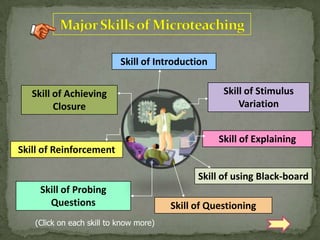
The document discusses various teaching skills including questioning skills, reinforcement, stimulus variation, explanation, blackboard usage, probing questions, and closure. It provides descriptions of each skill, their purpose, and techniques to employ or avoid for each skill. The document also discusses linking teaching skills together through link practice lessons to bridge microteaching and real classroom teaching.