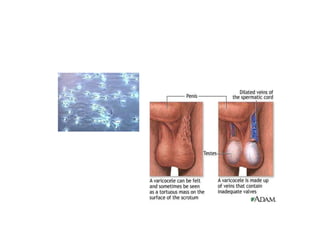
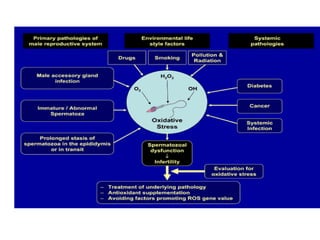
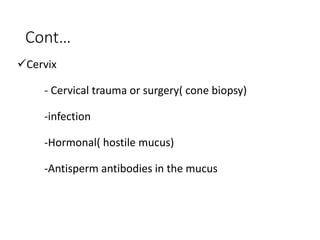
This document discusses infertility in females and males. It defines different types of infertility and lists numerous potential causes including issues with sperm production/function, egg production/ovulation, fallopian tube blockages, endocrine disorders, infections, genetic defects, obesity, stress, environmental toxins, and lifestyle factors. It also outlines tests and diagnostics used to evaluate infertility as well as various medical and surgical treatment options like fertility drugs, artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization, and adoption. Potential complications of treatment are mentioned.