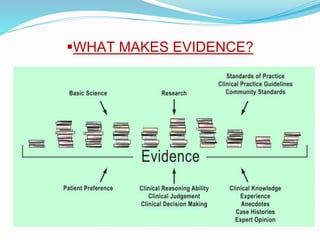
Evidence based practice (EBP) involves integrating the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to provide optimal care. EBP aims to move away from relying on "tried and true" practices and instead make decisions based on high-quality clinical research. The key steps of EBP include asking answerable clinical questions, searching for relevant evidence, appraising the evidence quality and applicability, integrating the evidence with expertise and context, and evaluating outcomes. EBP has benefits like improved patient outcomes, more efficient care, and keeping nursing practice current with the latest research findings.