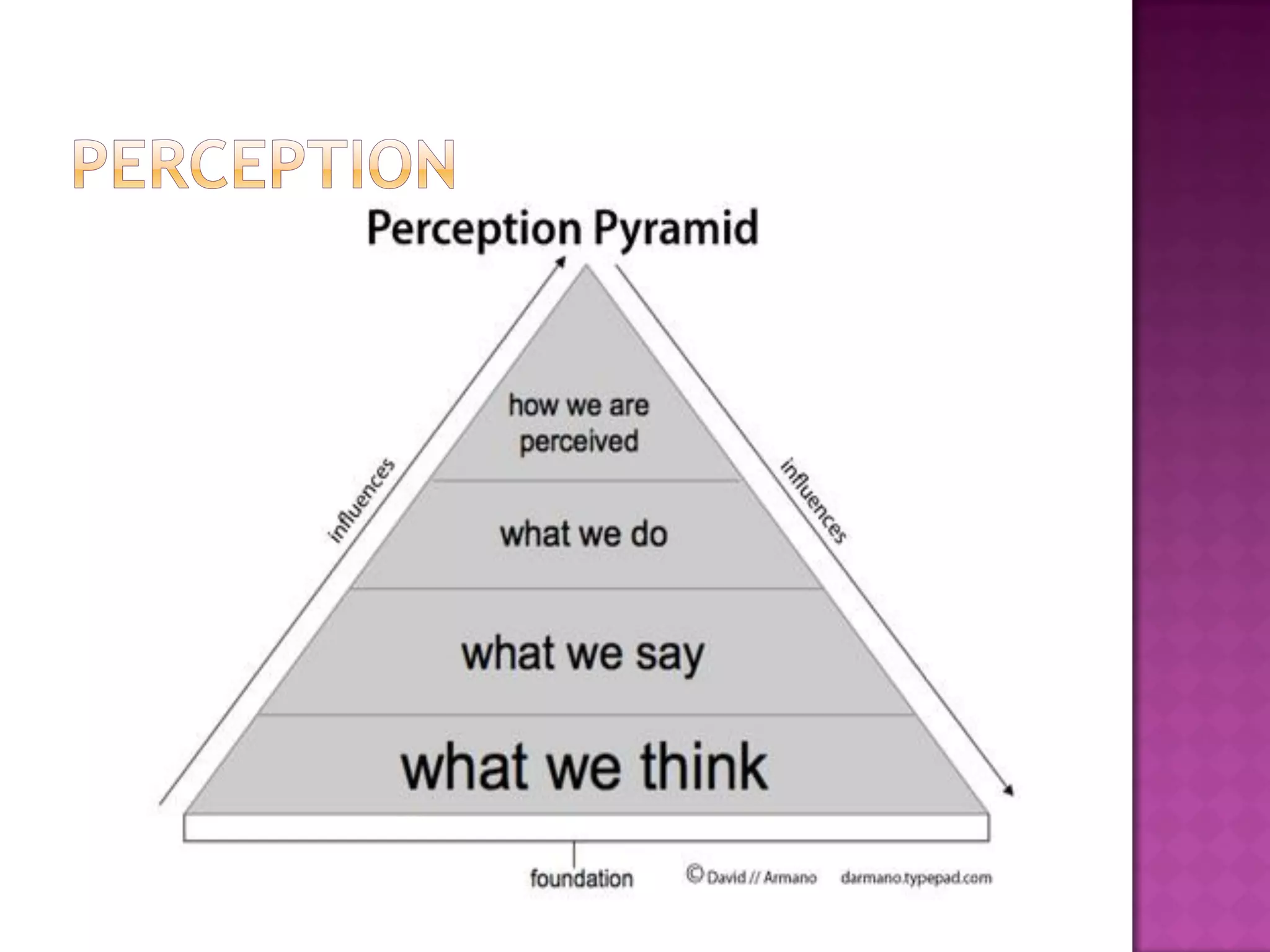
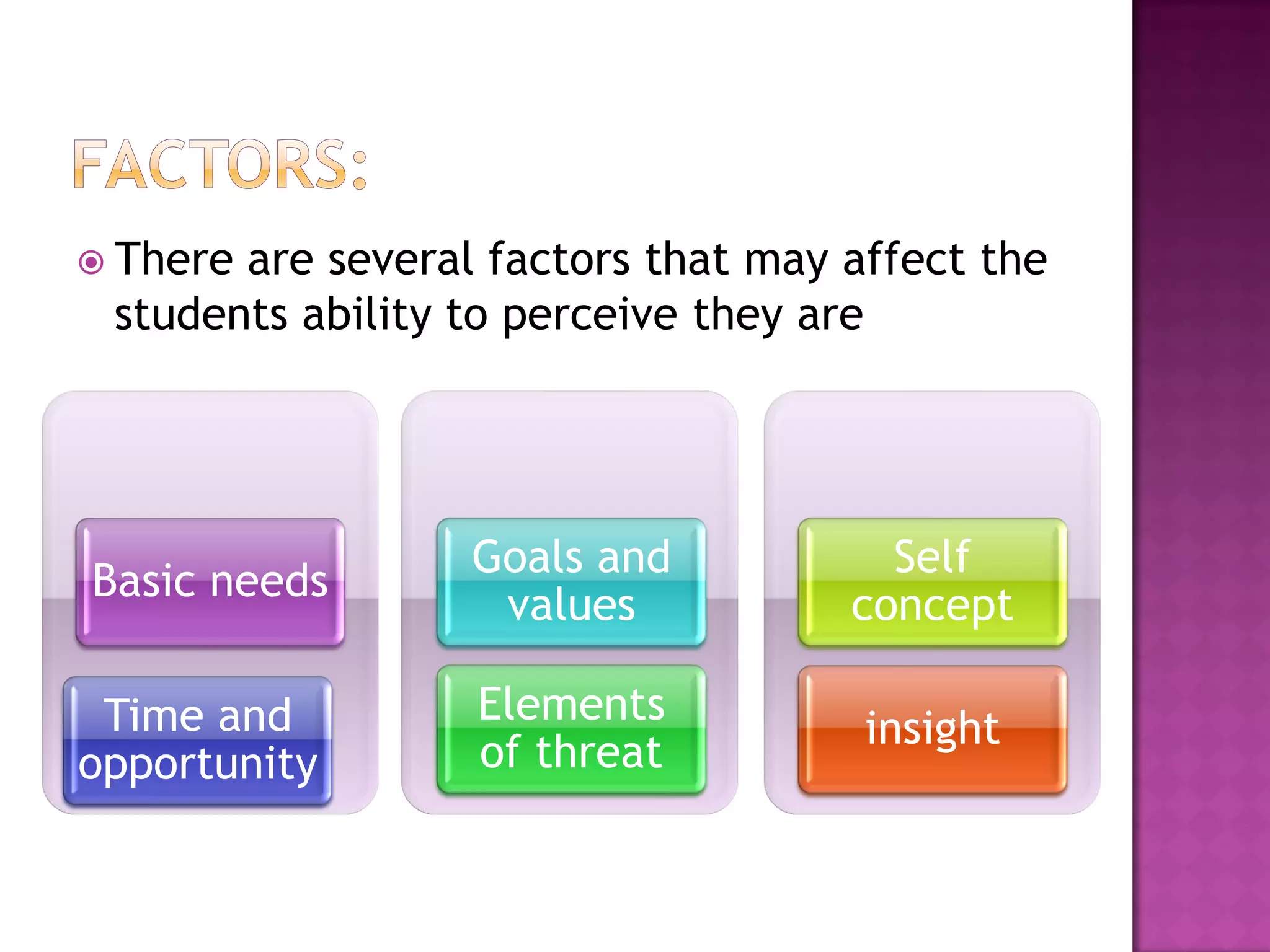
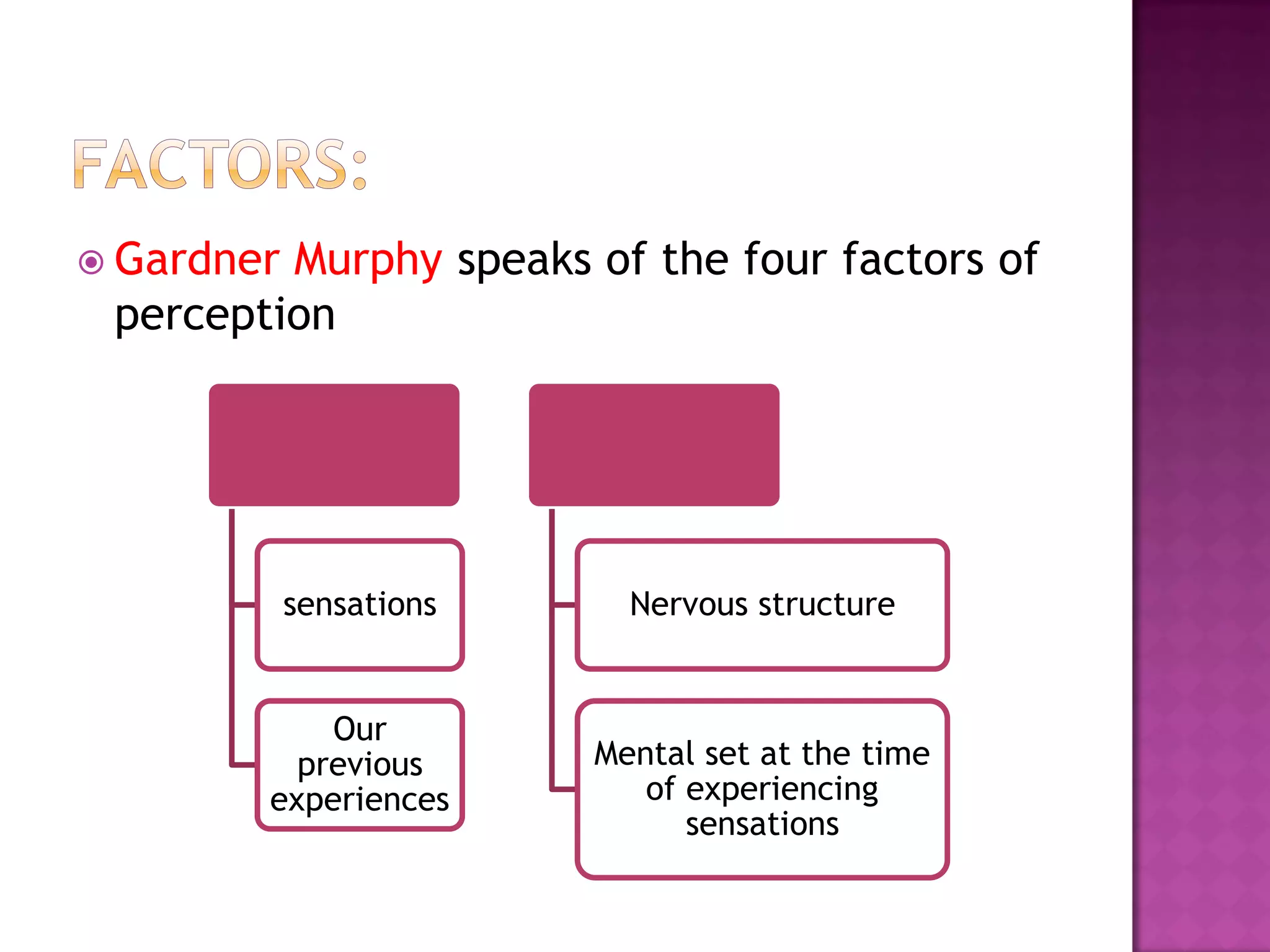
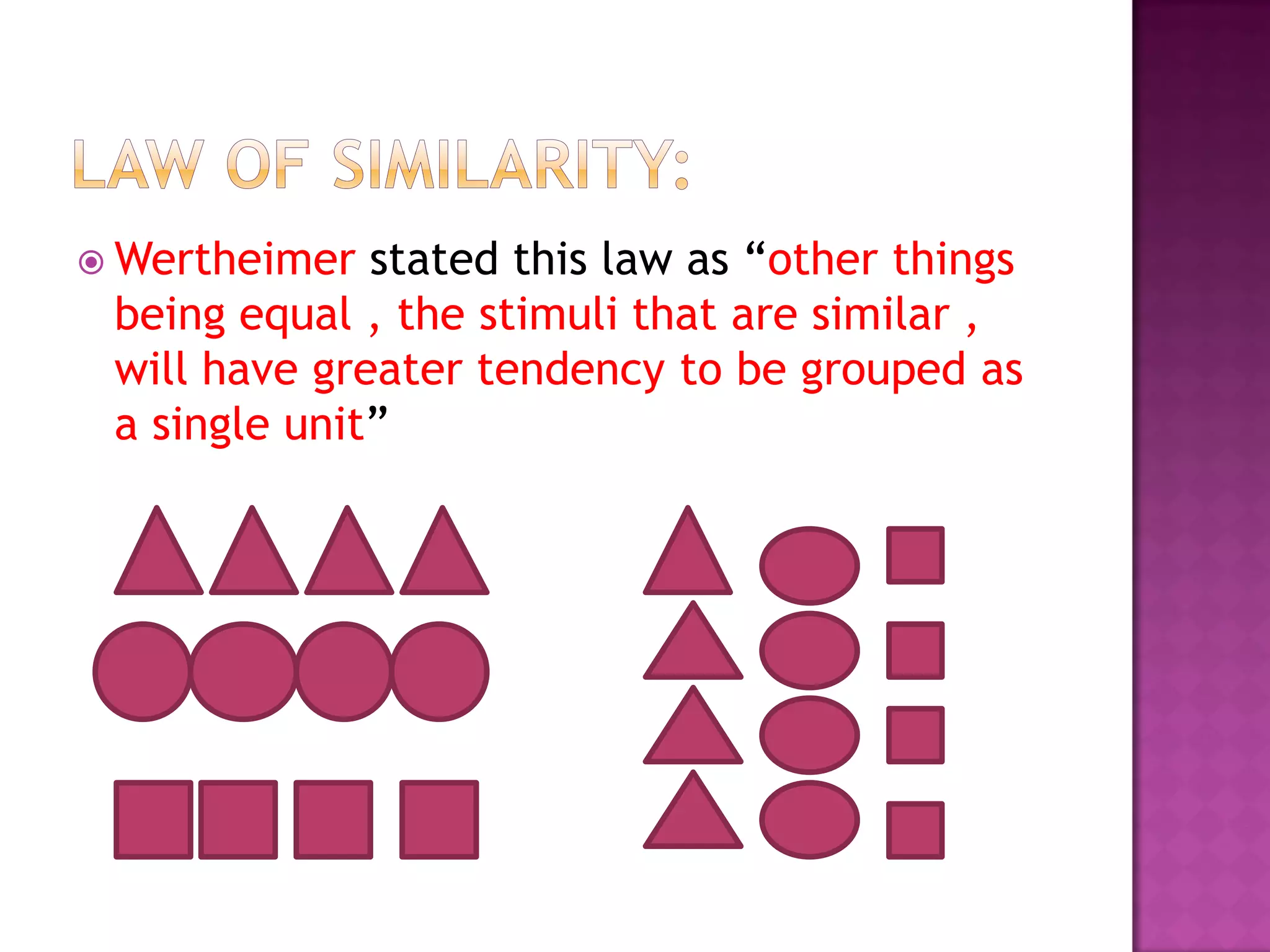
