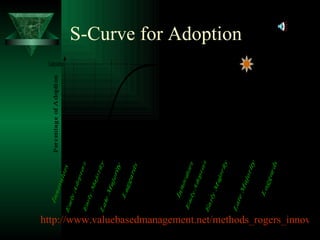
The document discusses the use of handheld wireless computers, specifically PDAs, in education. It outlines the history and development of PDAs, including key companies and thinkers involved. It then discusses findings from research on utilizing PDAs in education for tasks like communication, assessment, and multimedia access. The document proposes a process for innovating with PDAs that includes stages of knowledge, persuasion, decision, implementation, and confirmation and identifies strategies for different groups in the adoption process.