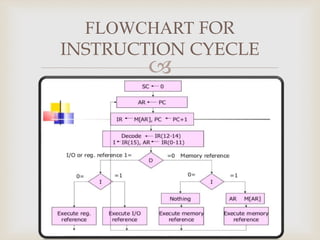
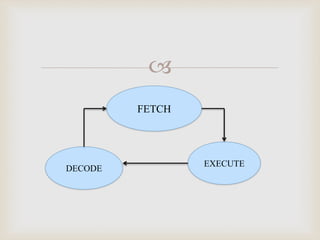
This document discusses the instruction cycle in a computer. It describes the four main phases of an instruction cycle: fetch, decode, execute, and write-back. It explains the fetch phase involves using the program counter to retrieve an instruction from memory and incrementing the program counter. The decode phase decodes the instruction using a decoder. The document provides details about the register transfers and timing signals involved in the fetch and decode phases. It also describes how the type of instruction, such as register reference, is determined during the instruction cycle.



![
The program counter PC is loaded with the
address of the first instruction in the program.
The sequence counter SC is cleared to 0,providing
a decoded timing signal T0.
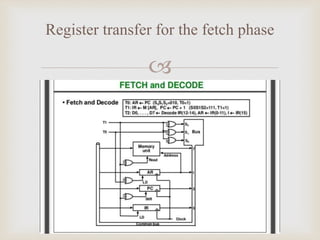
FETCH AND DECODE
T0:AR<-PC
T1:IR<-M[AR],PC<-PC+1
T2:D0……D7<-Decoder IR(12-14),AR<-IR(0-11),I<-IR(15)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/instructioncycle-181001063900/85/Instruction-cycle-5-320.jpg)
![
Place the content of PC onto the bus by making
the bus selection input s2,s1,s0 equal to 010.
Transfer the content of the bus to AR by enabling
the LD input of A.
T0 to achieve the following
connection:
T1:IR<-m[AR],PC<-PC+1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/instructioncycle-181001063900/85/Instruction-cycle-7-320.jpg)
![The timing signal that active after the decoding
is T3.
Decoder output D7 is equal to 1 if the operation
code is equal to binary bit 111.
The micro operation for the indirect address
condition can be symbolized by the register
transfer statement:
DETERMINE THE TYPE OF
INSTRUCTION
AR<-M[AR]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/instructioncycle-181001063900/85/Instruction-cycle-8-320.jpg)