what money is, how the money supply is controlled by central banks, and factors that influence the demand for money, including interest rates, prices, and income. A model of aggregate money demand is presented where real money demand depends on interest rates and income. The money market equilibrium sets money supply equal to demand. Changes in domestic or foreign money supplies can shift exchange rates by impacting interest rates and expectations. In the long run, increases in the money supply lead to proportional price inflation but leave real variables unchanged.