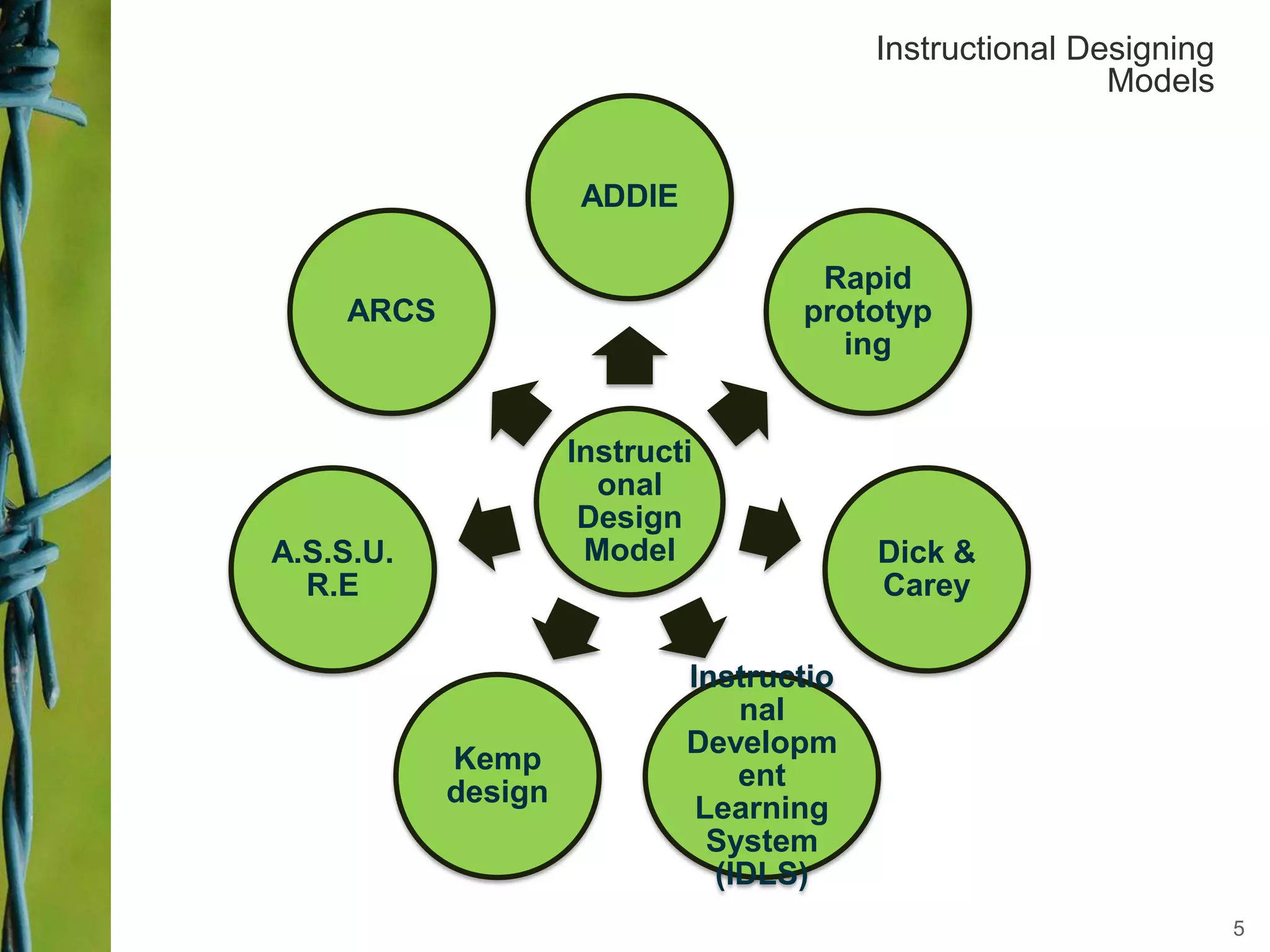
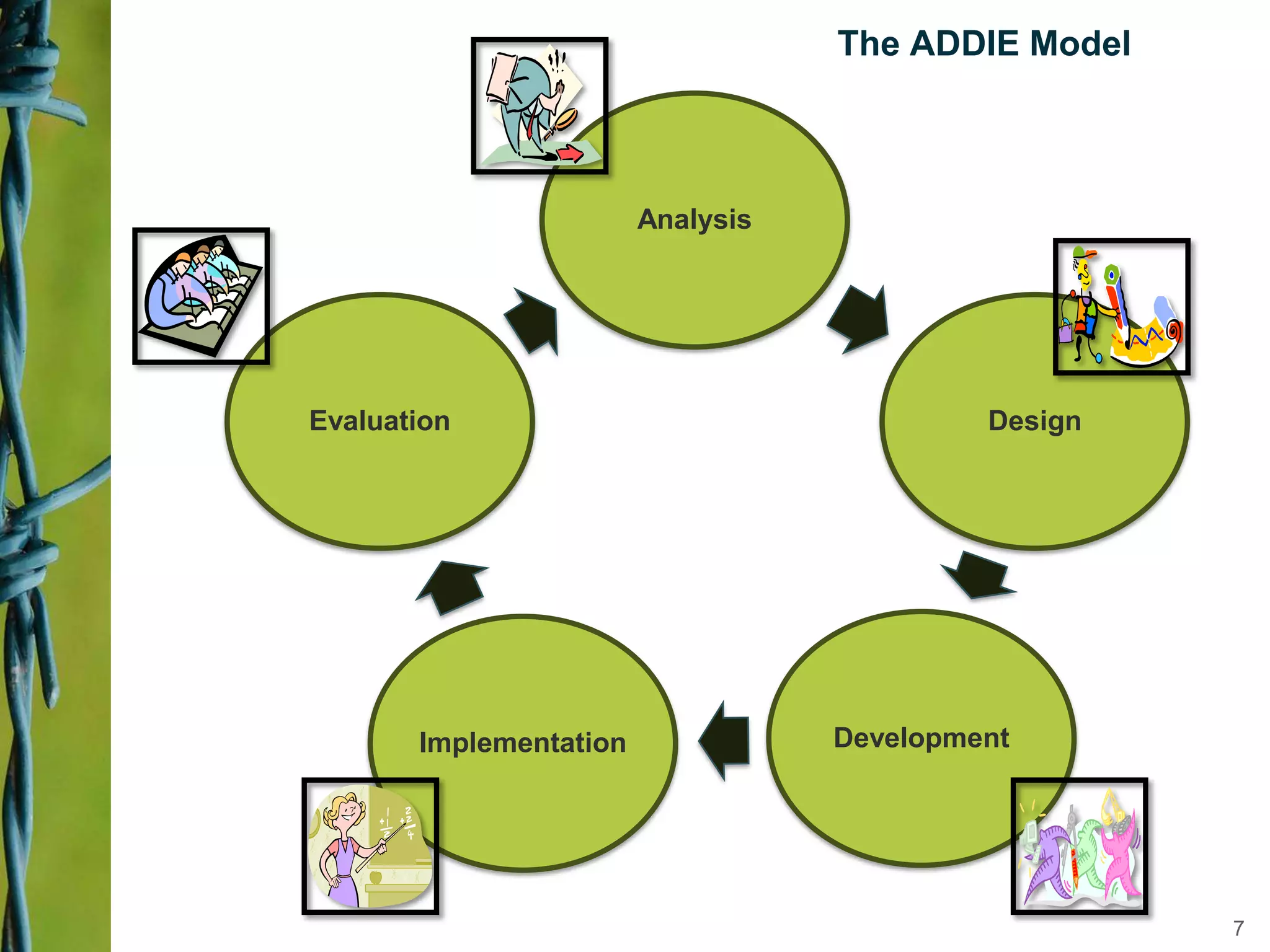
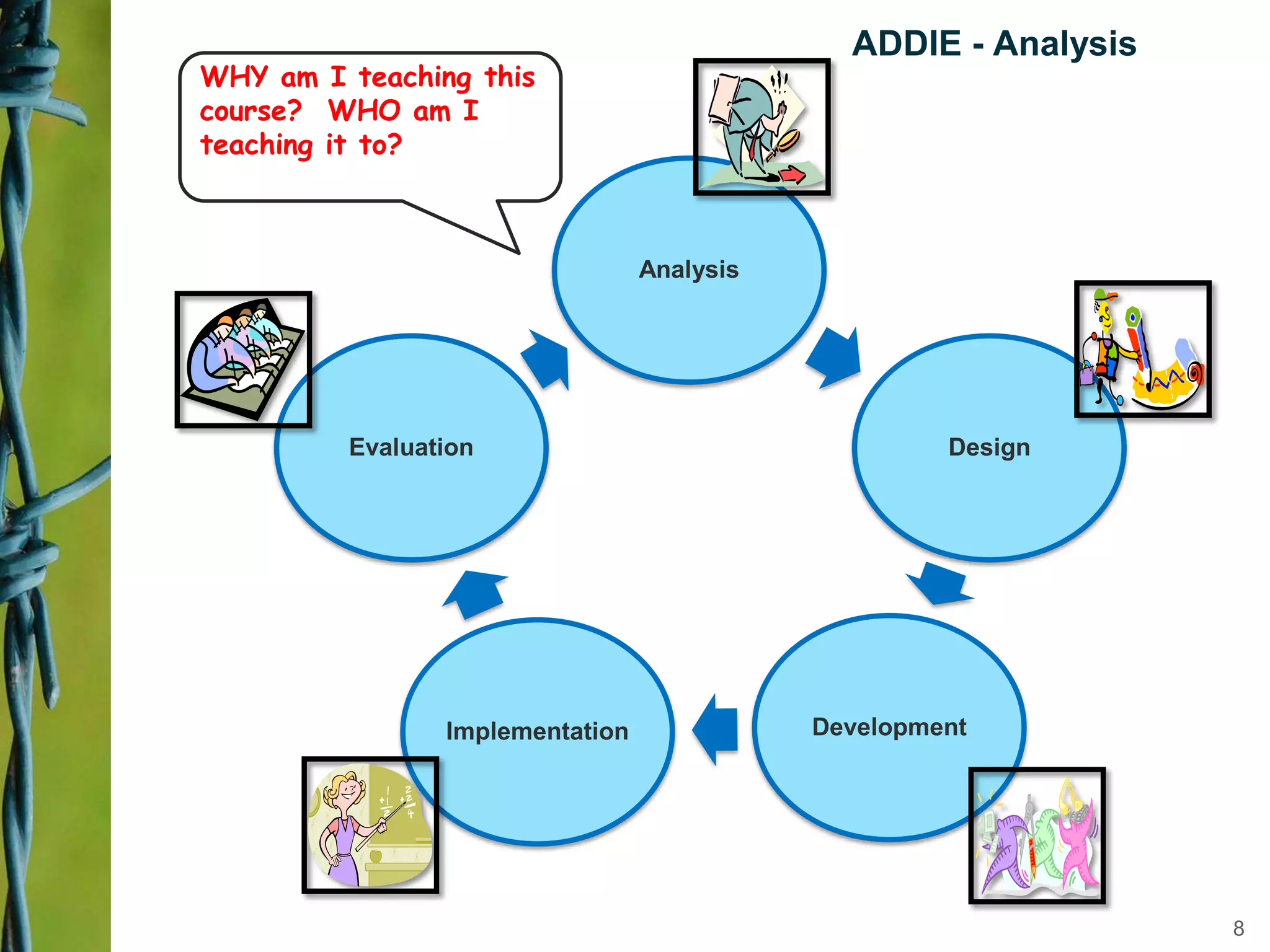
