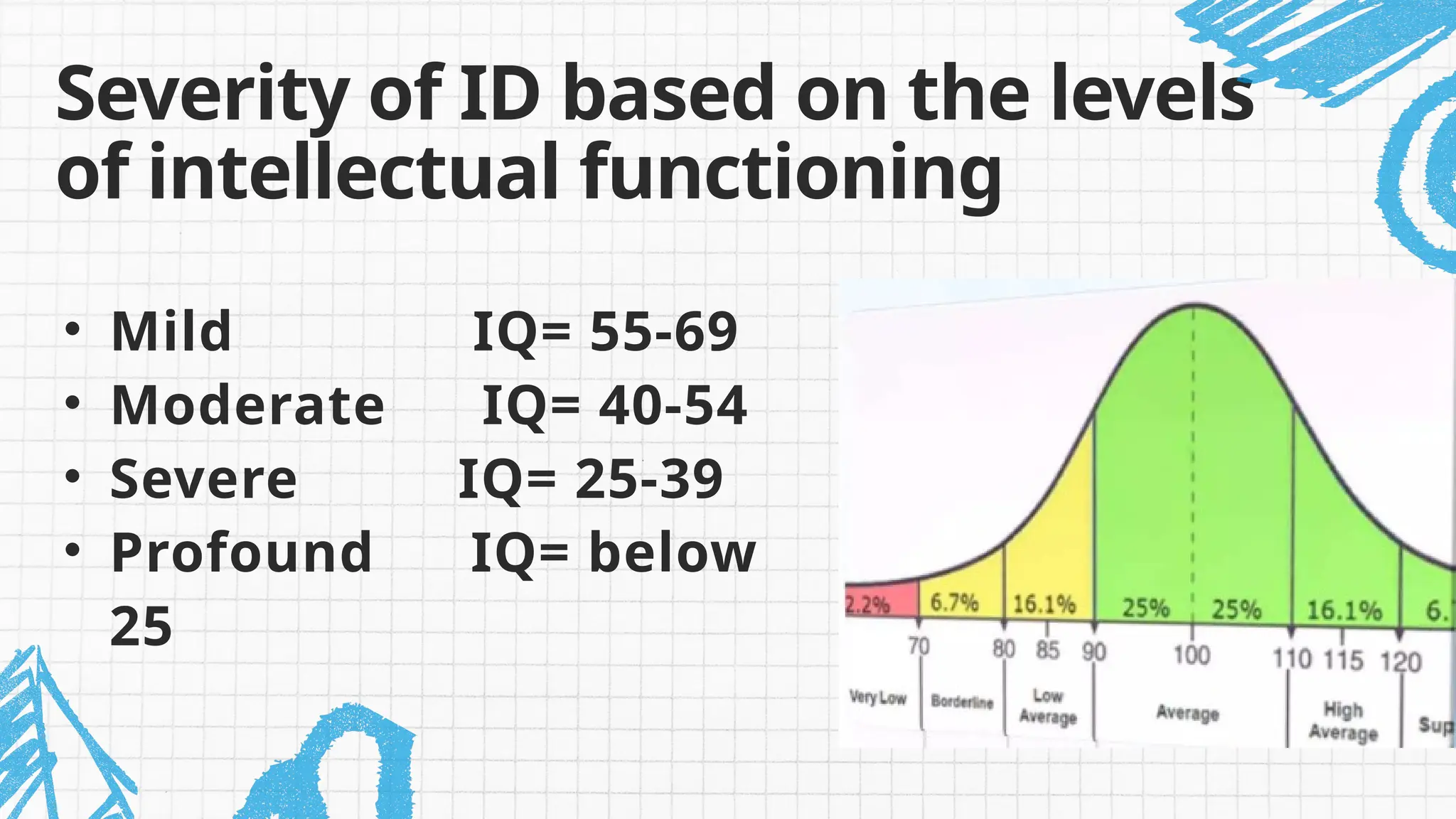
Intellectual disability (ID) is characterized by limitations in cognitive functioning and adaptive behavior, impacting communication, social skills, and self-care, often resulting in slower learning rates. The condition originates before age 18 and can arise from various causes including genetic disorders, prenatal factors, and environmental influences. Treatment typically involves behavioral and occupational therapy, and the severity of ID is categorized based on IQ levels and adaptive functioning.