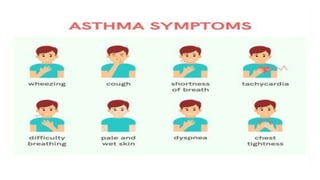
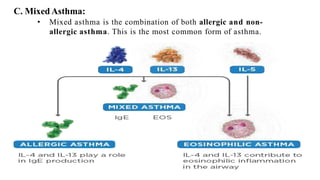
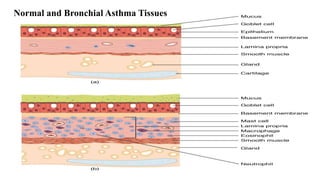
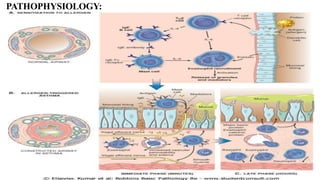
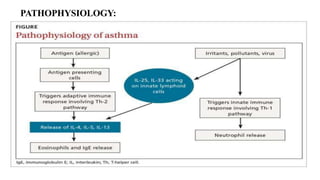
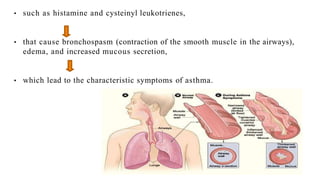
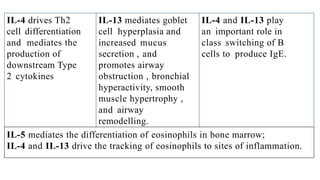
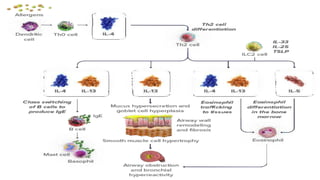
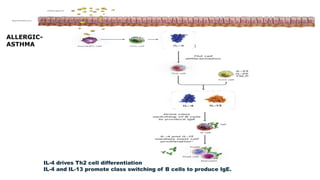
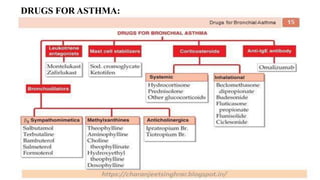
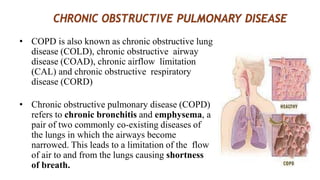
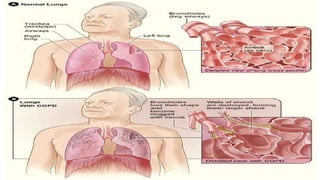
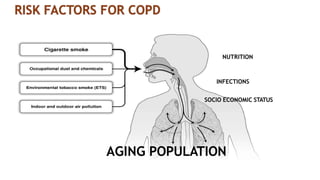
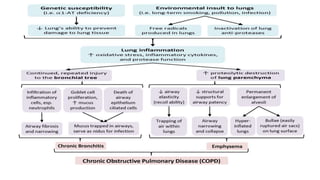
Asthma is a chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the airways causing coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. It is usually caused by allergic triggers like pollen, dust mites, or animal dander that lead to bronchospasms and airway obstruction. Diagnosis involves patient history, physical exam, pulmonary function tests, and allergy testing. Treatment includes bronchodilators, corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and monoclonal antibodies to reduce inflammation and prevent symptoms.