- The document discusses two-stroke and four-stroke engines, their working principles, types, and applications.
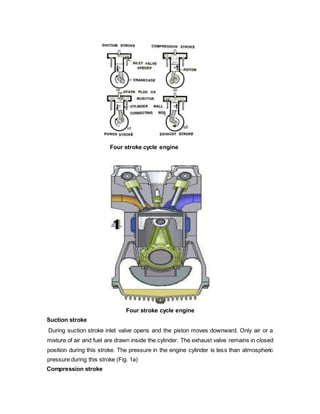
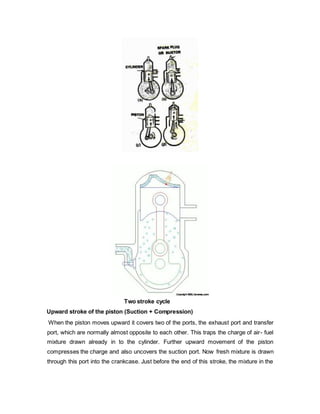
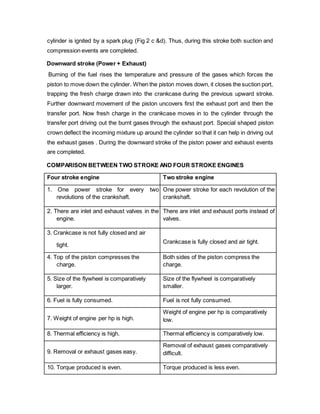
- Four-stroke engines complete their combustion cycle over four strokes of the piston requiring two revolutions of the crankshaft, while two-stroke engines complete combustion in just two strokes, one revolution of the crankshaft.
- The four main events in both engines are intake, compression, power, and exhaust, but they are arranged differently between the two types due to differences in valve and port timing.