This document provides an overview of Confucianism, including its history, key figures, teachings, and influence. Some of the main points covered include:
- Confucius lived in 551-479 BCE in China and was the founder of Confucianism. He taught principles of virtue, ethics, and morality that focused on social harmony through strong family and social values.
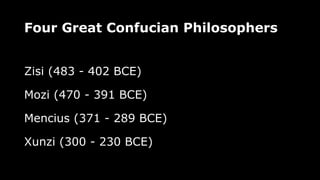
- Other major Confucian philosophers included Mencius, Xunzi, Mozi, and Zisi, who expanded on Confucius' teachings in subsequent centuries. Central concepts included benevolence, righteousness, propriety, wisdom, and integrity.
- Confucianism became the dominant philosophy and basis for



































































![Economic Confucianism
Over our decades…“four little dragons”- Taiwan, South Korea, Hong Kong and
Singapore…progressed toward becoming…the three mainstays of the advanced
economic world order…Their achievement…originated from…social practices
established in the Confucian custom…adjusted to the necessities of a modern
society- [known as] “neo-Confucianism." This economic philosophy incorporates a
meritocratic organization, a selection test framework, the signi
fi
cance of gathering
knowledge, and the goal of advancement.
Dangayach & Gupta. (2018). Four Asian Dragons . International Journal of Advance Research. 3 (1):158 - 162. http://www.ijarnd.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confucianism-231201184319-749ff26f/85/INT-244-Topic-6b-Confucianism-73-320.jpg)



