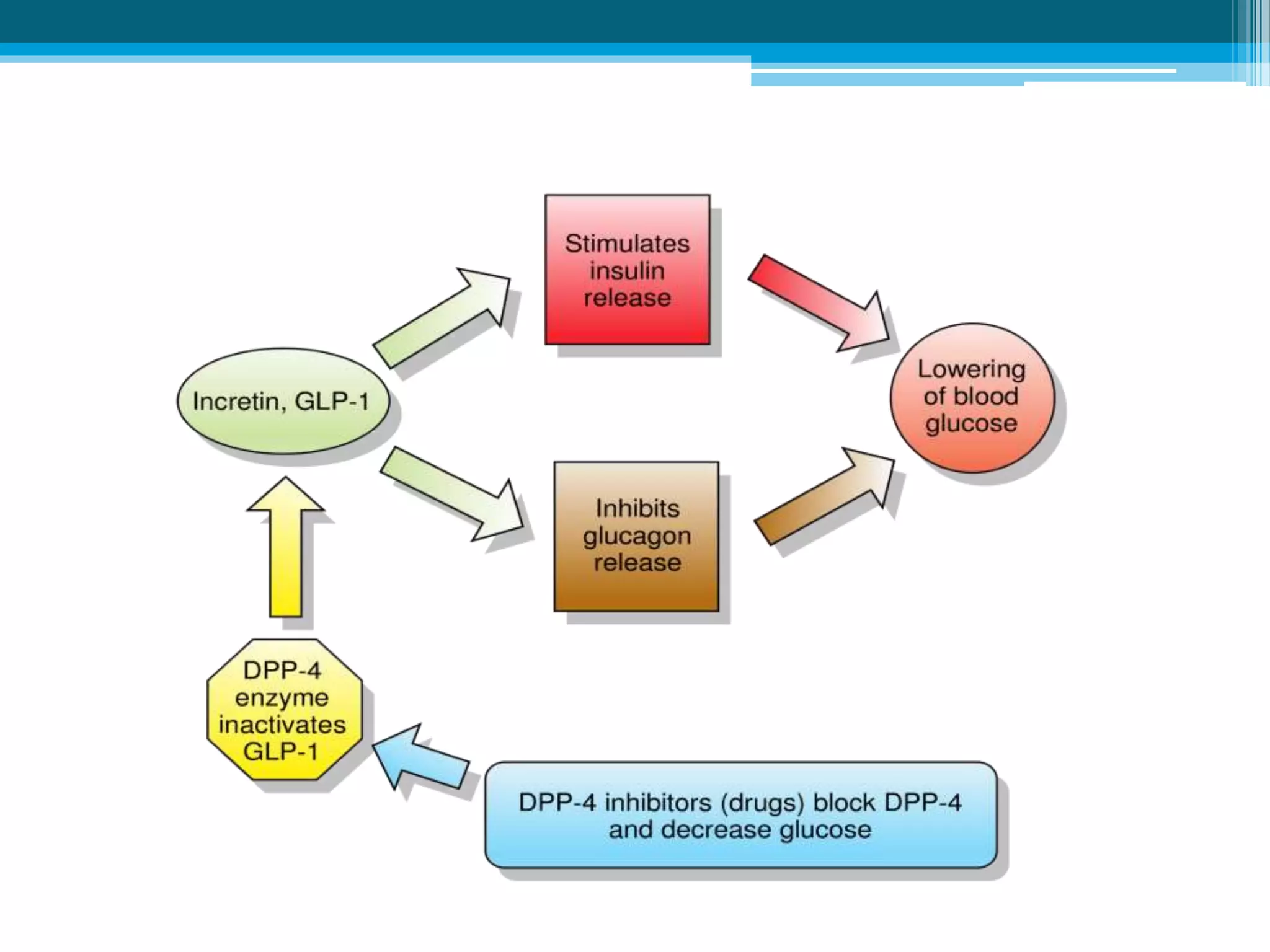
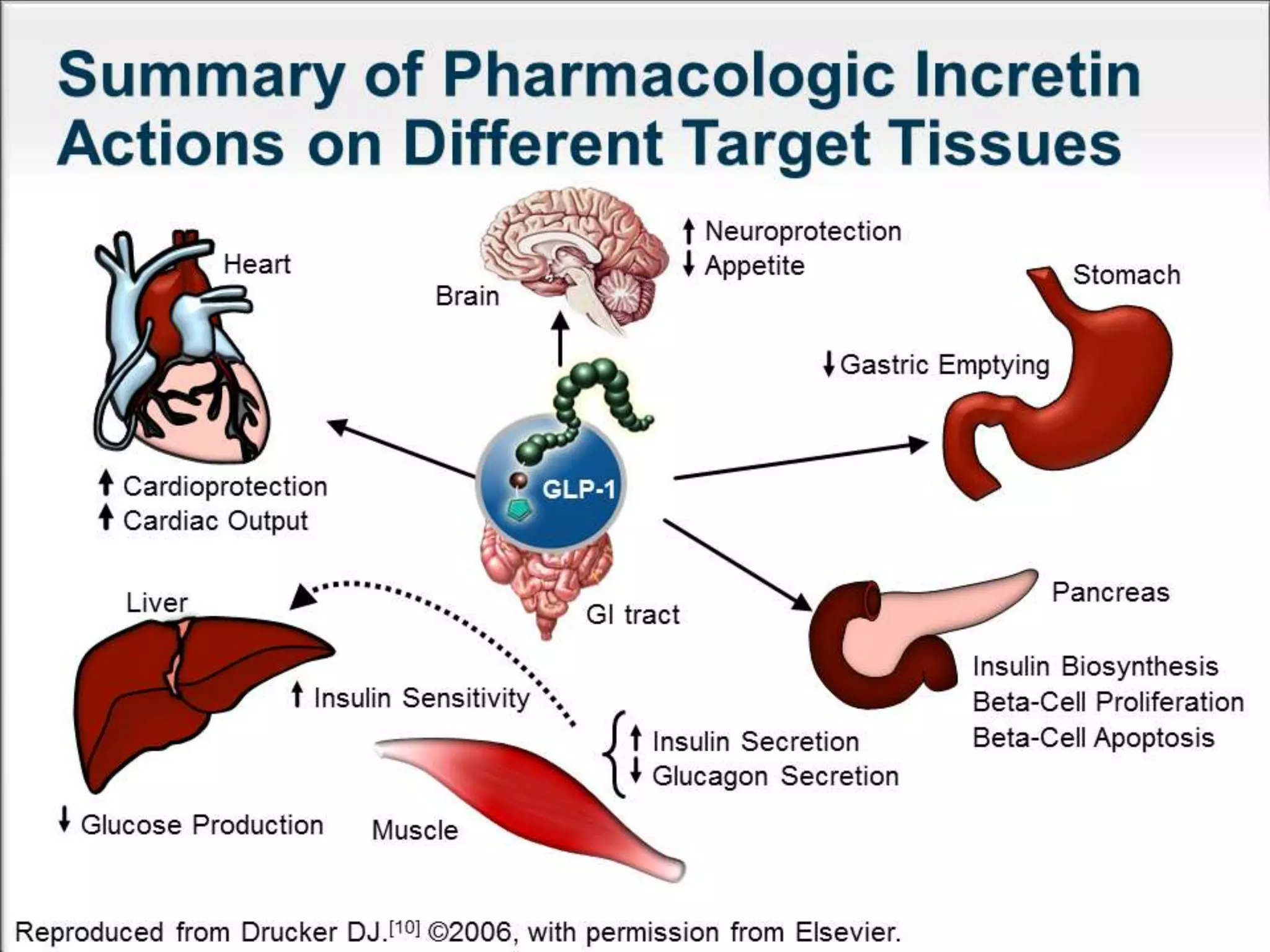
The document discusses incretin hormones like GLP-1 and GIP, which are secreted from the gut in response to food intake and stimulate insulin secretion. It describes the properties and roles of these two incretin hormones, their effects on glucose metabolism, and their deficiencies in type 2 diabetes patients. The document also outlines the treatment options of DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists that enhance the effects of incretin hormones, along with their dosages, precautions, and side effects. Key similarities and differences between incretin-based therapies as well as their clinical benefits and potential adverse outcomes are highlighted.






















