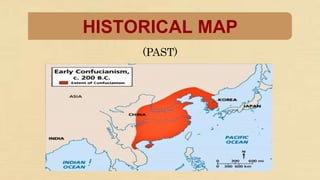
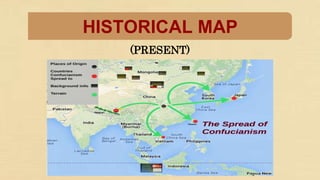
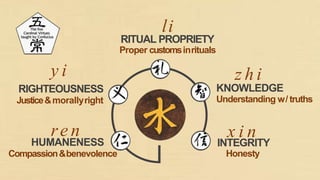
Confucianism is a major philosophical system in China, developed from the teachings of Confucius and his disciples, influencing social values, political theories, and education. It emphasizes virtues such as humaneness and propriety, with core teachings recorded in texts like the Analects. Confucianism has evolved through different dynasties, maintaining influence alongside Buddhism and Taoism, and encouraging respect within societal relationships.



















![• Britannica (2019) Confucianism. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/topic/Confucianism
• Adhikari, S. (2019, August 13). Top 10 Contributions of Confucius. Retrieved from
https://www.ancienthistorylists.com/china-history/contributions-of-confucius/
• Anon, (2019). [online] Available at: https://brainly.ph/question/410994 [Accessed 17 Oct. 2019].
• Berling, J. A. (n.d). Confucianism [blog]. Retrieved from https://asiasociety.org/education/confucianism
• Eighty Six (n.d). The Confucian Education System – Can It Positively Influence U.S. Education? [blog].
Retrieved fromhttps://www.brighthubeducation.com/education-industry/129048-confucianism-can-
change-modern-education/
• Goscha, C. (2017, March 9). What is Confucianism? A short introduction to the Chinese ethical system.
Retrieved from https://www.historytoday.com/history-matters/what-confucianism
• McEnroe, A. M. (2014, April 30). Confucius's Educational Theory. Retrieved from
https://www.newfoundations.com/GALLERY/Confucius.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confucianismgroupreport-231014092550-9936b113/85/Confucianism-Group-Report-pptx-23-320.jpg)





