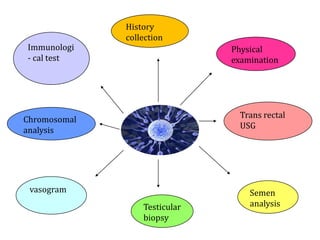
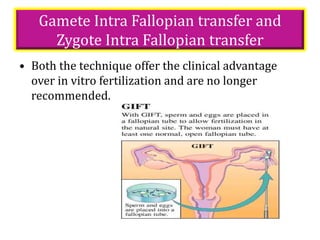
This document provides an overview of infertility, including its definition, types, incidence, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and the role of midwives. It defines infertility as the inability to conceive after one year of unprotected sex. Various female and male factors that can cause infertility are described. Diagnostic tests for both men and women are outlined. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, fertility drugs, surgery, and assisted reproductive technologies like IUI, IVF, and ICSI. The importance of infertility counseling to help couples cope with emotional aspects is also discussed.