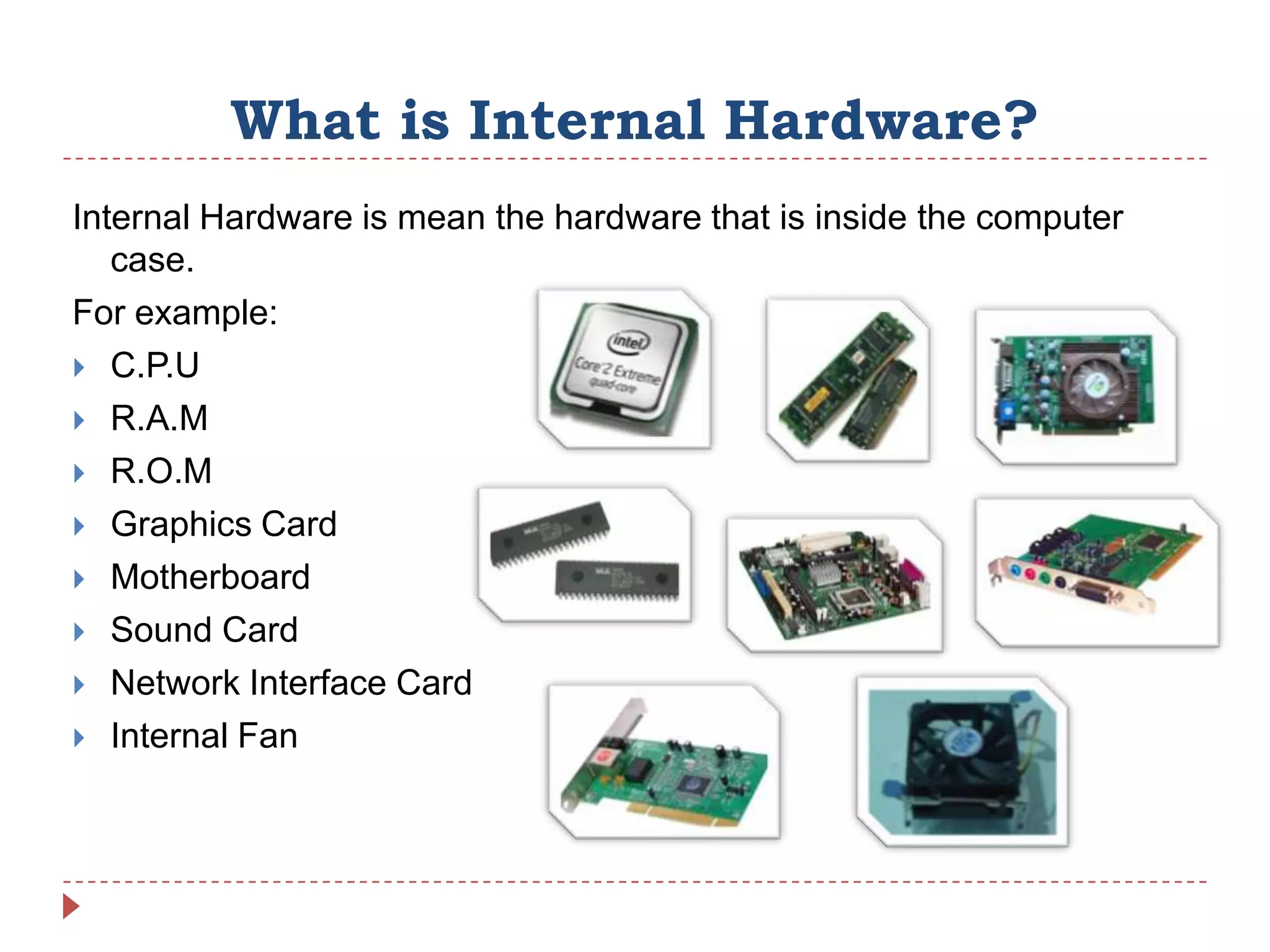
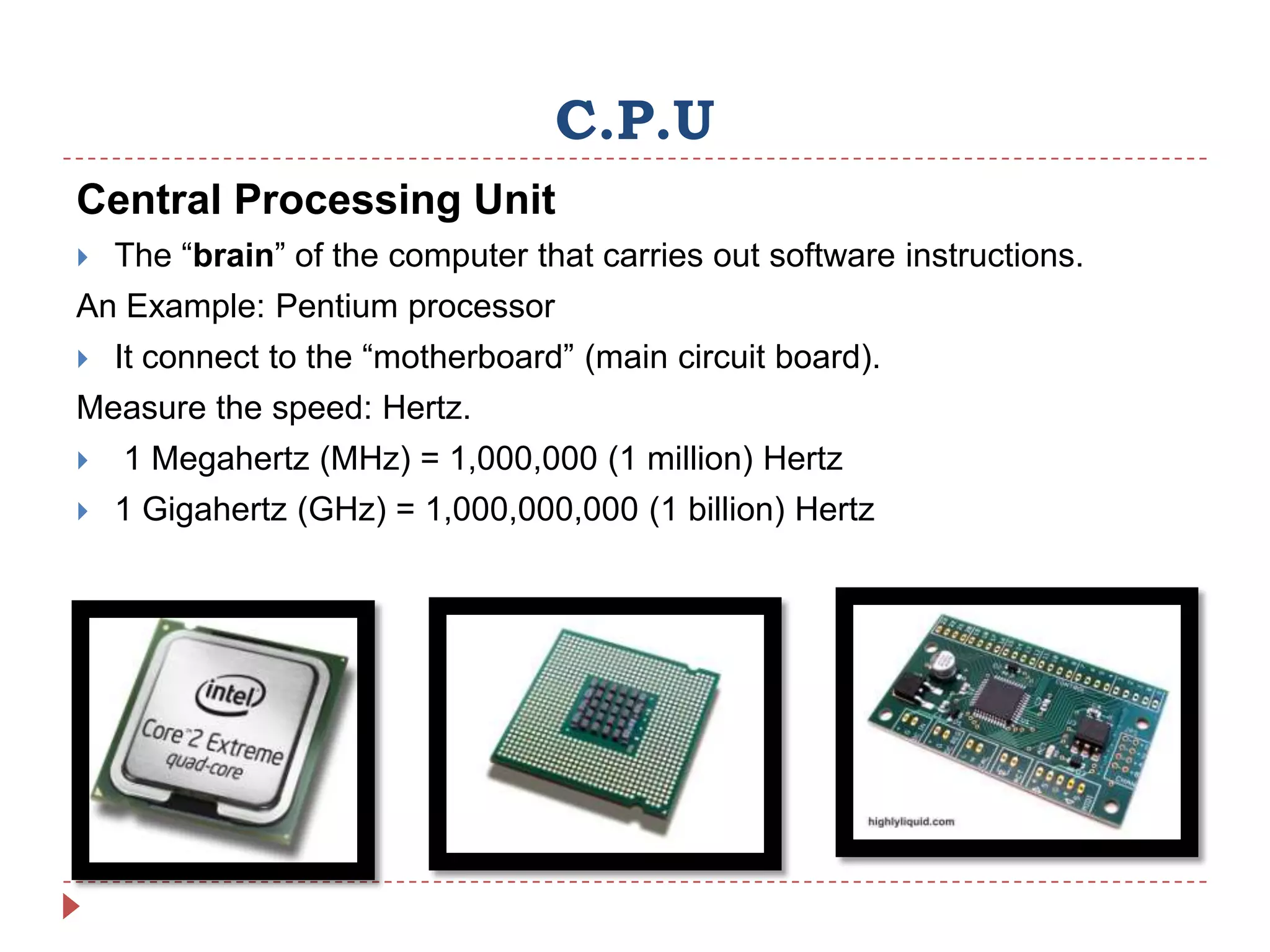
