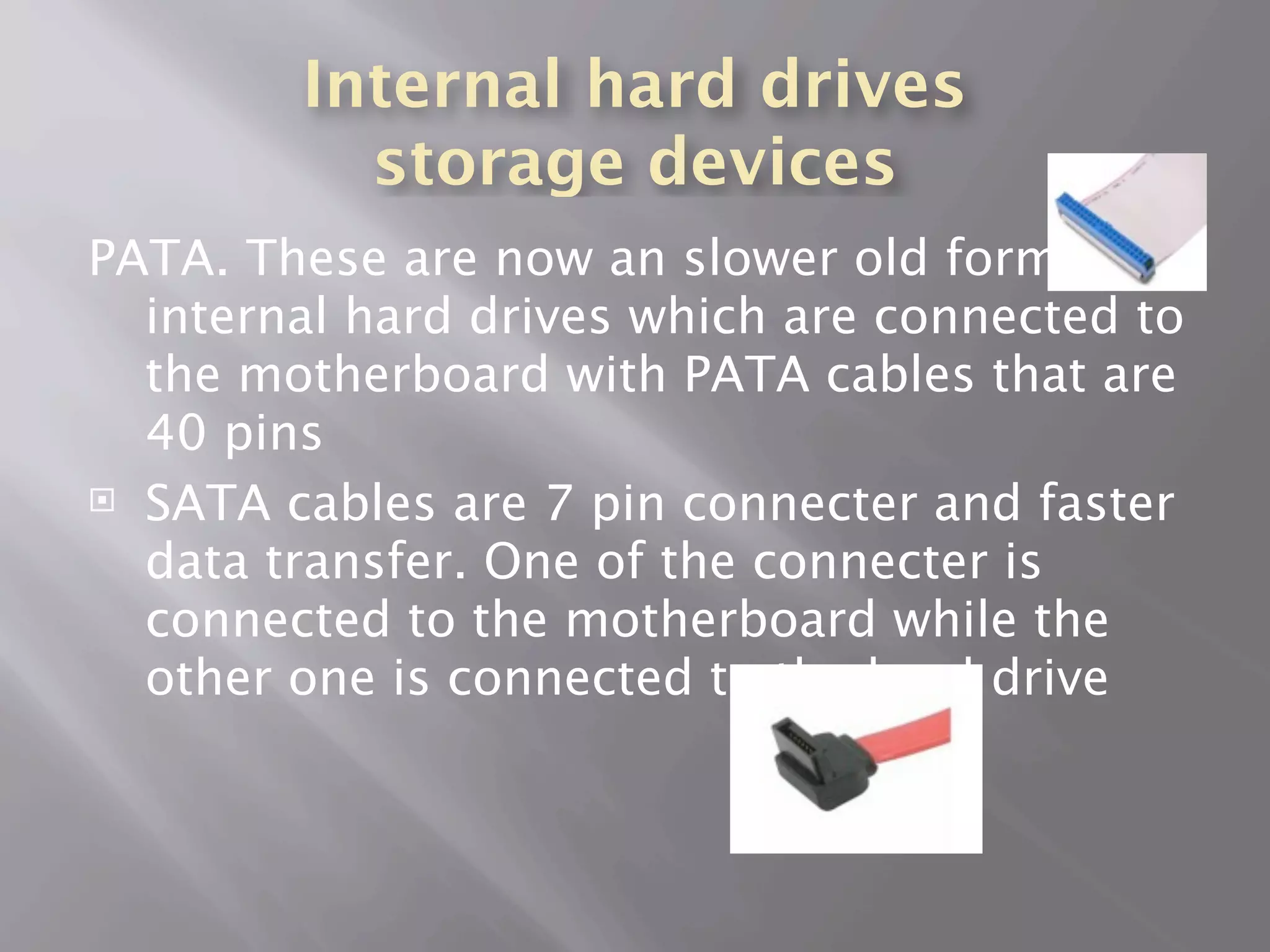
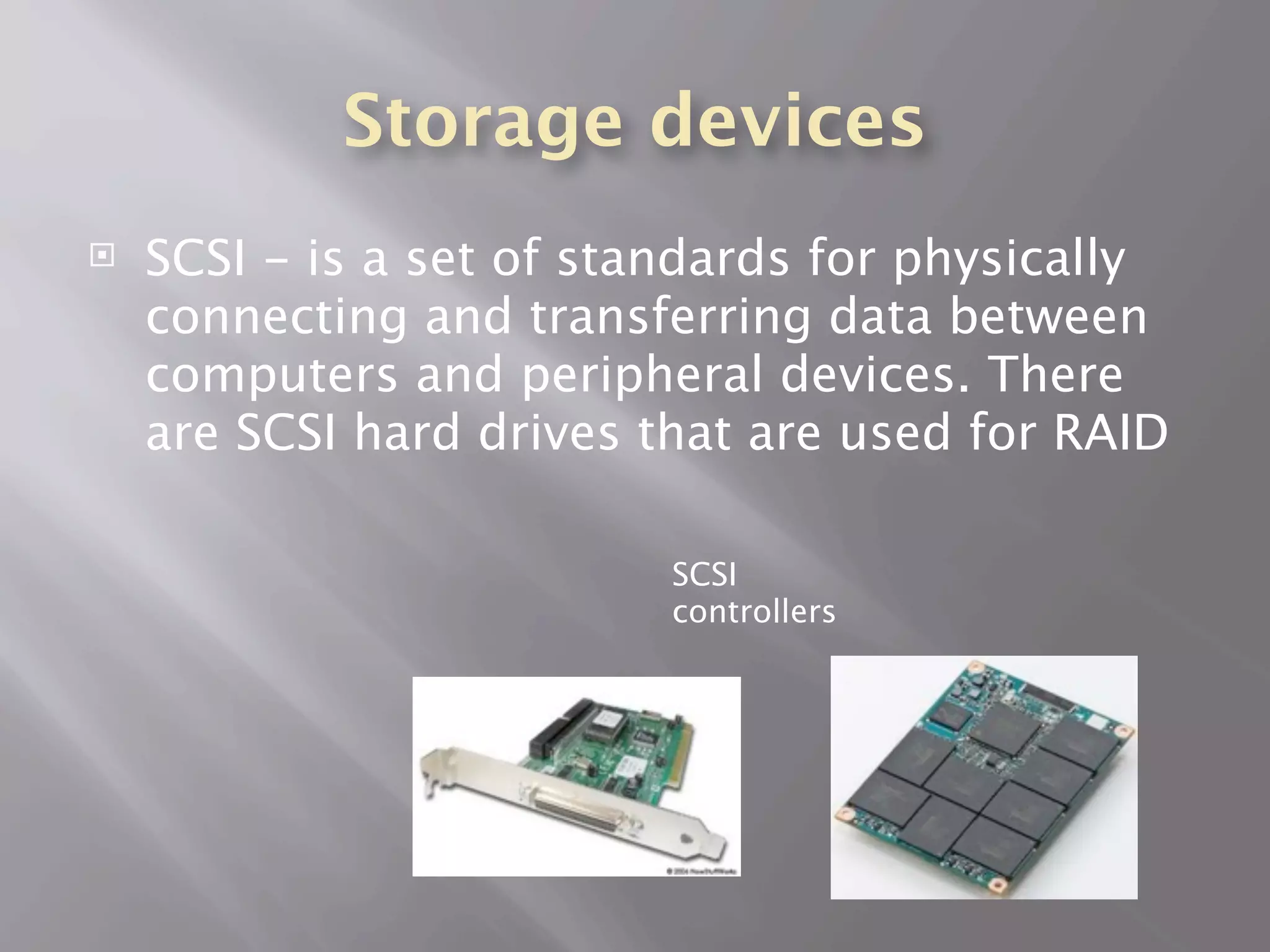
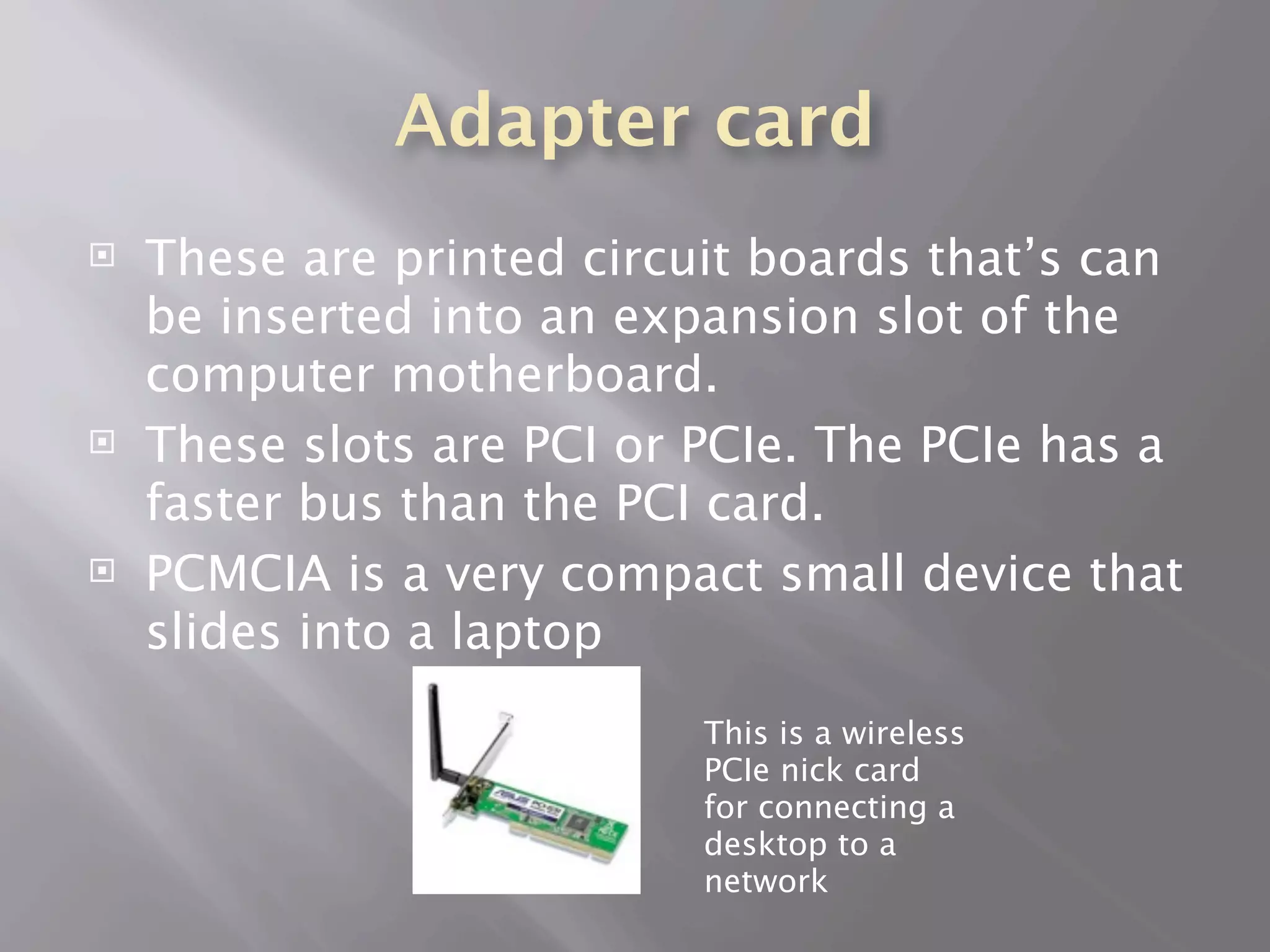
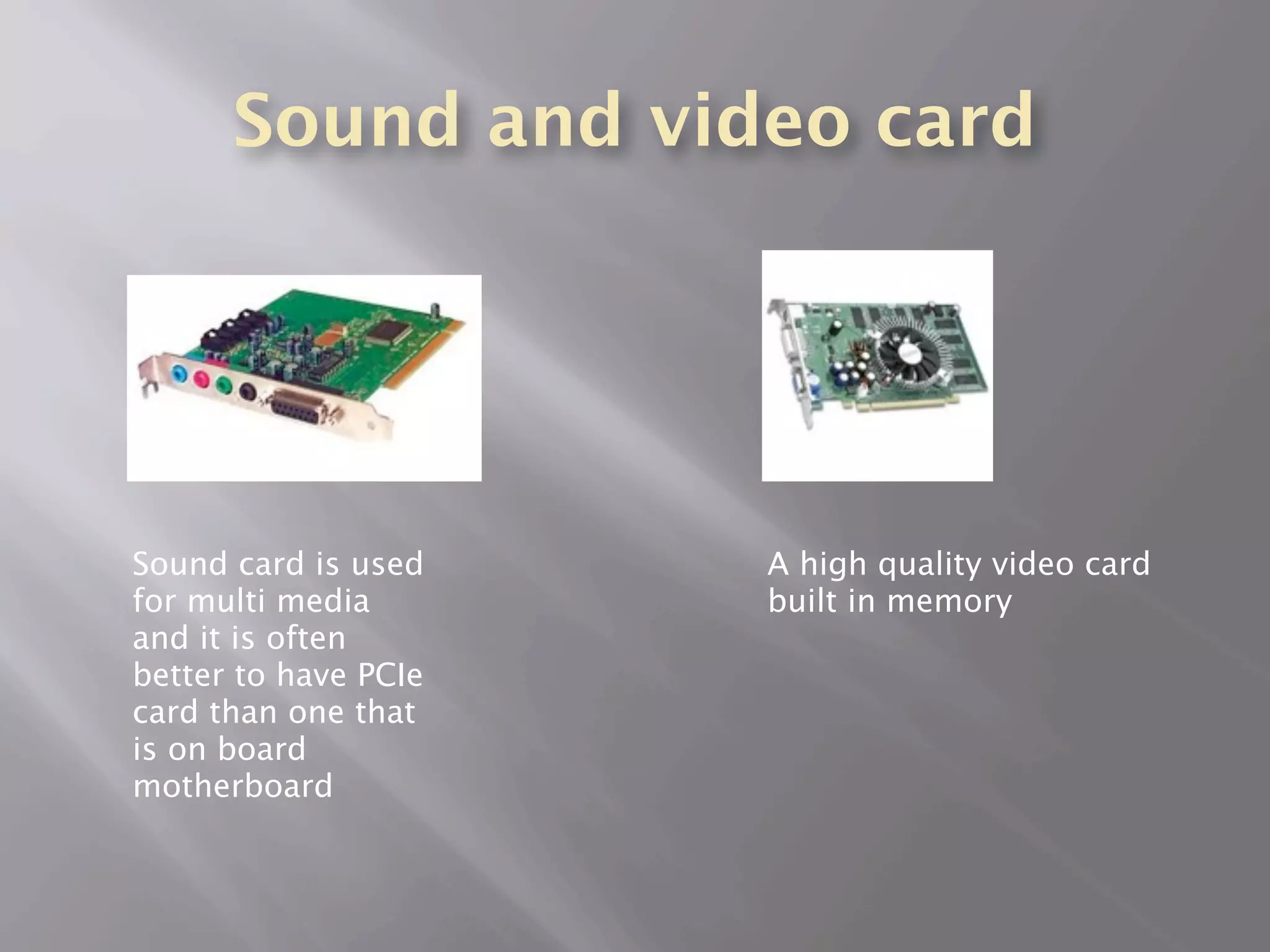
The central processing unit (CPU) carries out the computer's instructions and communicates with other components. A heat sink cools the CPU using thermal compound. There are two main processor manufacturers, AMD and Intel, which make dual and quad-core processors. Memory includes RAM, ROM, cache memory, and solid state drives. Storage devices include hard disk drives, solid state drives, external hard drives, and SCSI devices. Other components are adapter cards, sound/video cards, the motherboard, and the power supply.