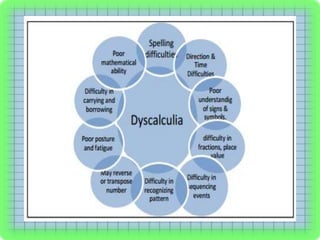
Dyscalculia is a specific learning disorder involving difficulty with numbers and math concepts. It was formerly known as Mathematics Disorder. There are several types of dyscalculia depending on the skills affected, such as verbal, practical, or operational skills. Characteristics include difficulties with counting, calculations, numbers with zeros, measures, direction/orientation, and working memory related to numbers. Causes may be genetic, related to brain development or injury, or environmental factors like prematurity. Treatment involves visual aids, connecting math to real life, graph paper, games, and diagrams to help those with dyscalculia learn.