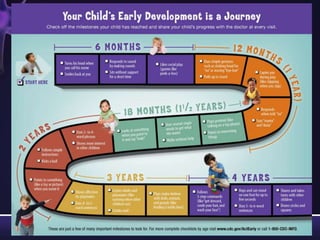
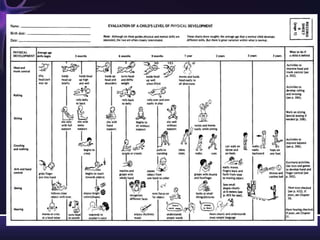
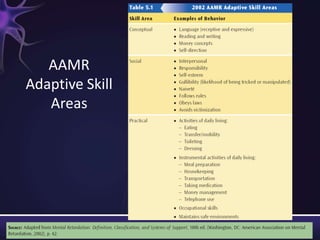
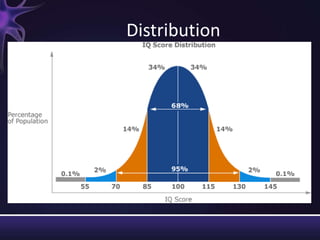
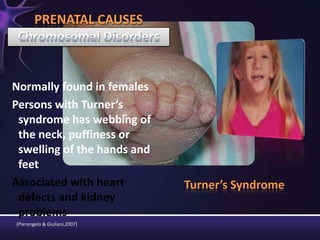
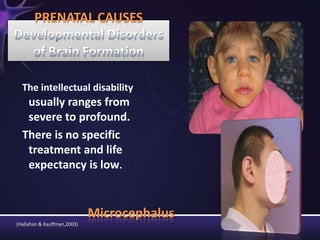
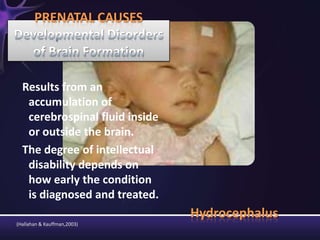
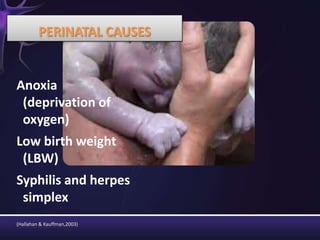
Intellectual disabilities are characterized by deficits in cognitive functioning and adaptive behavior that develop during childhood. They are diagnosed when a person has an IQ of 70 or below along with impairments in daily living skills.
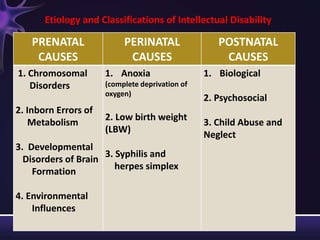
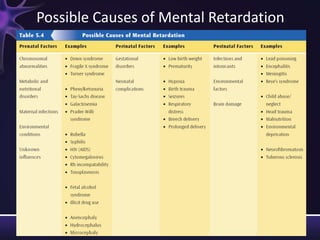
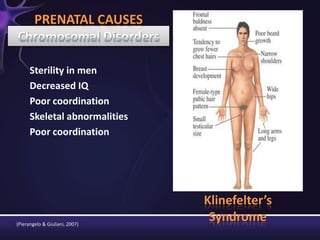
Intellectual disabilities can have prenatal, perinatal, or postnatal causes such as genetic syndromes, low birth weight, brain injuries, or environmental factors. They are classified based on severity of the deficit. Early intervention programs focus on developing skills, while K-12 programs may include inclusion, functional academics, behavior therapy, or vocational training depending on the child's needs. Teaching students with intellectual disabilities requires direct instruction broken into clear steps with a focus on sequencing, practice, and presentation of material