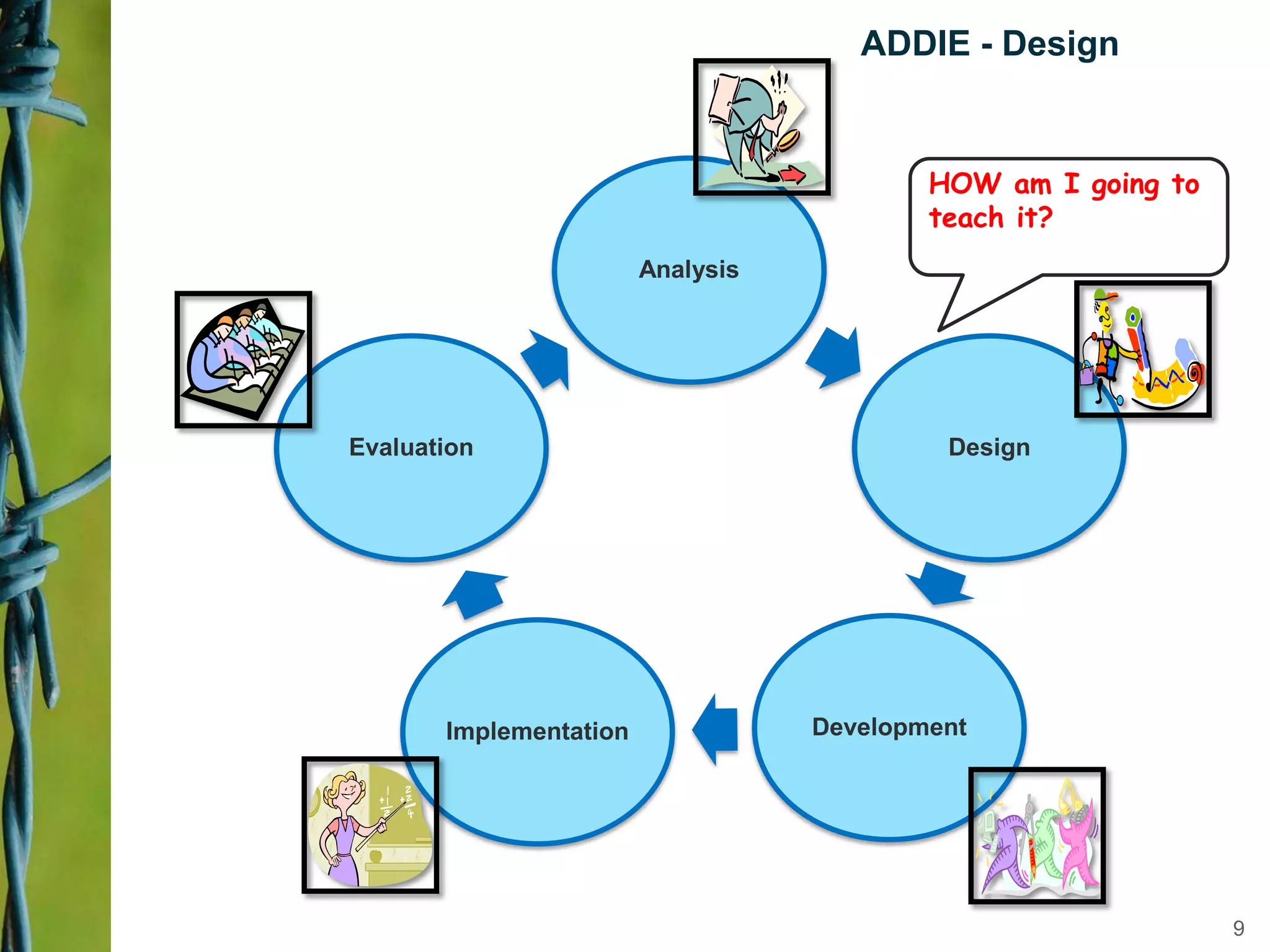
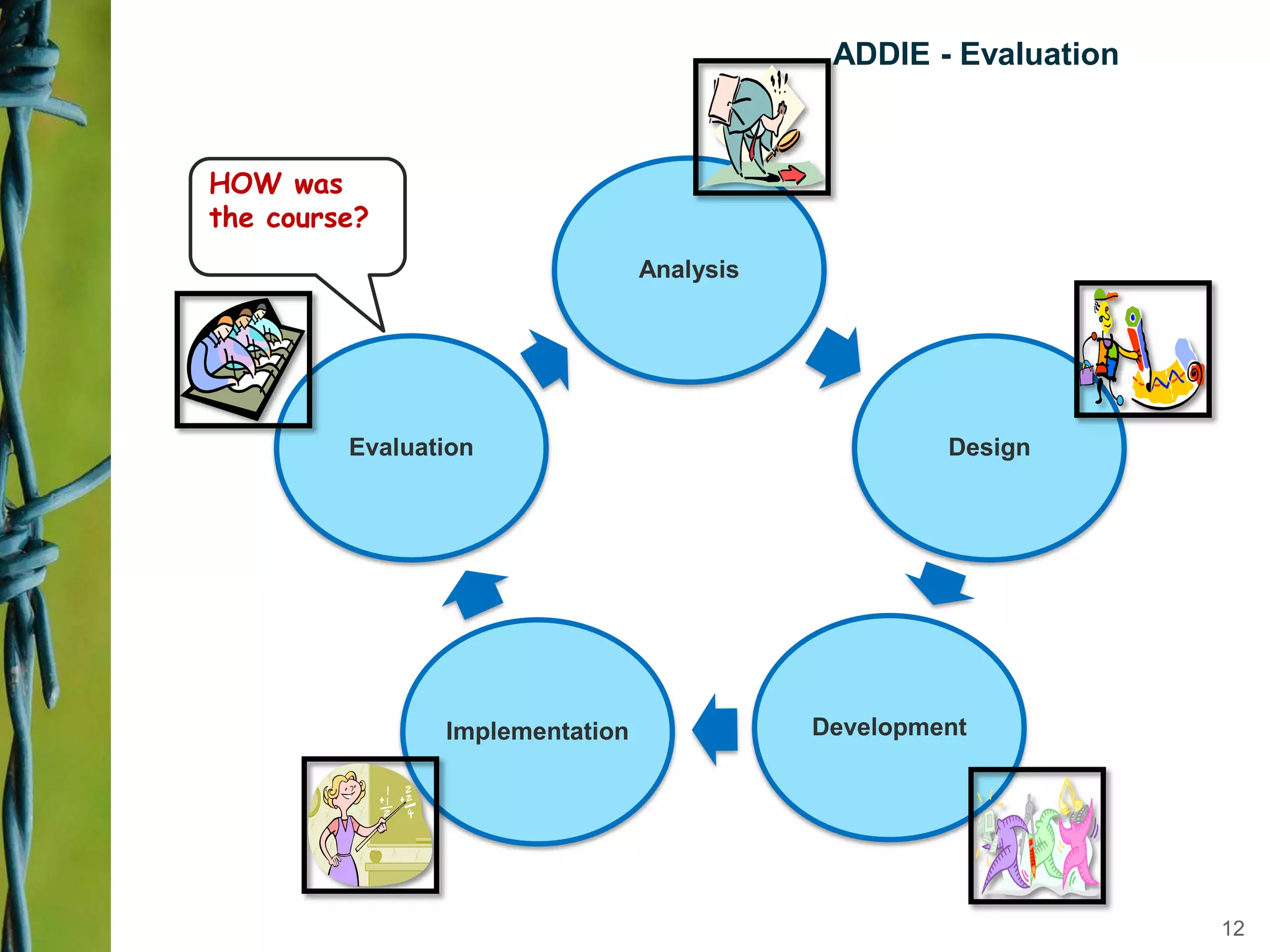
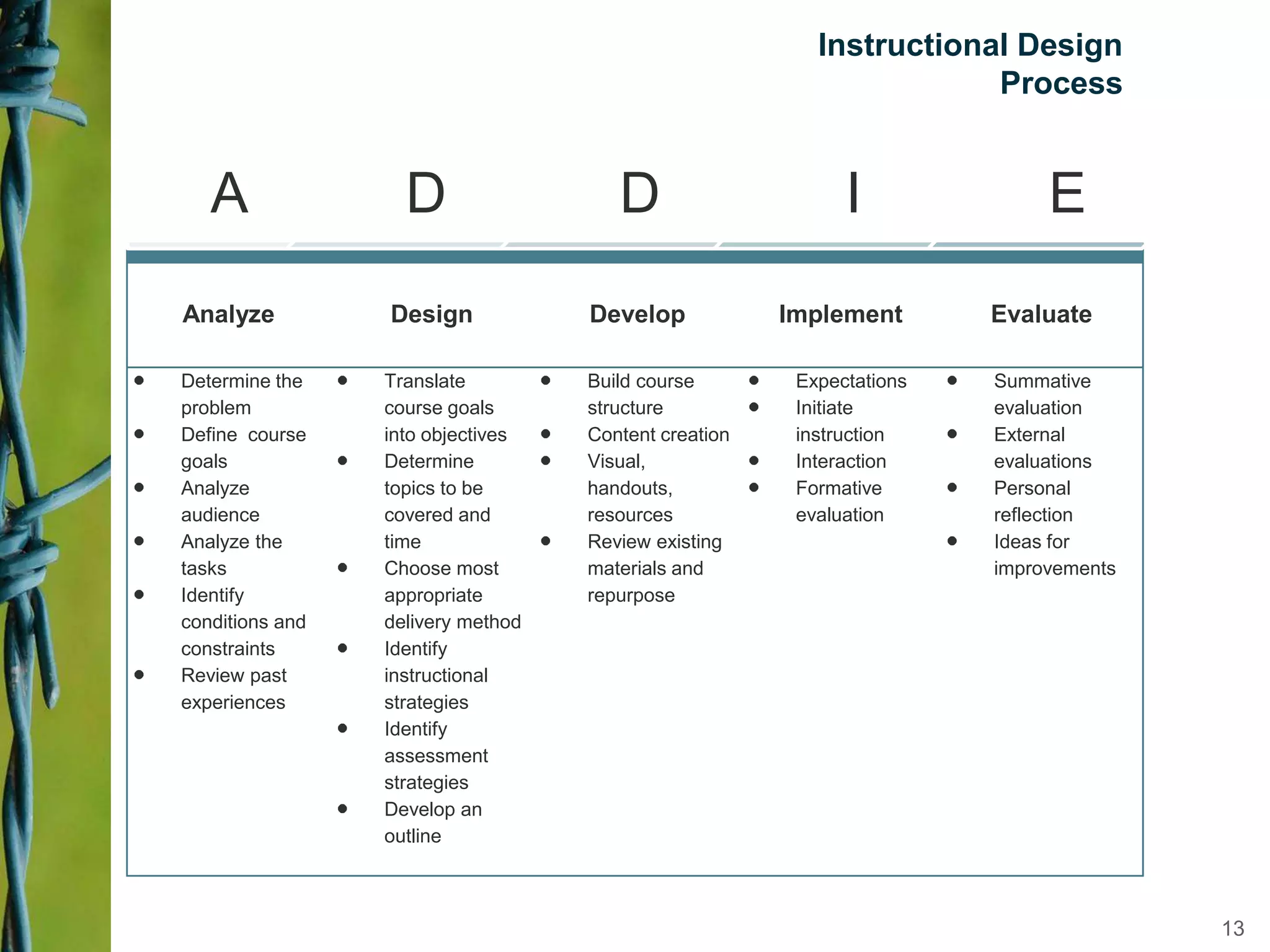
