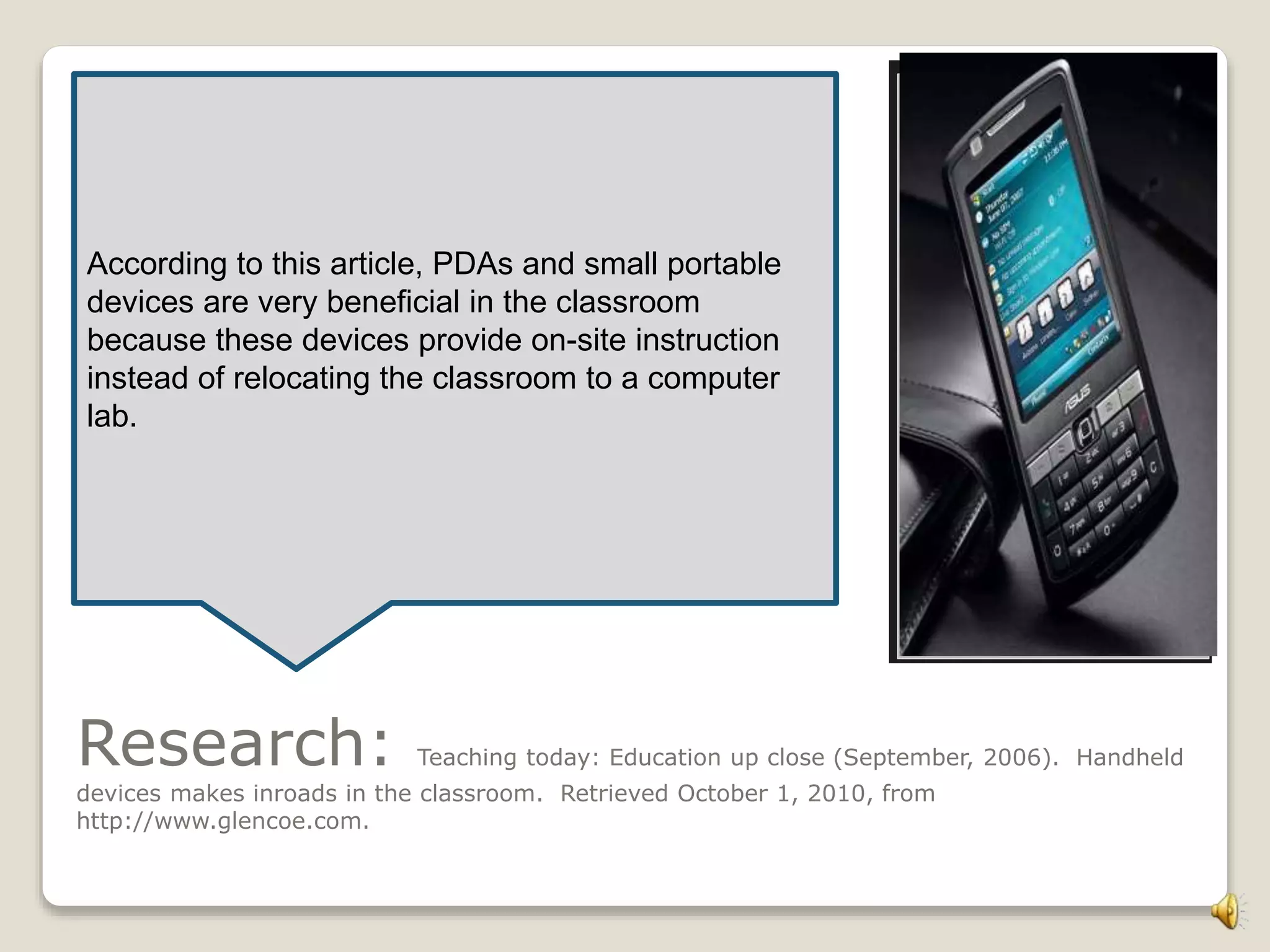
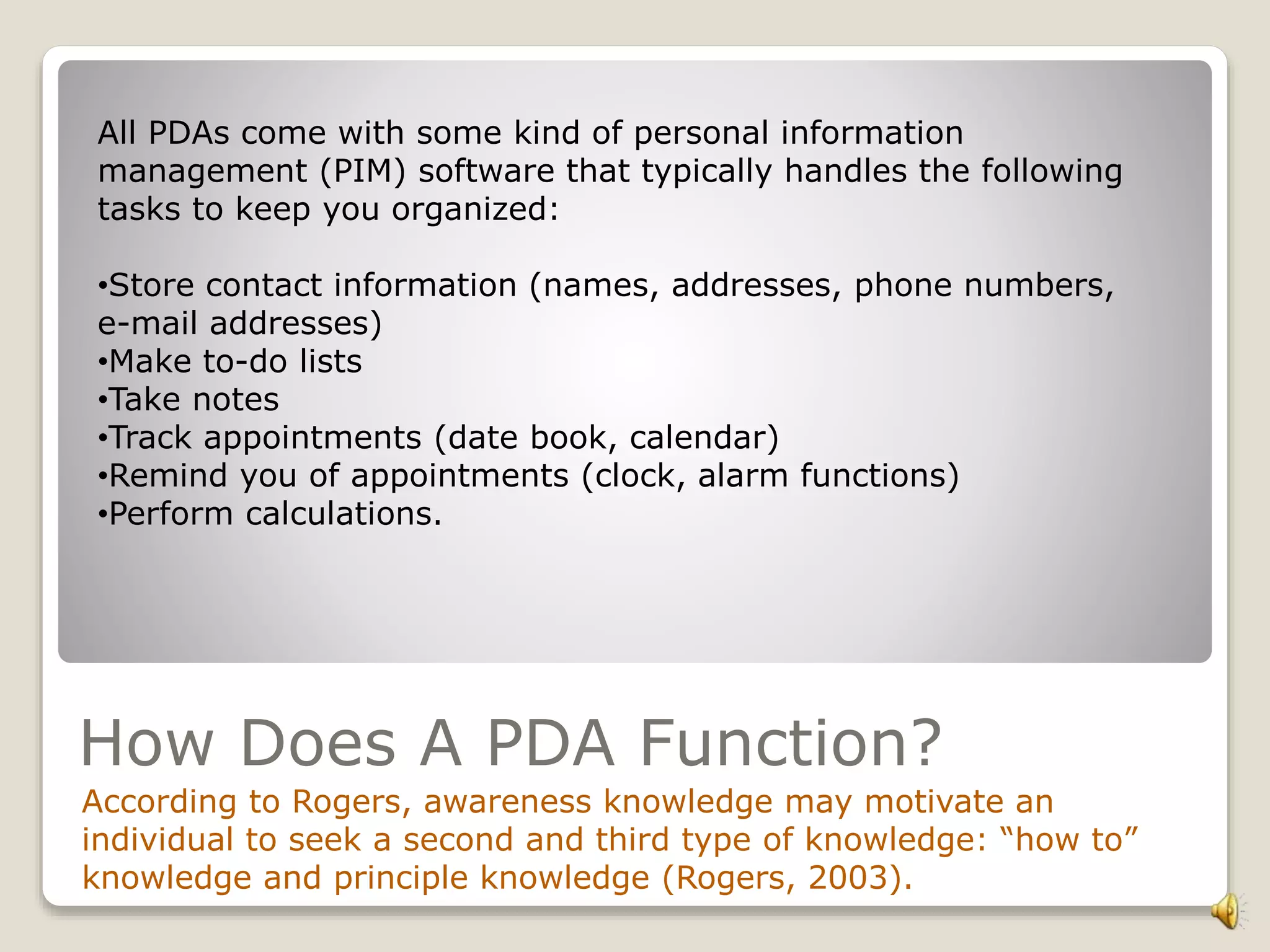
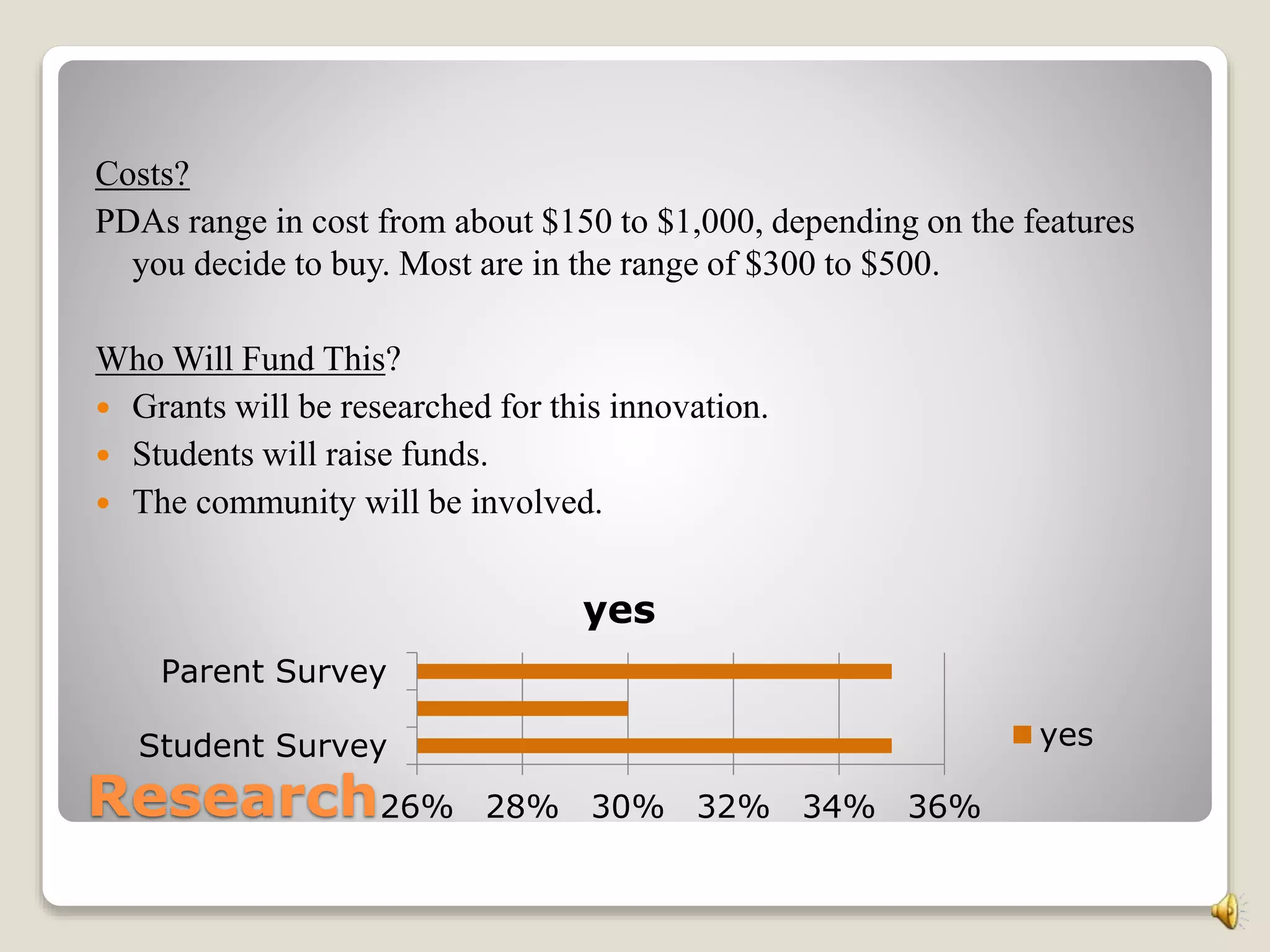
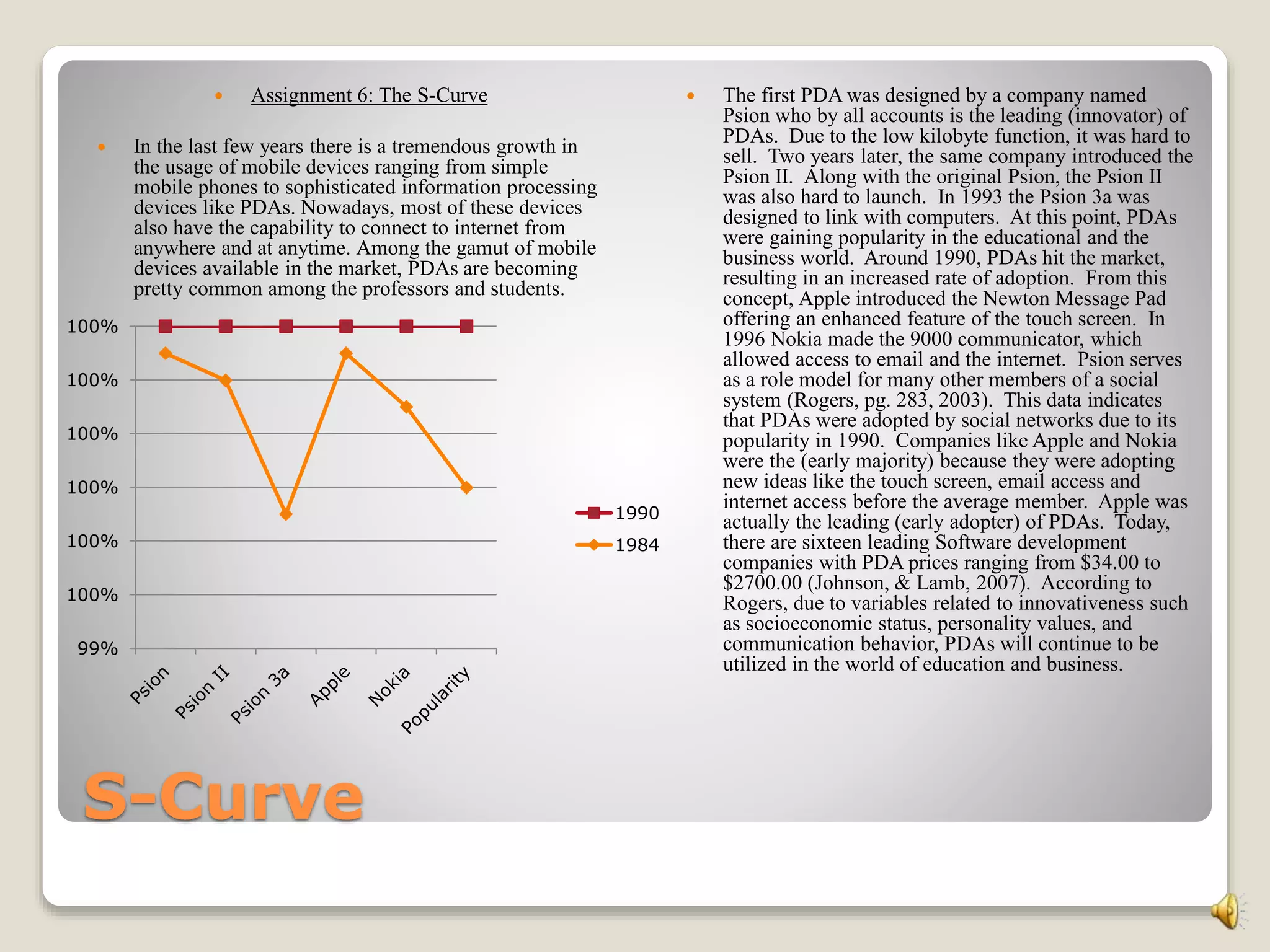
The document discusses research on PDAs and small portable computers in education. It notes that a research team presented six years of documentation showing these devices could provide an affordable digital learning environment. The study focused on the capabilities of "smart probes" using small computers. These devices were found to allow easy, real-time data acquisition. Additional resources were provided to support the use of handhelds in education. In closing, the document states that PDAs and small portable computers paired together provide a dynamic learning environment worth exploring further.