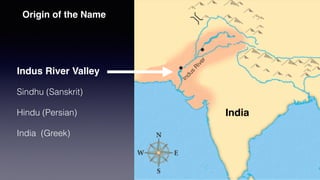
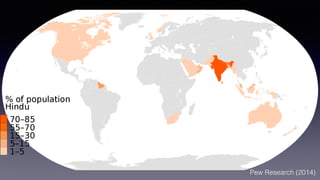
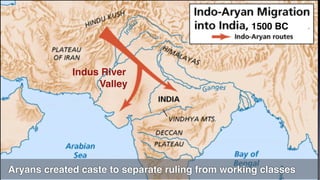
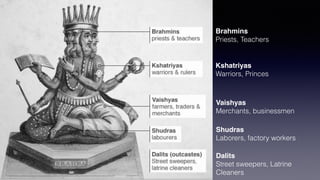
1. Hinduism originated around 1500 BC in the Indus River Valley in present-day India and Pakistan. It has evolved over time and is considered one of the oldest religions in the world with over 1 billion followers globally.
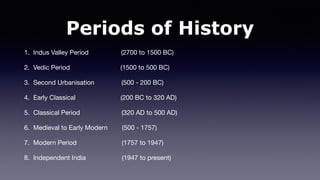
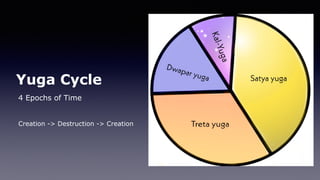
2. The history of Hinduism can be broken down into periods: the Indus Valley Period, the Vedic Period, the Second Urbanization, the Early Classical period, the Classical period, the Medieval to Early Modern period, the Modern period, and Independent India. Key developments include the Vedic texts, the Upanishads, concepts of dharma and samsara.
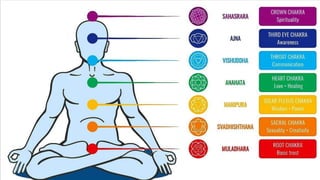
3. Central beliefs of Hinduism include Brahman as the ultimate reality, atman as the