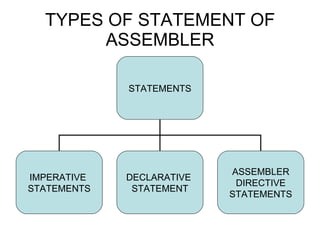
An assembler is a program that converts assembly language code into machine language code. It has two passes: in the first pass, it scans the program and builds a symbol table with label addresses; in the second pass, it converts instructions to machine language using the symbol table and builds the executable image. The assembler converts mnemonics to operation codes, symbolic operands to addresses, builds instructions, converts data, and writes the object program and listing. The linker then resolves symbols between object files before the loader copies the executable into memory and relocates it as needed. The assembler uses symbol tables from both passes and databases to perform its functions of translating and building the executable.