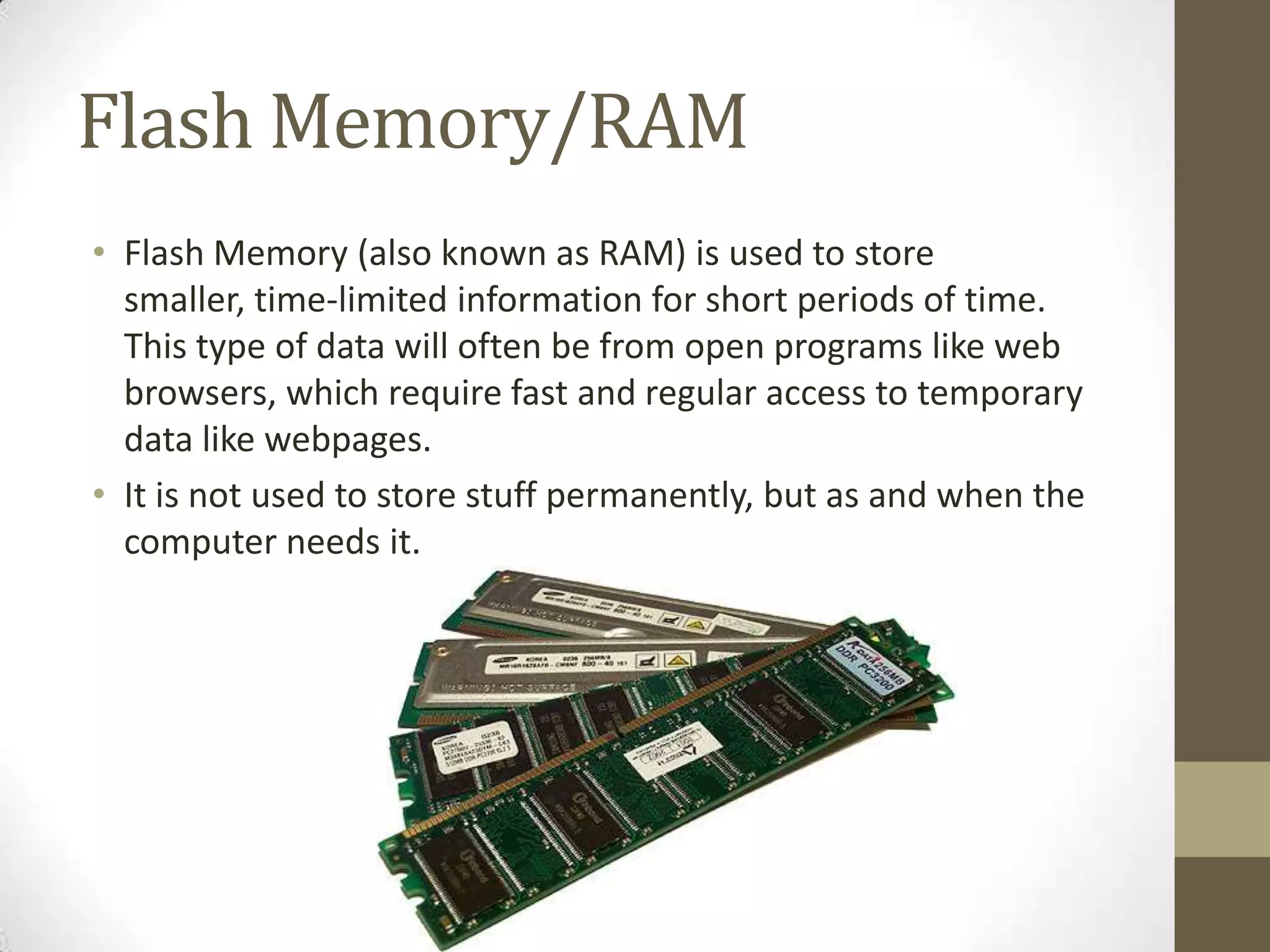
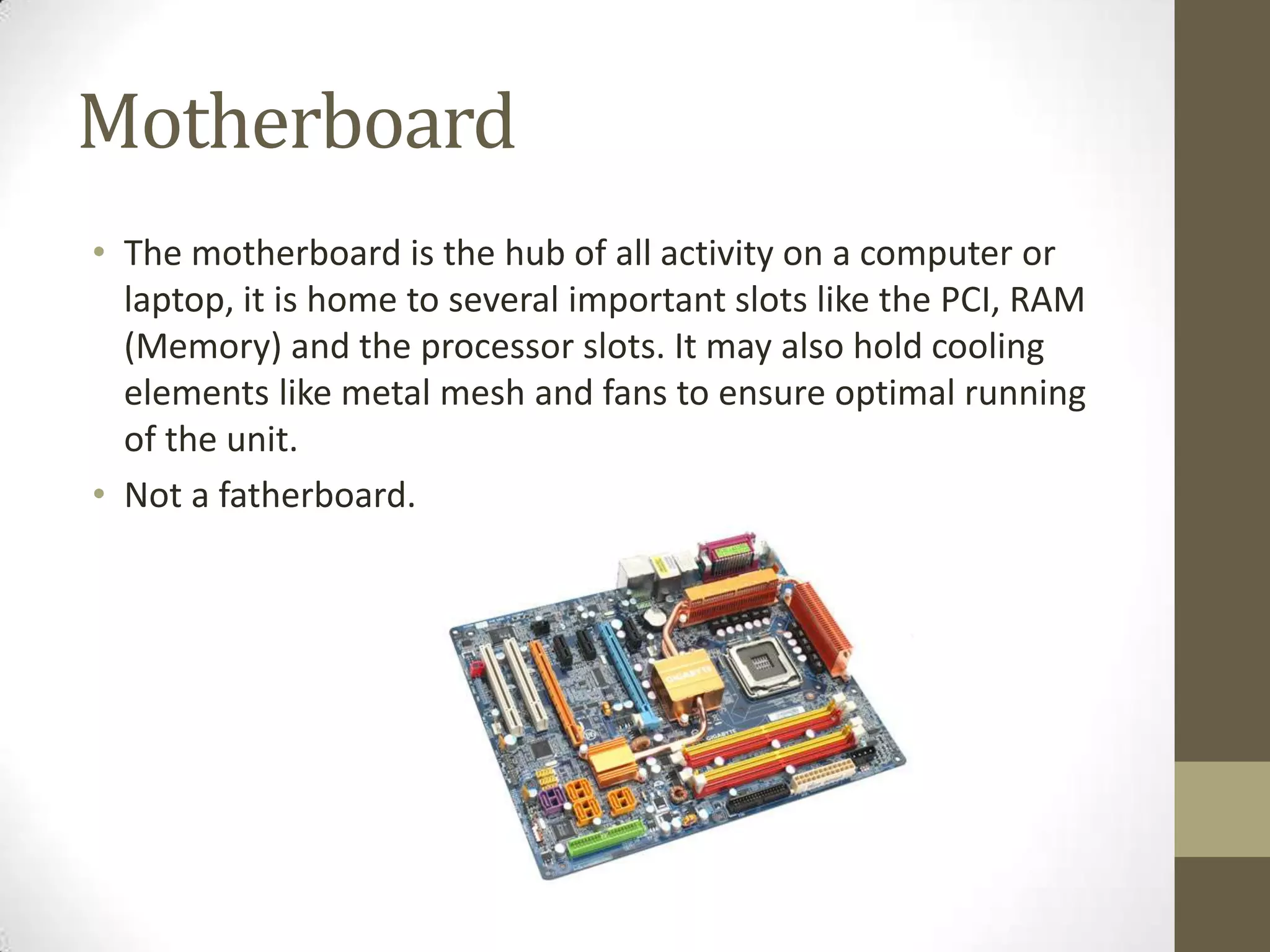
This presentation outlines various internal components of a computer for intermediate learners, focusing on their functions and applications. Key components discussed include memory cards, flash memory, hard drives, solid-state drives, power supplies, wireless cards, sound cards, processors, and motherboards. The document emphasizes the differences between these components regarding data storage, speed, and connectivity.