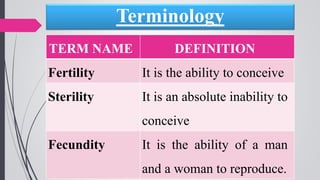
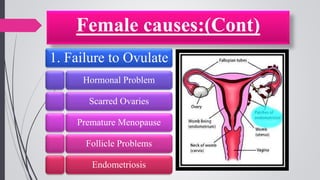
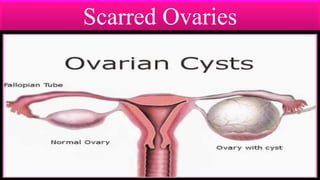
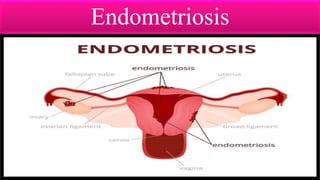
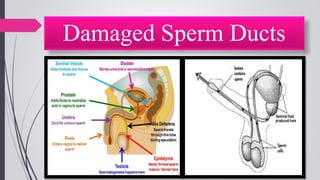
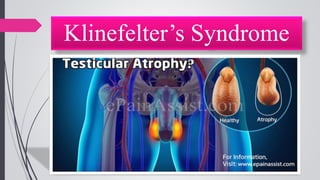
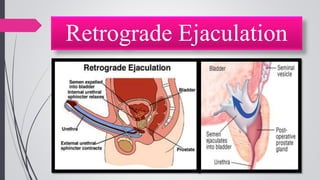
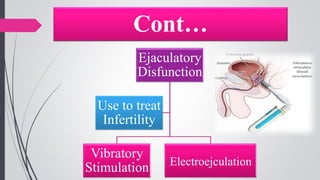
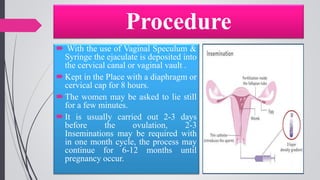
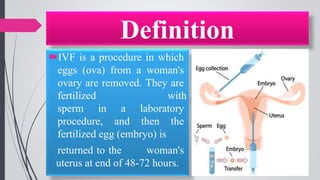
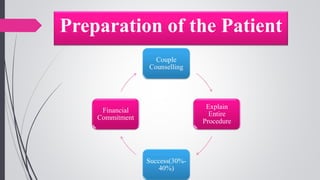
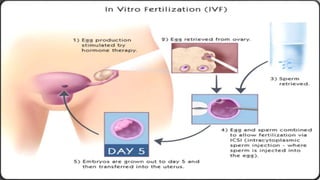
Infertility is defined as the failure to conceive after one year of unprotected intercourse. It affects around 10-15% of couples. The main causes of infertility in females are ovulation disorders (40%) and fallopian tube damage (30-40%), while in males it is poor sperm quality (30-40%). Diagnostic tests include hormone levels, ultrasound, HSG and laparoscopy. Treatment depends on the cause but may include fertility drugs, IUI, IVF or surgery. IVF involves fertilizing eggs with sperm in a lab and then transferring the embryos into the uterus.