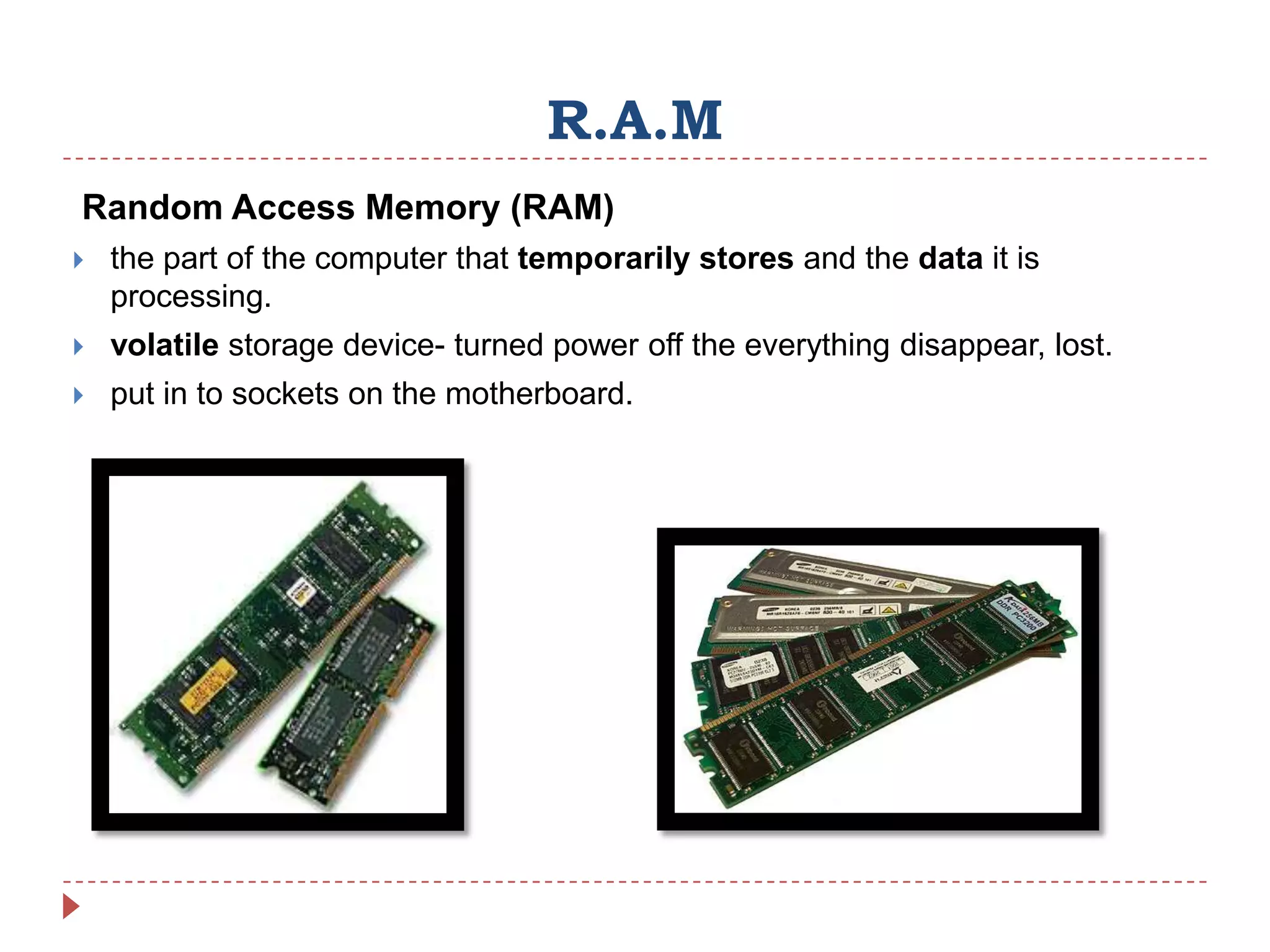
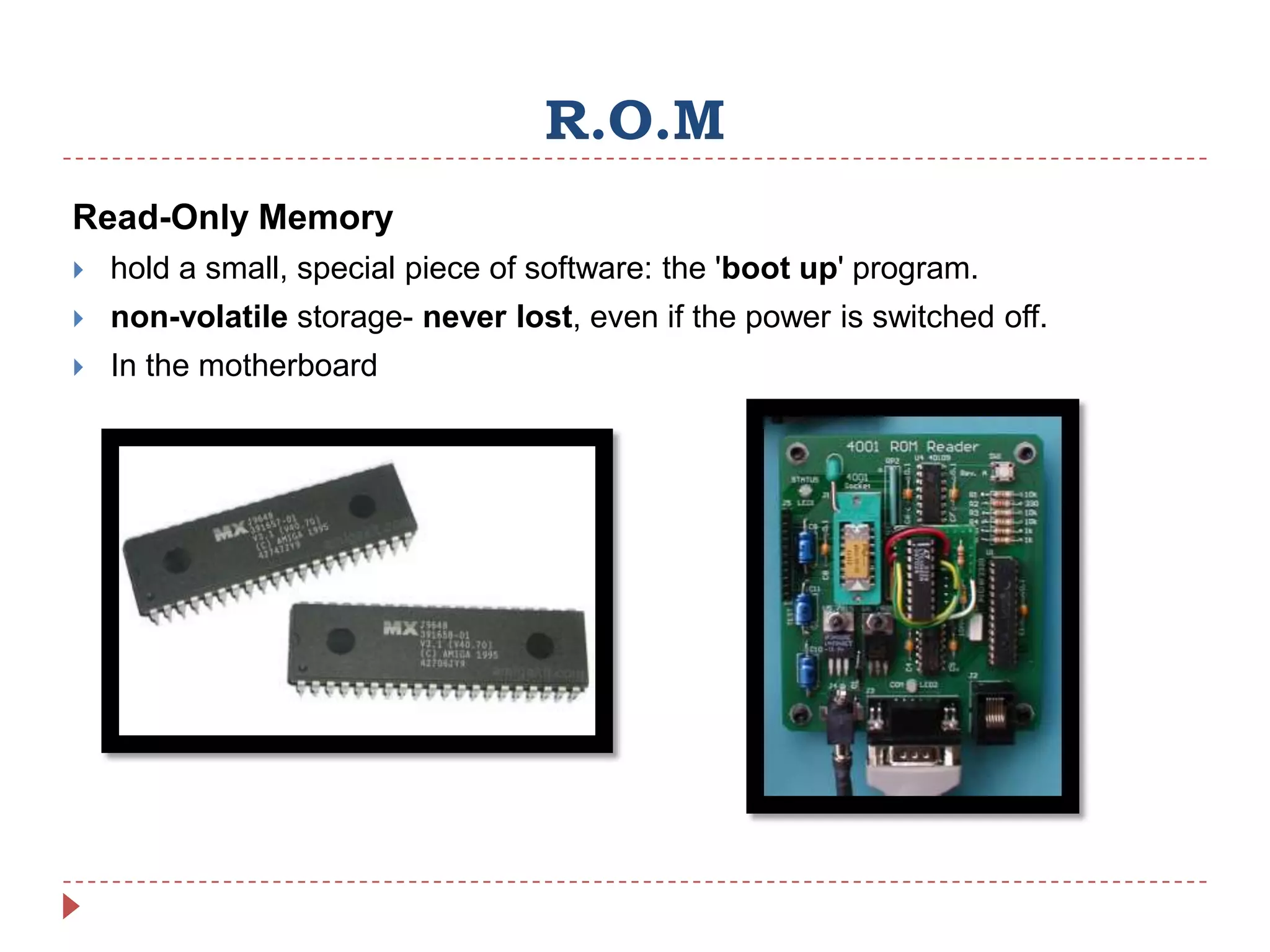
