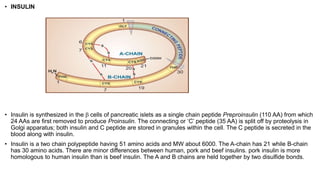
Insulin is a peptide hormone synthesized in the pancreatic beta cells. It facilitates glucose entry into cells, glycogen synthesis, and inhibits gluconeogenesis and lipolysis. Insulin analogues have been developed with altered pharmacokinetics to better mimic physiological insulin release. Oral hypoglycemic drugs include sulfonylureas which stimulate insulin secretion, biguanides like metformin which reduce hepatic glucose production and enhance glucose uptake, thiazolidinediones which reduce insulin resistance, and DPP-4 inhibitors which prolong the effects of incretins. Sulfonylureas block KATP channels, meglitinides have a quick onset and offset of action, while metformin reduces gluconeogenesis and stimulates