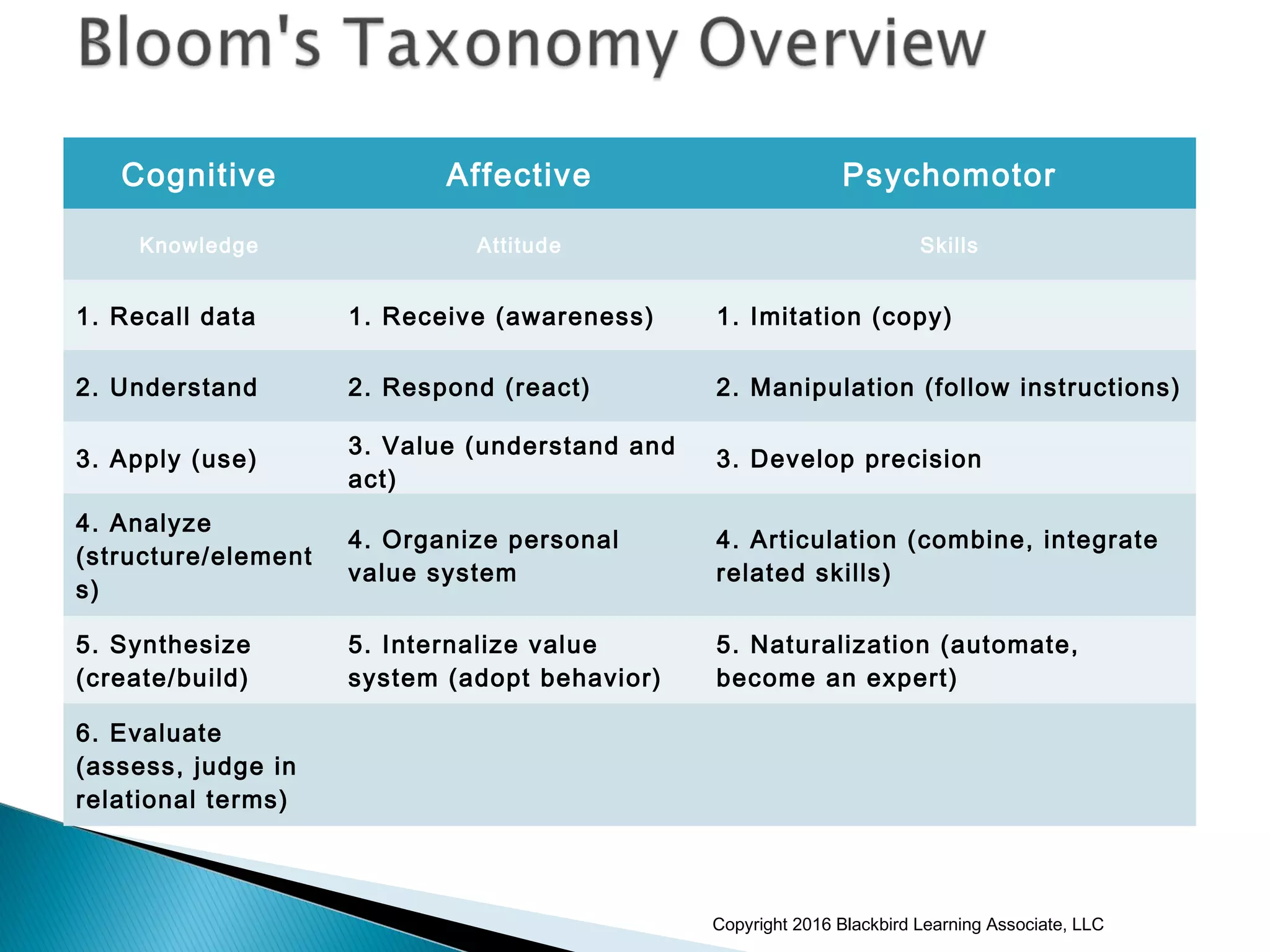
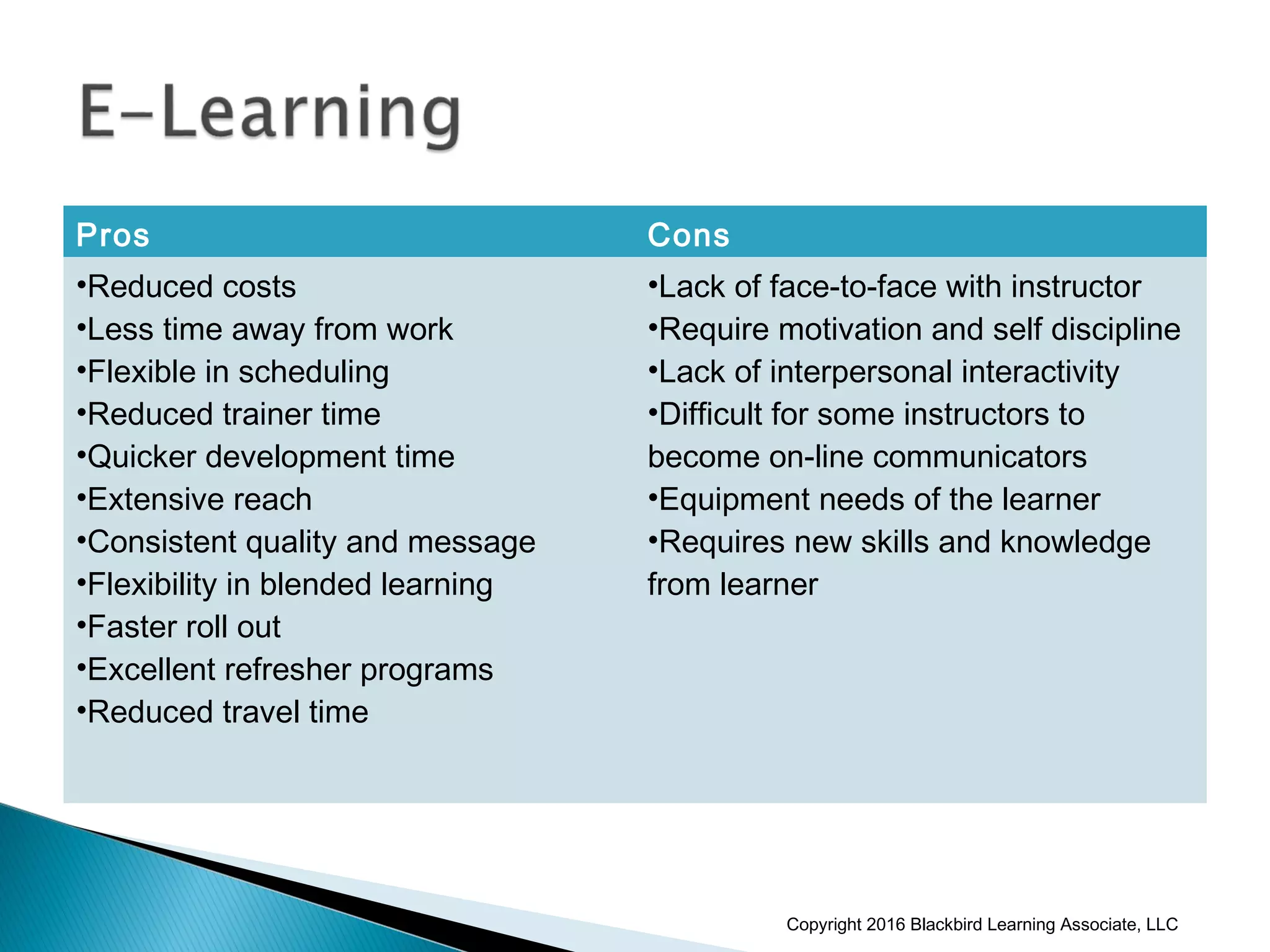
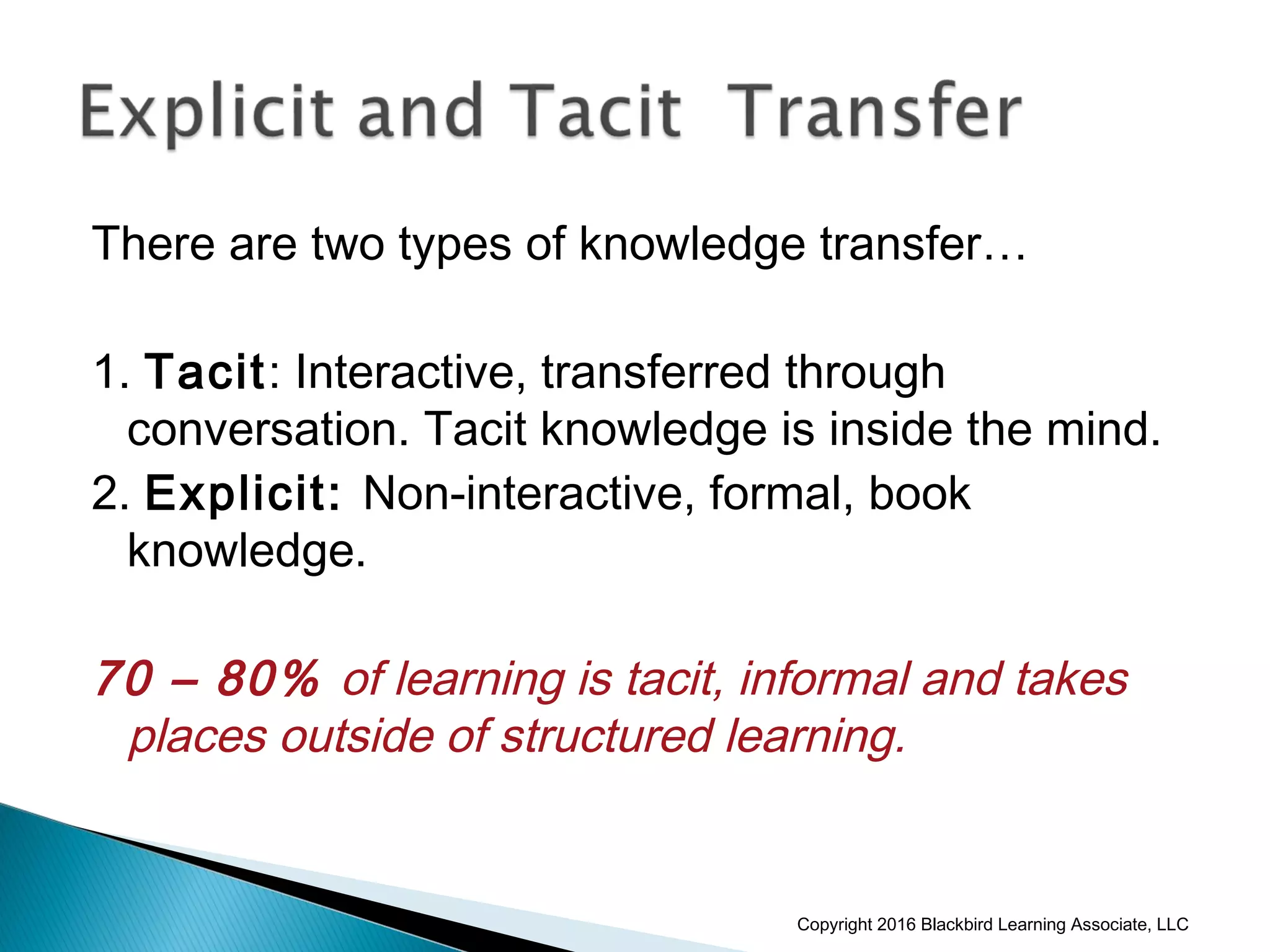
