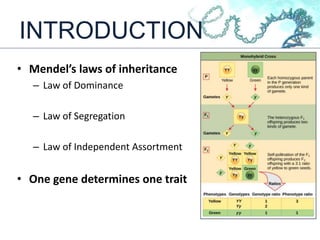
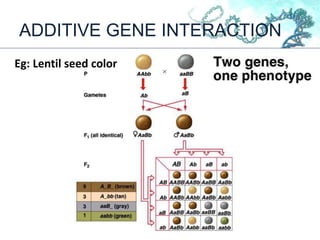
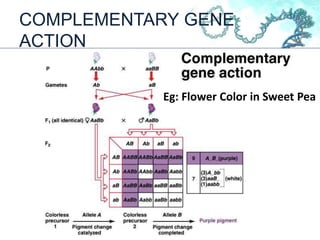
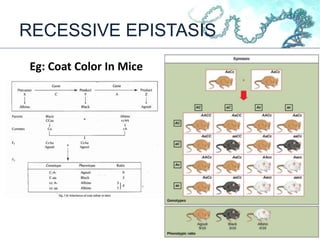
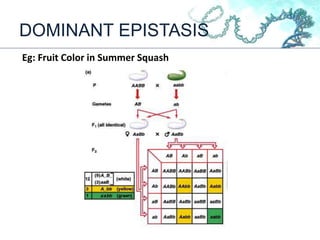
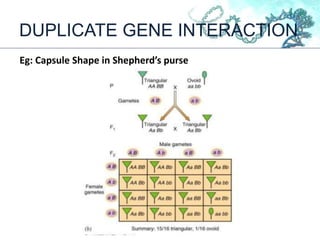
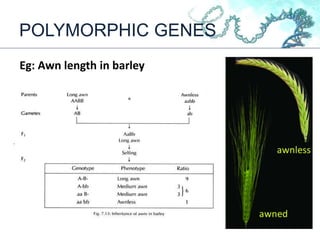
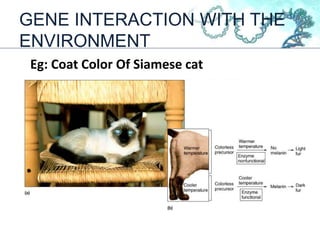
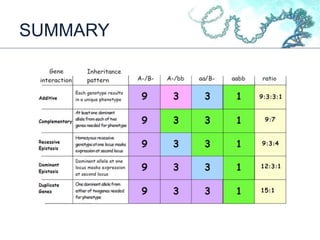
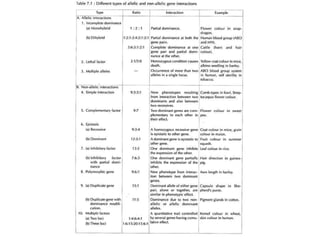
This document discusses gene interactions and their mechanisms. It describes how genes interact with each other and the environment to influence phenotypes. The main types of gene interactions are allelic, including complete dominance, incomplete dominance and co-dominance, and non-allelic, such as additive, duplicate, dominant suppression, dominant and recessive epistasis. Examples are provided for each type of interaction.