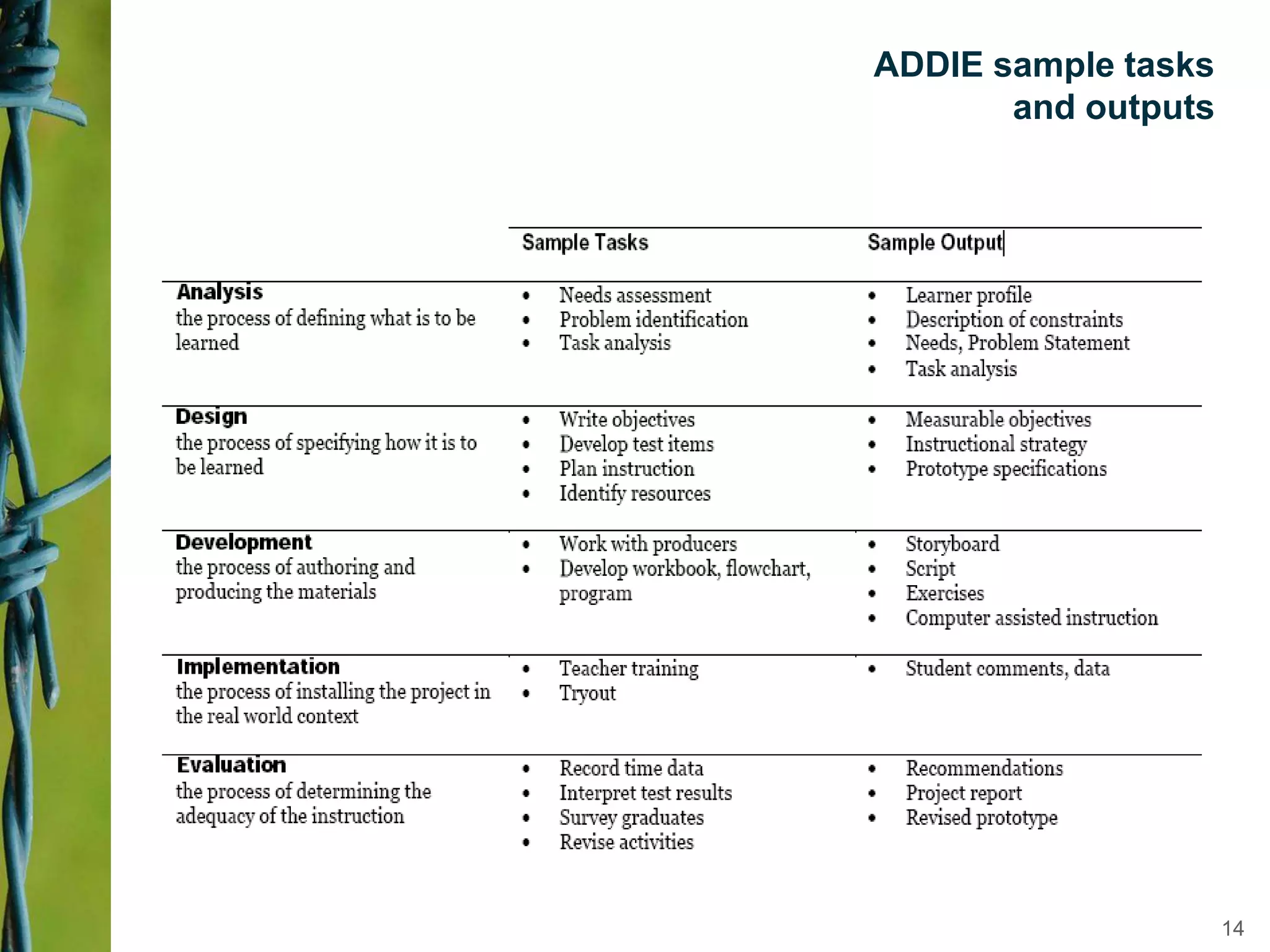
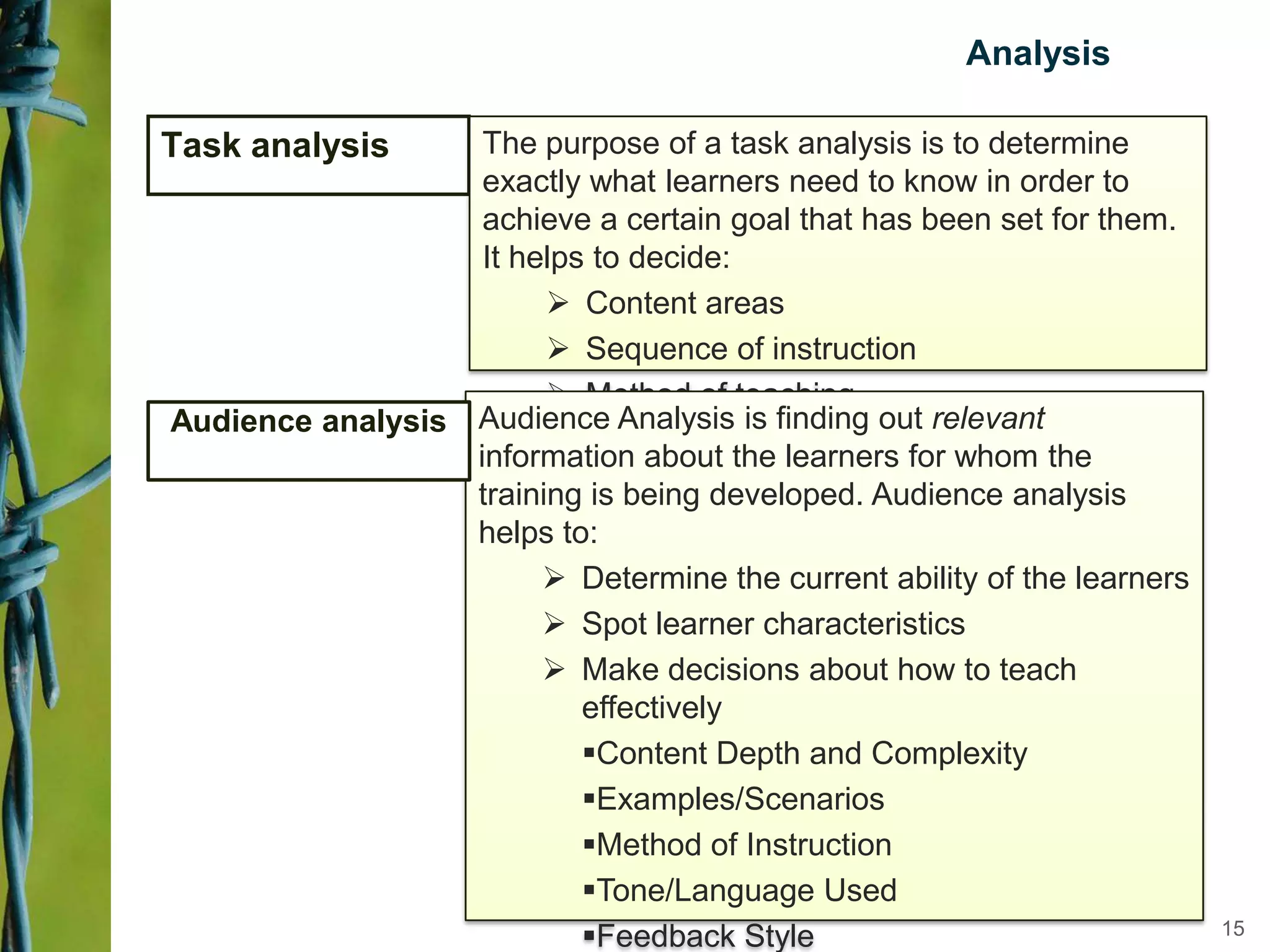
Instructional design is a science, discipline, and process that involves systematically analyzing learning needs, designing instructional experiences to address those needs, developing instructional materials, implementing instruction, and evaluating learning outcomes and the instructional process. Several instructional design models are presented, including the ADDIE model which involves analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation phases to create effective instruction that meets learners' needs. The document discusses tasks and outputs involved in each phase of the ADDIE model to illustrate the instructional design process.