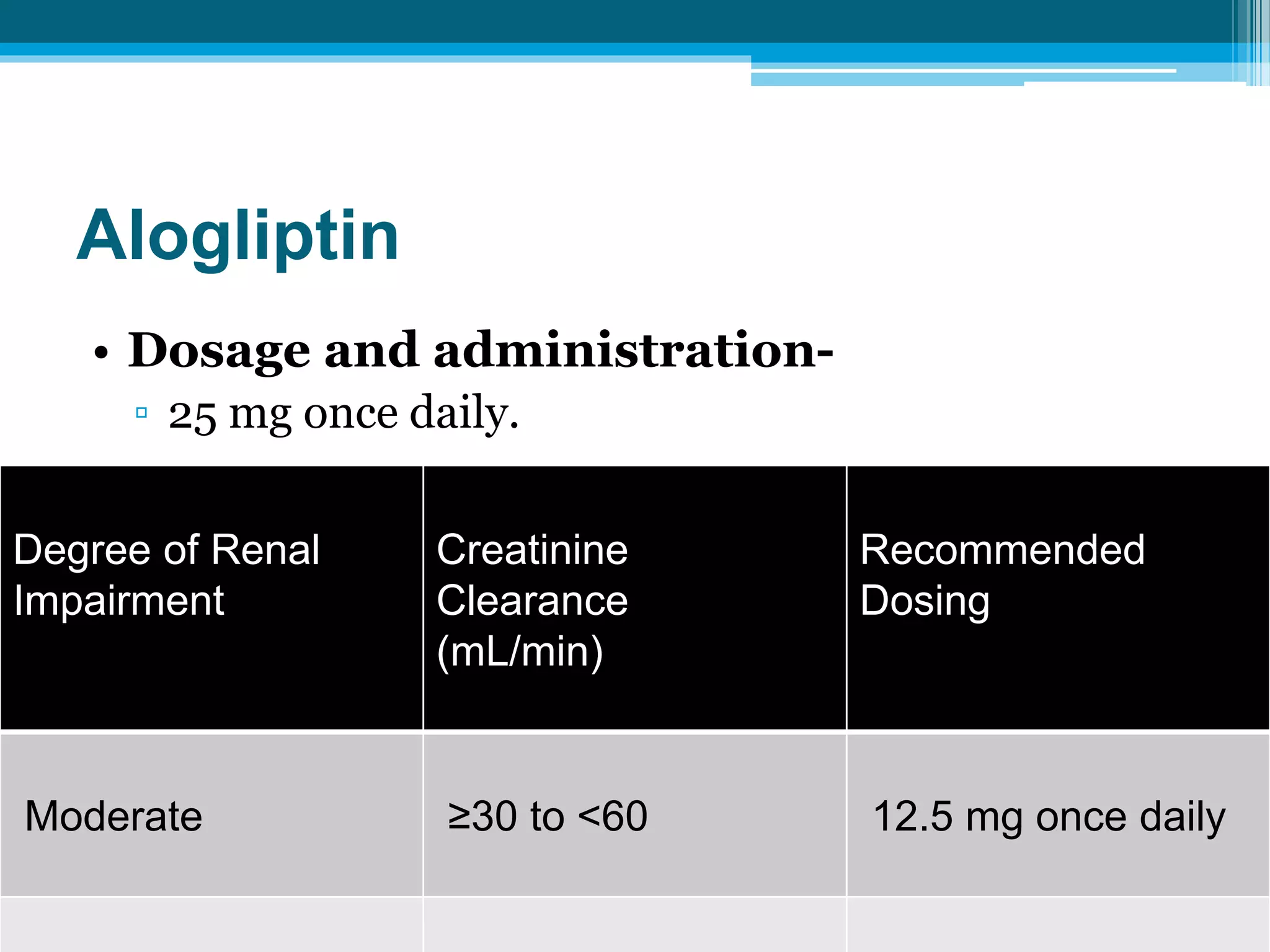
![Dosage Adjustment in Patients With Moderate, Severe
and End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Moderate Severe and ESRD
50 mg once daily 25 mg once daily
(CCr >30 to <50 mL/min
~Serum Cr levels [mg/dL]
Men: >1.7– ≤3.0;
Women: >1.5– ≤2.5)
(CCr <30 mL/min
~Serum Cr levels [mg/dL]
Men: >3.0;
Women: >2.5;
or on dialysis)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/incretinsabhijit-161220150655/75/Incretins-In-Diabetes-Mellitus-25-2048.jpg)