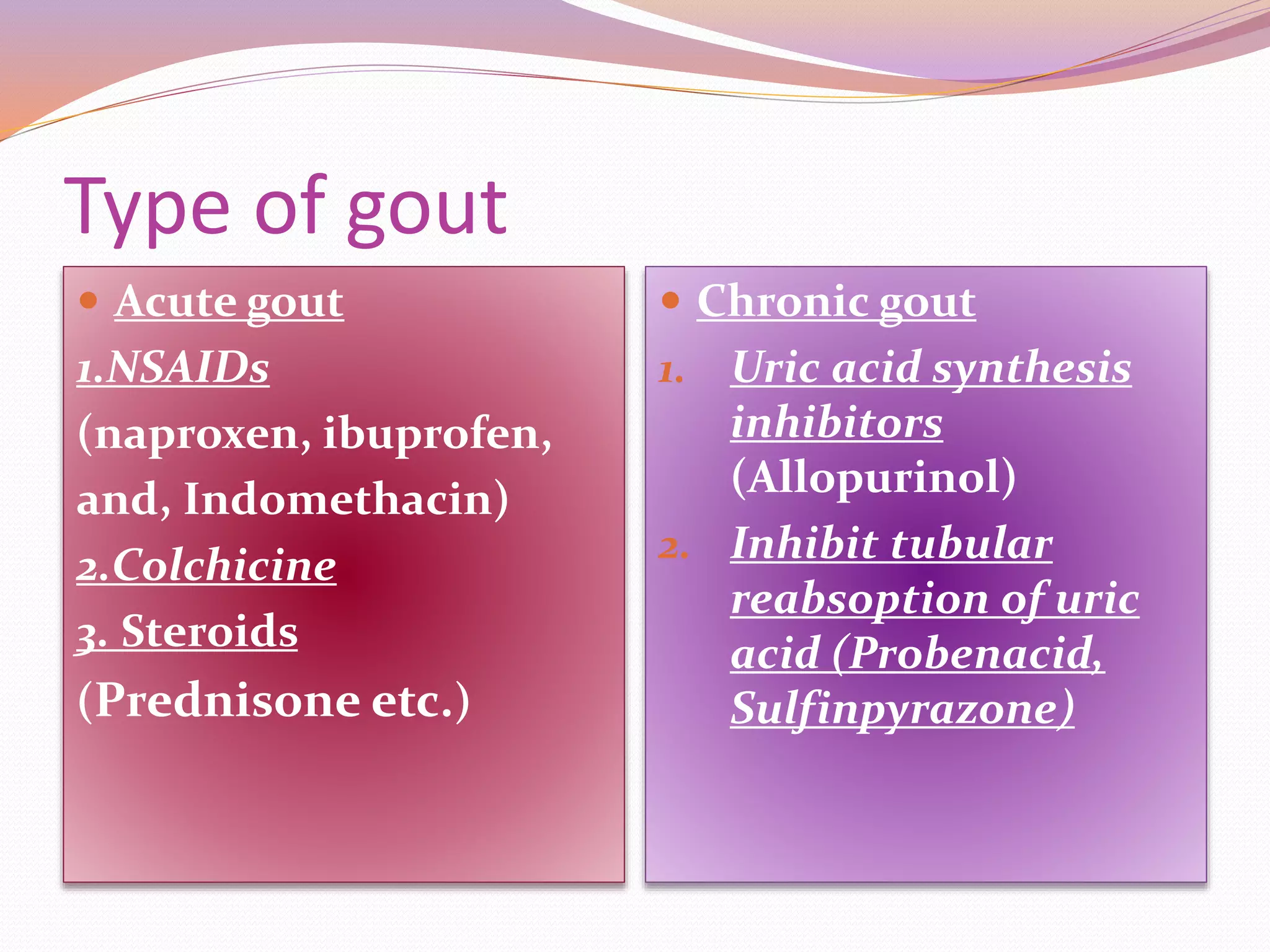
Gout is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood which can crystallize and deposit in the joints, causing inflammation and pain. It is usually characterized by recurrent attacks of inflammatory arthritis in the joint at the base of the big toe. Treatment involves medications like NSAIDs to reduce inflammation during acute attacks and allopurinol or probenecid for long-term prevention by lowering uric acid levels through inhibition of uric acid synthesis or reabsorption. Lifestyle changes and a diet low in purine-rich foods can also help prevent gout attacks.