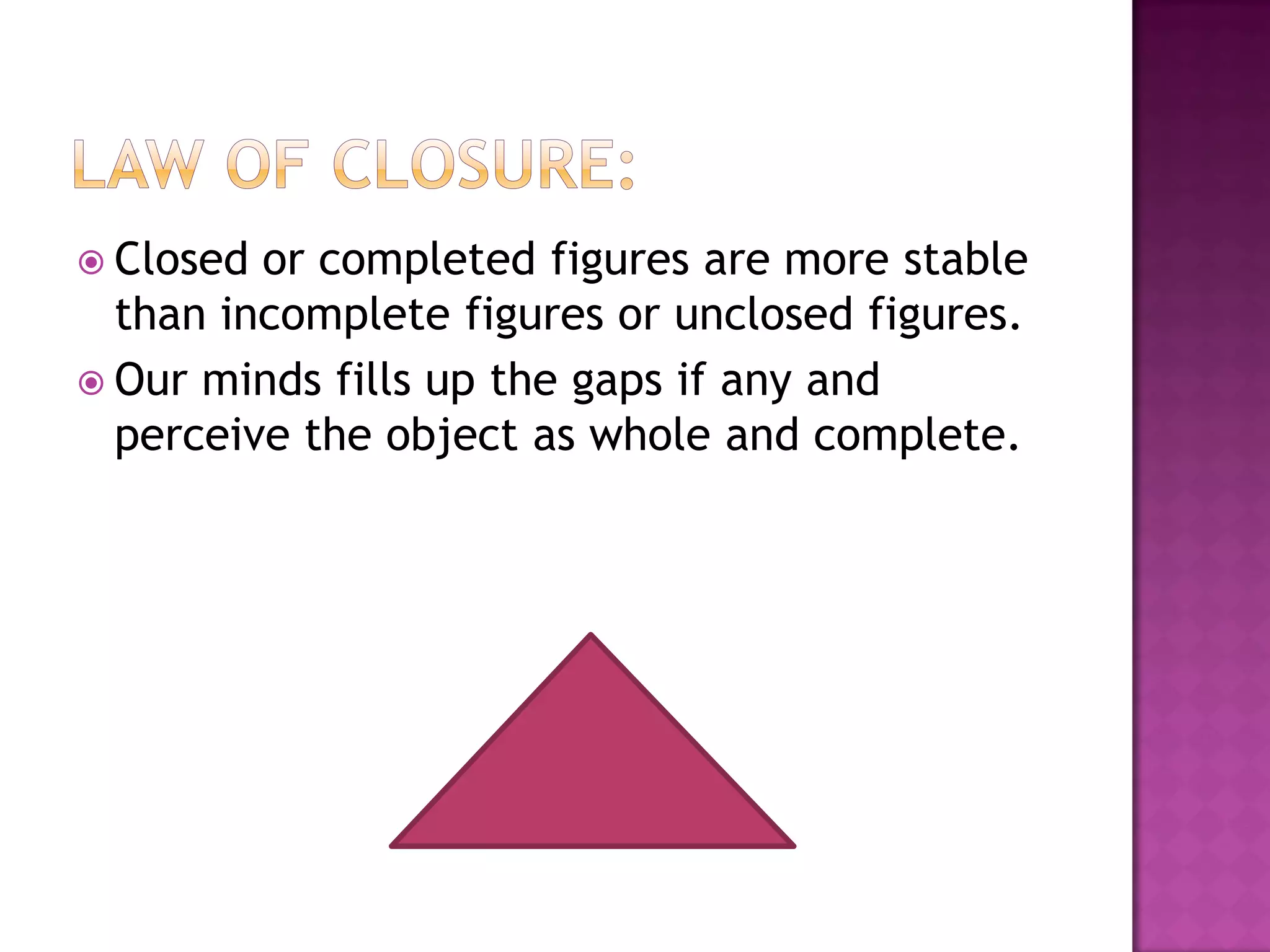
This document discusses perception and the factors that affect a student's ability to perceive. It defines perception as a psychological process where sensory inputs are processed, organized, and interpreted based on past experiences to understand stimuli. There are several factors, like basic needs, time, goals, threats, self-concept, and insight, that can influence a student's perception. Gardner Murphy identified four factors of perception: sensations, previous experiences, nervous structure, and mental set. Organization and integration are important aspects of the perception process. Perception is determined by both external stimuli and our past experiences.