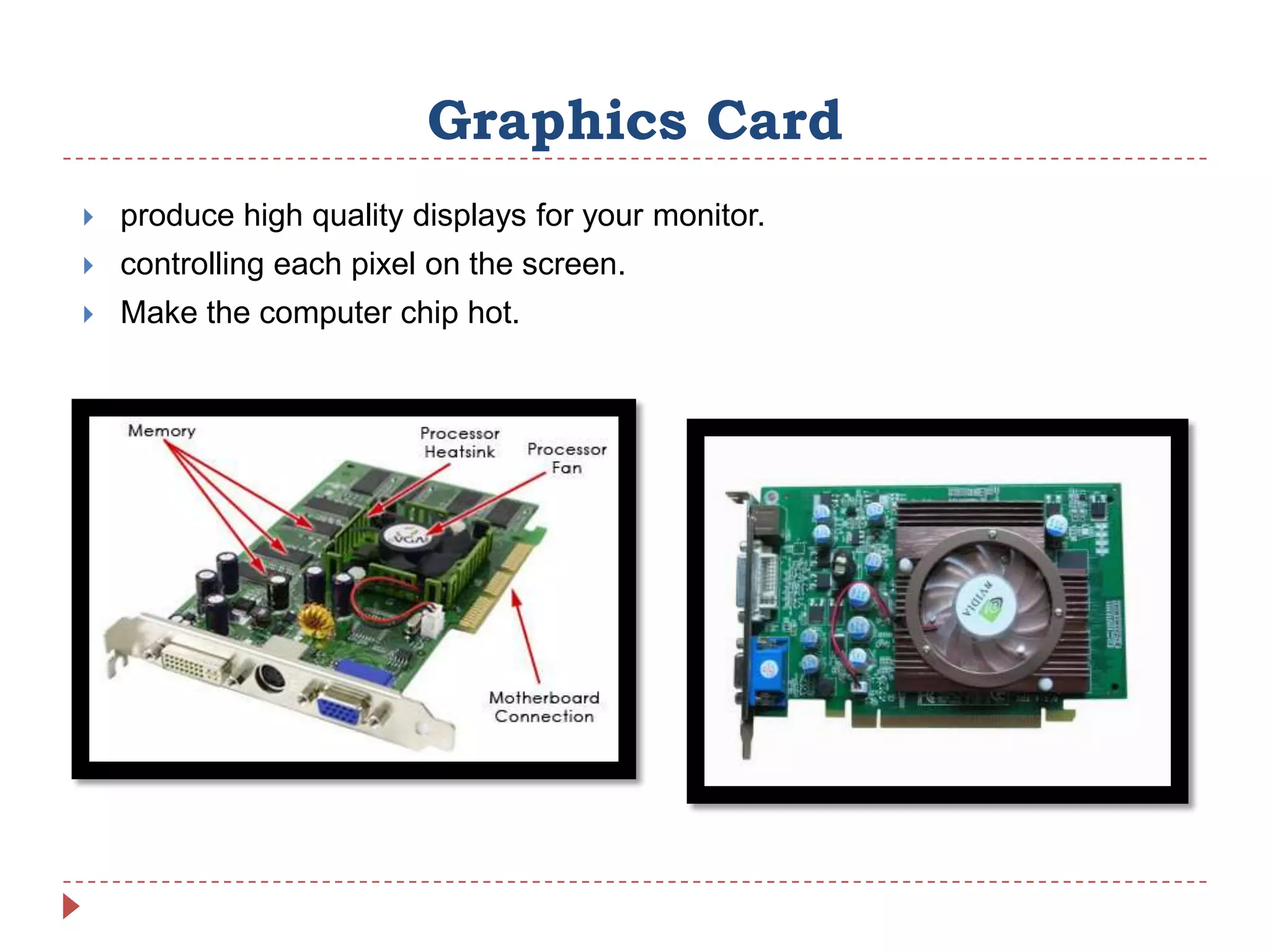
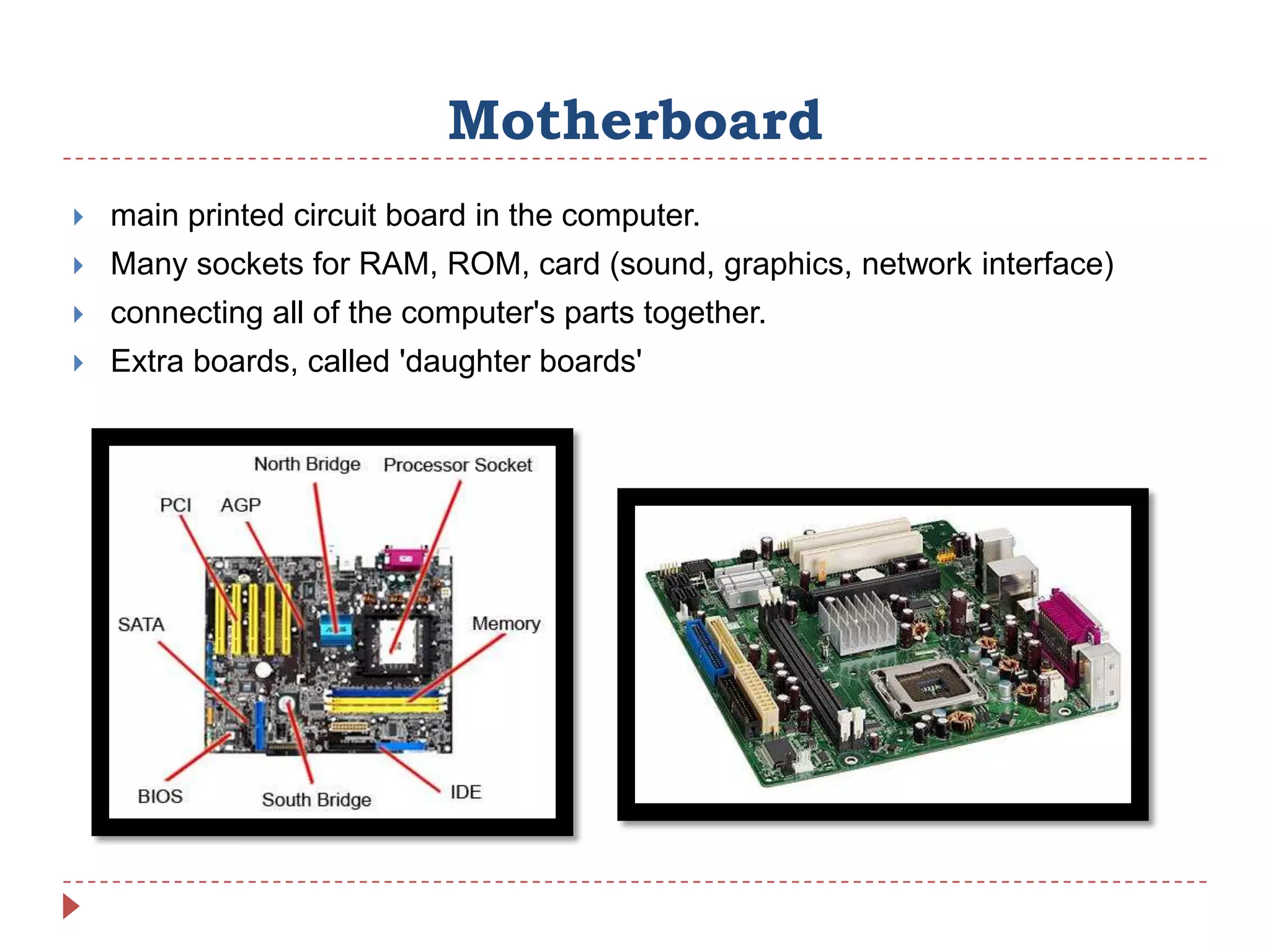
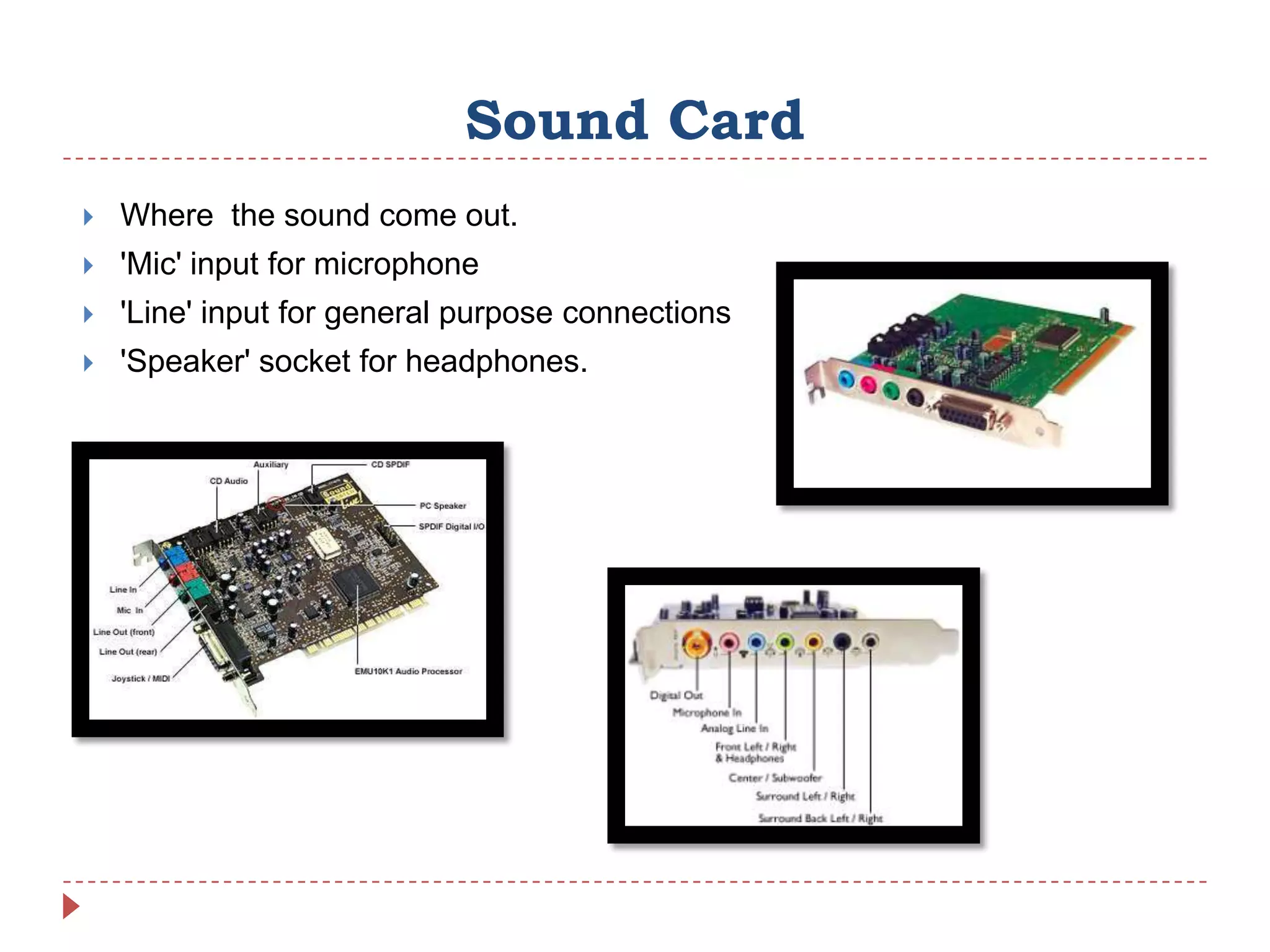
