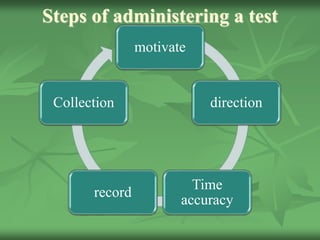
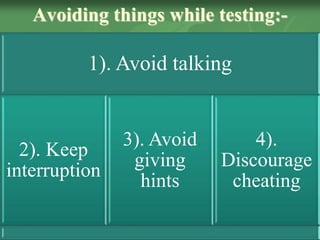
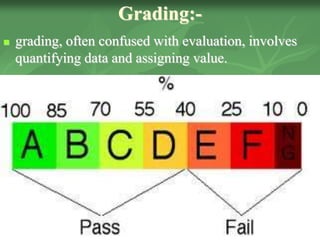
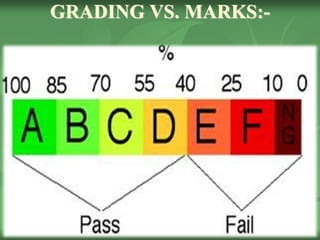
This document discusses administering tests, scoring tests, grading tests, and the differences between grading and marking. It provides steps for administering tests, including motivating students, giving directions, monitoring time, ensuring accuracy, and collecting materials. It also discusses principles of fair testing, avoiding distractions during testing, and preventing cheating. The document then covers scoring tests, including issues with human scoring variability, and methods for grading tests both analytically and globally. Finally, it discusses the differences between grading systems and marking/points systems for assessing student achievement.