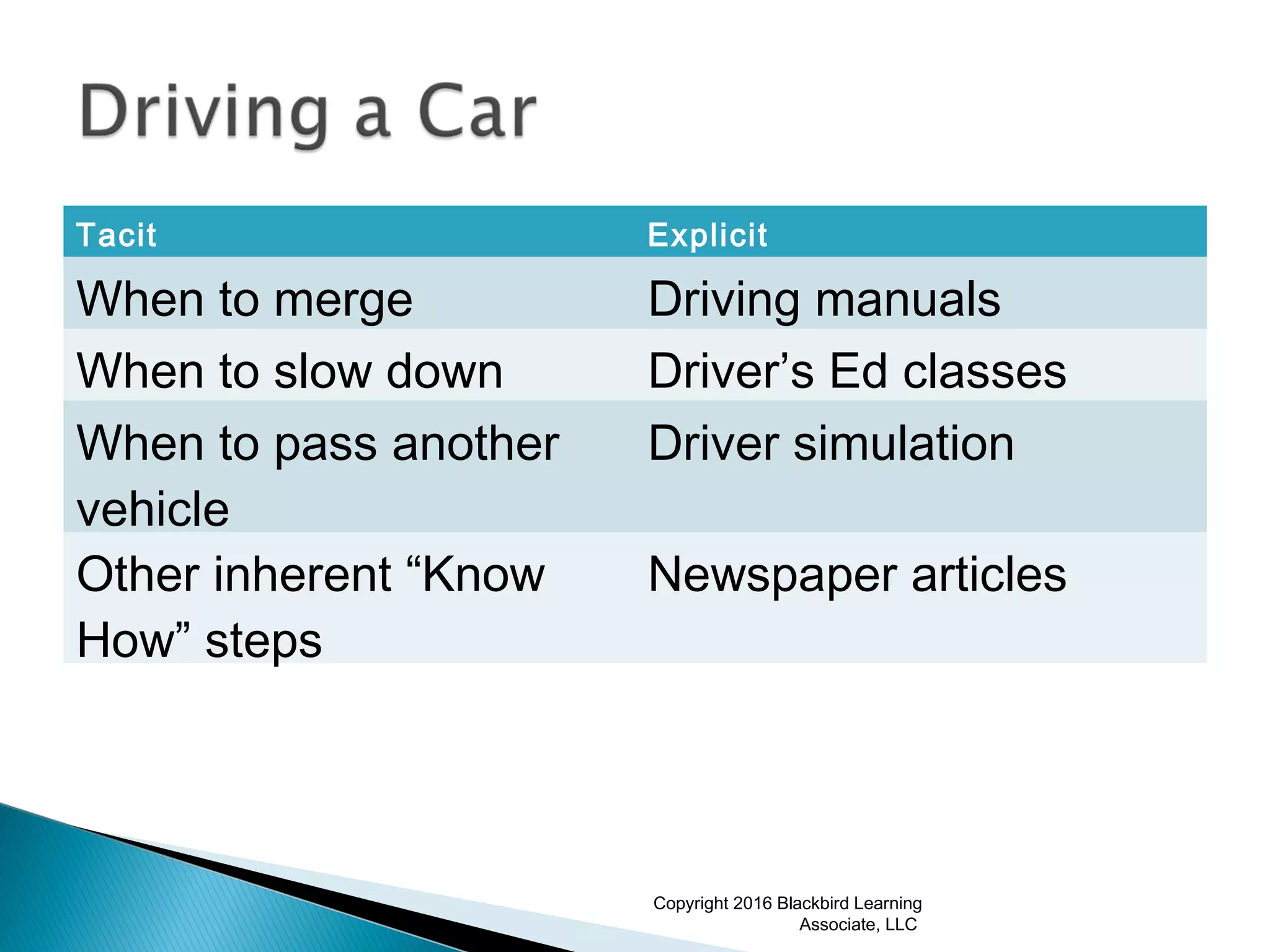
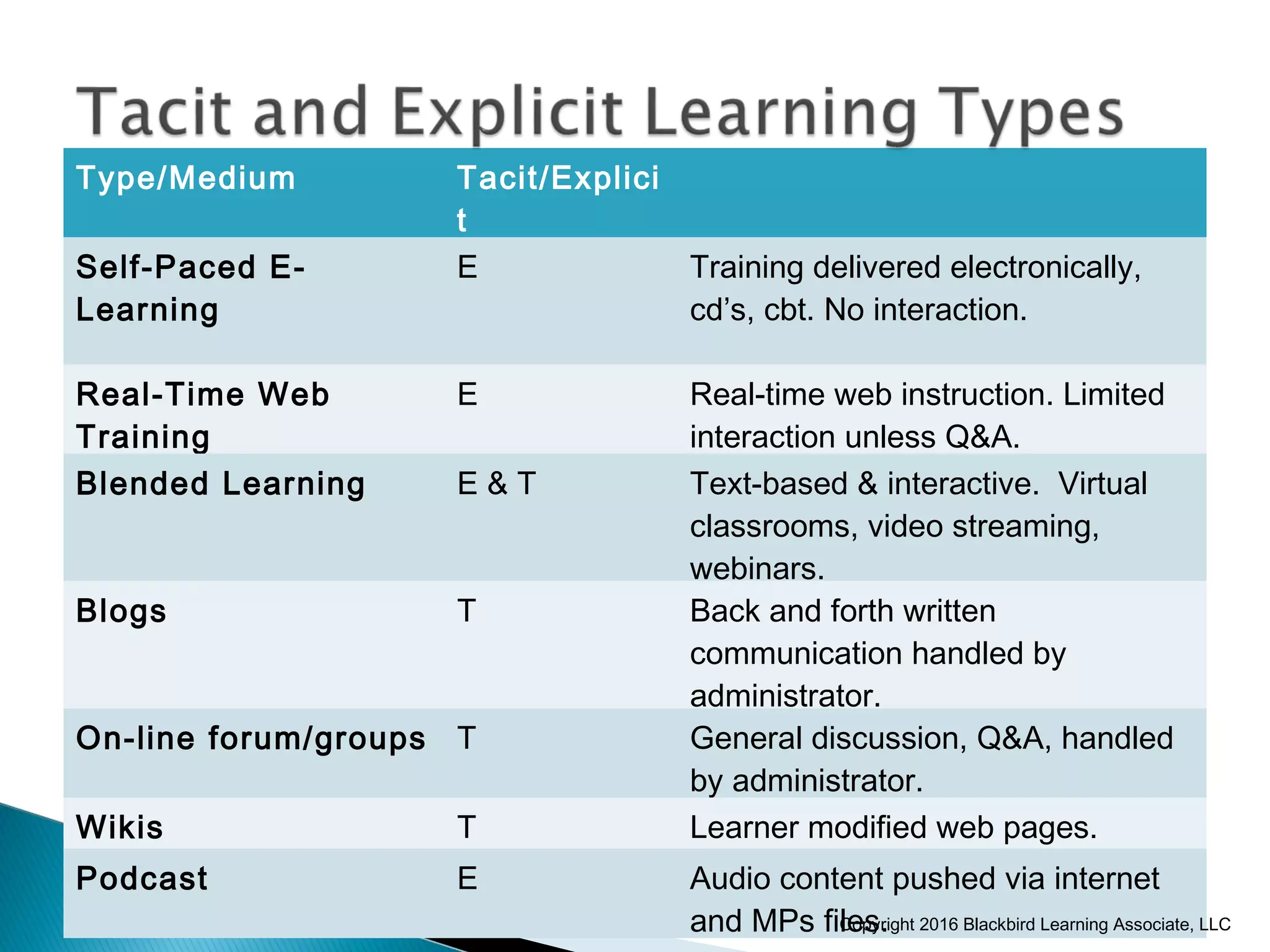
This document provides an overview of instructional design and adult learning theories presented in a workshop by Nancy Anderson of Blackbird Learning Associates. It discusses key topics like the ADDIE model of instructional design, principles of adult learning theory, learning styles, learning management systems, and e-learning approaches. The workshop aims to help participants understand adult learning concepts, instructional design processes, and how to apply these ideas in a real-world context.