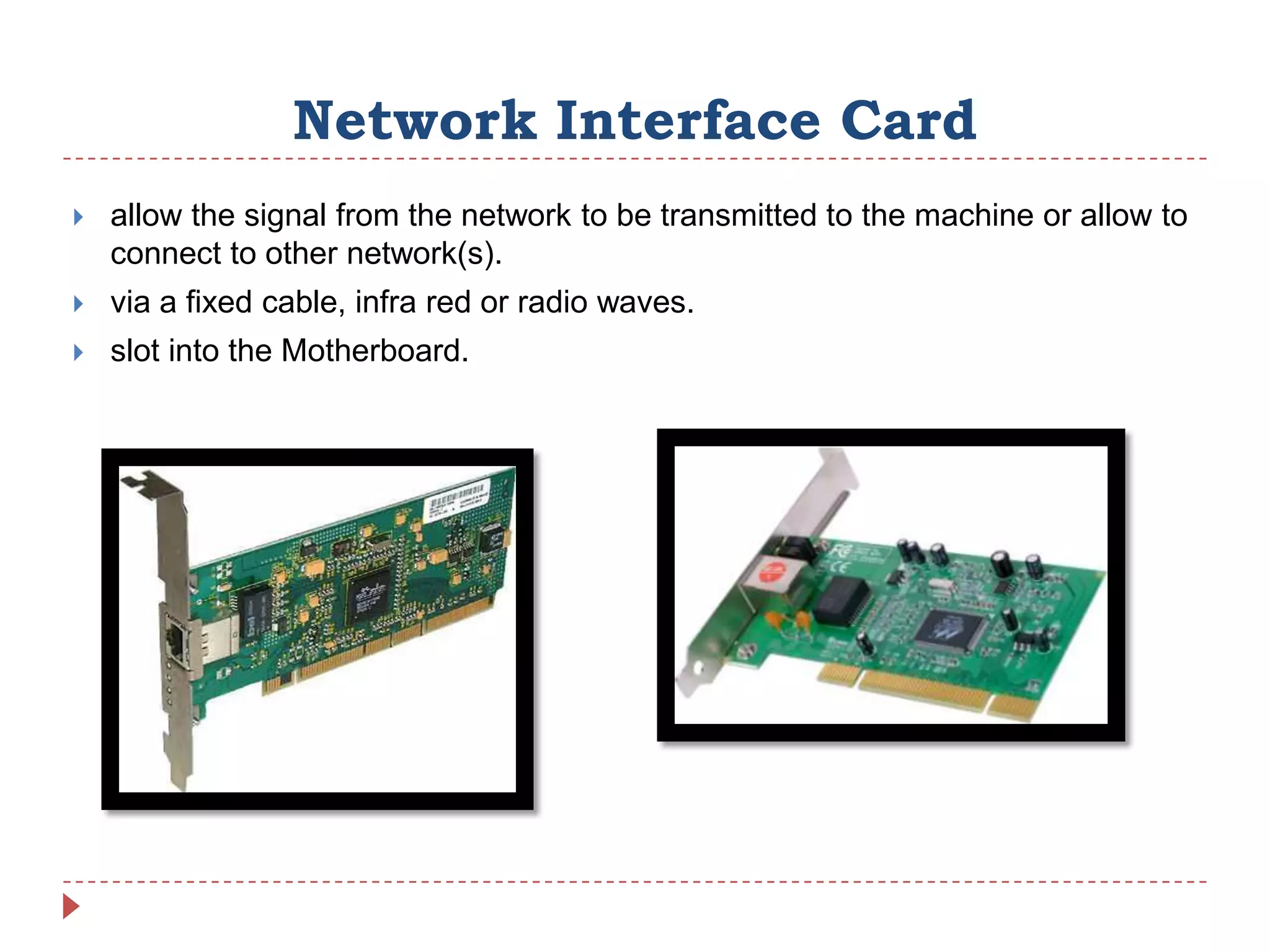
Internal hardware refers to the components inside a computer case that work together to process instructions and transfer data. This includes the CPU for running software, RAM for temporary data storage, ROM for startup instructions, a graphics card for displaying visuals, a motherboard connecting all parts, optional sound and network cards, and cooling fans to prevent overheating.